Solar eclipse of November 10, 1920
A partial solar eclipse occurred on November 10, 1920. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A partial solar eclipse occurs in the polar regions of the Earth when the center of the Moon's shadow misses the Earth.
| Solar eclipse of November 10, 1920 | |
|---|---|
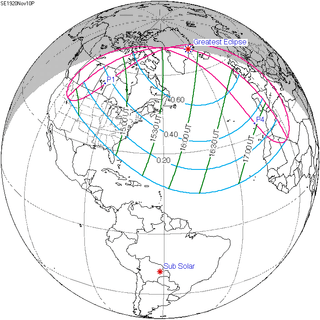 Map | |
| Type of eclipse | |
| Nature | Partial |
| Gamma | 1.1287 |
| Magnitude | 0.742 |
| Maximum eclipse | |
| Coordinates | 69.9°N 29.8°W |
| Times (UTC) | |
| Greatest eclipse | 15:52:15 |
| References | |
| Saros | 151 (9 of 72) |
| Catalog # (SE5000) | 9329 |
Related eclipses
Solar eclipses 1916–1920
This eclipse is a member of a semester series. An eclipse in a semester series of solar eclipses repeats approximately every 177 days and 4 hours (a semester) at alternating nodes of the Moon's orbit.[1]
| Solar eclipse series sets from 1916–1920 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ascending node | Descending node | |||
| 111 | December 24, 1916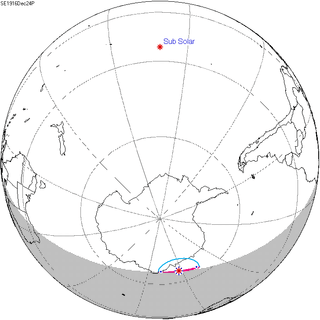 Partial |
116 | June 19, 1917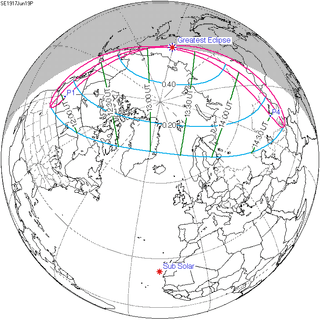 Partial | |
| 121 | December 14, 1917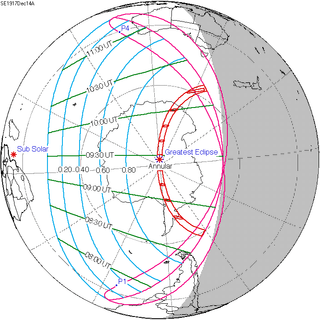 Annular |
126 | June 8, 1918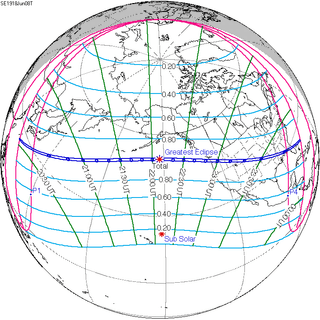 Total | |
| 131 | December 3, 1918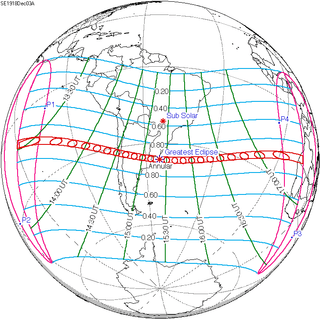 Annular |
136 | May 29, 1919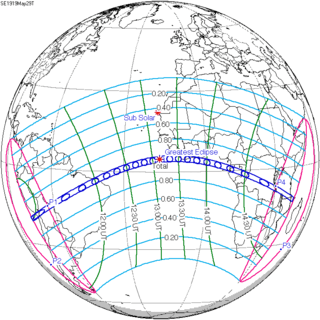 Total | |
| 141 | November 22, 1919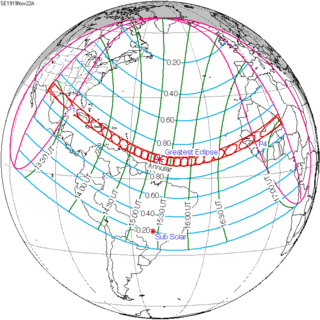 Annular |
146 | May 18, 1920 Partial | |
| 151 | November 10, 1920 Partial | |||
Notes
- van Gent, R.H. "Solar- and Lunar-Eclipse Predictions from Antiquity to the Present". A Catalogue of Eclipse Cycles. Utrecht University. Retrieved 6 October 2018.
gollark: I would tell you a UDP joke, but I don't know if you would get it.
gollark: But I meant actual Haskell. Just communicate with the server over UDP.
gollark: Or frege.
gollark: That fixes all bugs.
gollark: We should rewrite it in Haskell.
References
- Earth visibility chart and eclipse statistics Eclipse Predictions by Fred Espenak, NASA/GSFC
External links
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.
.jpg)
