Sagami Railway
The Sagami Railway Company, Ltd. (相模鉄道株式会社, Sagami tetsudō Kabushikigaisha), or Sotetsu (相鉄), is a private railway company operating three lines in Kanagawa Prefecture, Japan. It is a wholly owned subsidiary of holding company Sotetsu Holdings, Inc.; Sotetsu Holdings is listed on the Tokyo Stock Exchange.
 | |
Native name | 相模鉄道株式会社 |
|---|---|
| Public KK (Sotetsu Holdings) | |
| Traded as | TYO: 9003 (Sotetsu Holdings) |
| Genre | Rail transport |
| Founded | November 1964 |
| Headquarters | 2-9-14 Kitasaiwai, Nishi-ku, Yokohama , Japan |
Area served | Kanagawa |
| Services | Passenger railway |
| Owner | Sotetsu Holdings, Inc. (100%) |
Number of employees | 1,117 (As of September 16, 2009) |
| Website | https://www.sotetsu.co.jp/about/companies/sagami-railway/ |
Overview
Sagami Railway is one of the core companies of the Sotetsu group. Sotetsu focuses on railway operations, although formerly it had a more diversified set of holdings, such as bus lines and supermarkets. Sotetsu is the smallest company of the "Big 15" railways in Japan, as it has only short lines, but it succeeded in developing towns along its lines in the 1960s and 1970s, with many passengers ride this line. In May 1990, Sotetsu joined the major railways. In 2010 it had a daily ridership of 623,500[1]
Lines
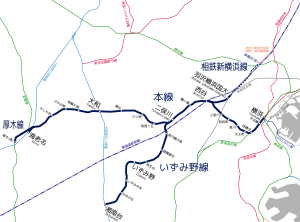
The company operates three passenger (commuter) lines and a freight-only line. All lines are electrified.
Passenger
- Main Line from Yokohama Station in Yokohama to Ebina Station in Ebina via Futamatagawa Station in Yokohama, 18 stations, 24.6 km
- Izumino Line from Futamatagawa Station in Yokohama to Shōnandai Station in Fujisawa, 8 stations, 11.3 km
- Shin-Yokohama Line from Nishiya to Hazawa yokohama-kokudai (1st stretch), 2 stations
Freight
- Atsugi Line (厚木線, Atsugi-sen) in Ebina
Fleet
As of 1 April 2016, Sotetsu operates the following electric multiple unit (EMU) train types.[2]
- 7000 and New 7000 series EMUs (introduced 1975)
- 8000 series EMUs (introduced 1990)
- 9000 series EMUs (introduced 1993)
- 10000 series EMUs (introduced 2002)
- 11000 series EMUs (introduced 2009)
- 12000 series EMUs
- 20000 series EMUs (introduced 11 February 2018)[3]
- 700 series 2-car EMUs modified in 2006 from 7000 series for use as an inspection and rescue train
 A 7000 series EMU in original livery October 2008
A 7000 series EMU in original livery October 2008 A New 7000 series EMU in revised livery in November 2013
A New 7000 series EMU in revised livery in November 2013- An 8000 series EMU in revised livery in April 2014
- A 9000 series EMU in revised color scheme in May 2016
- A 700 series inspection and rescue train
 A brand-new 20000 series train on display ahead of service entry in February 2018
A brand-new 20000 series train on display ahead of service entry in February 2018
Further 20000 series trains will be delivered ahead of the start of inter-running services to and from Tokyu Corporation lines scheduled to commence in late fiscal 2022.[4]
Past
EMUs
- 1000 series
- 2000 and 2100 series EMU (introduced 1951)
- 3000 series EMU (introduced 1951)
- 5000 series EMU (introduced 1955)
- 6000 and New 6000 series EMU (introduced 1961)
Locomotives
- Class ED10 electric locomotive
Preserved fleet
Some withdrawn rolling stock is preserved at Kashiwadai depot.
- 2000 series EMU car 2005
- 6000 series EMU cars 6001 and 6021
- ED10 electric locomotive No.11
- Jinchu Railway Class 3 steam locomotive
- Jinchu Railway Class Ha20 coach
- Preserved Jinchu Railway steam locomotive and coach
- 2000 series in September 2009
 2100 series
2100 series 5000 series in February 2009
5000 series in February 2009 6000 series cars in revised color scheme awaiting scrapping in June 1993
6000 series cars in revised color scheme awaiting scrapping in June 1993- Preserved 6000 series car in original livery in June 2009
- Class ED10 electric locomotive
History
The Sagami Railway was established in Chigasaki, Kanagawa, in January 1917, to transport gravel along the Sagami River valley. The first section, between Chigasaki and Samukawa was opened in 1919, and the line was extended gradually to Hashimoto in 1931.[5] Sagami Railway started direct operation to Hachioji, but performance was sluggish during the economic depression, so Sagami Railway became a subsidiary of Tokyu in 1941.
The Jinchu Railway was established in Seya village (now, Seya-ku, Yokohama) in 1917, and opened its first section from Futamatagawa to Atsugi in May, 1926. Jinchu Railway extended to Yokohama Station in 1933, but its management had financial difficulties, so the company also became a subsidiary of Tokyu in 1939, prior to Sagami Railway. The two companies' rail lines were connected at Atsugi Station.
In April 1943, Sagami Railway took over Jinchu Railway and named two lines "Sagami Line" (original section) and "Jinchu line" (acquired section). However, in June 1944, the Sagami Line and Nishi-Samukawa branch line were purchased by the government to use the bypass between Tokaido main line and Chuo main line. At the same time, Imperial Japanese Navy Atsugi Airport was opened, so the number of passengers and amount of freight increased sharply. As a result, Sagami Railway released all management and delegated it to Tokyu. Under Tokyu, the line gained electrification to increase the carrying capacity and in 1944, all passenger lines were electrified.
In June 1947, Sagami Railway employees bought their own shares from Tokyu and resolved the commission.
In 1952, Sagami Railway purchased the 25,000 ㎡ of land around Yokohama Station's west entrance from Esso, and began to develop to attract department stores.
JR and Tōkyū Link Lines
The Kanagawa Eastern Line is an approximately 10 km link, which is constructed from Nishiya via Hazawa yokohama-kokudai and Shin-Yokohama to Hiyoshi, that'll enable through services between the JR East Saikyō Line and the Sōtetsu Main Line by late 2019, and between the Tōkyū Tōyoko Line, the Tōkyū Meguro Line & Toei Mita Subway Line and the Sōtetsu Main Line by late 2022, joining Sōtetsu's network to JR, Tōkyū and Toei Subway, towards the center of Tokyo Metropolis.
References
- http://www.train-media.net/report/1110/soutetsu.pdf
- 私鉄車両編成表 2016 [Private Railway Rolling Stock Formations - 2016] (in Japanese). Japan: Kotsu Shimbunsha. 25 July 2016. pp. 82–83. ISBN 978-4-330-70116-5.
- 相鉄20000系,2月11日から営業運転を開始 [Sotetsu 20000 series to enter revenue service from 11 February]. Japan Railfan Magazine Online (in Japanese). Japan: Koyusha Co., Ltd. 22 December 2017. Archived from the original on 22 December 2017. Retrieved 22 December 2017.
- 都心直通用新型車両「20000系」を導入 [New 20000 series trains to be introduced on Tokyo through-running services] (PDF). News letter (in Japanese). Japan: Sotetsu. 5 June 2017. Archived (PDF) from the original on 5 June 2017. Retrieved 5 June 2017.
- 『相鉄七十年史』相模鉄道
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Sagami Railway. |
- Sotetsu Group (in Japanese)
- English part of official site
- Sotetsu Lines history (site for kids) (in Japanese)