Skagit County, Washington
Skagit County /ˈskædʒɪt/ is a county in the U.S. state of Washington. As of the 2010 census, the population was 116,901.[1] The county seat and largest city is Mount Vernon.[2] The county was formed in 1883 from Whatcom County[3] and is named for the Skagit Indian tribe, which has been indigenous to the area prior to European-American settlement.
Skagit County | |
|---|---|
 Skagit County Courthouse | |
 Seal | |
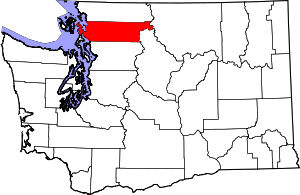 Location within the U.S. state of Washington | |
 Washington's location within the U.S. | |
| Coordinates: 48°29′N 121°47′W | |
| Country | |
| State | |
| Founded | November 28, 1883 |
| Named for | Skagit tribes |
| Seat | Mount Vernon |
| Largest city | Mount Vernon |
| Area | |
| • Total | 1,920 sq mi (5,000 km2) |
| • Land | 1,731 sq mi (4,480 km2) |
| • Water | 189 sq mi (490 km2) 9.8%% |
| Population (2010) | |
| • Total | 116,901 |
| • Estimate (2019) | 129,205 |
| • Density | 71/sq mi (27/km2) |
| Time zone | UTC−8 (Pacific) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC−7 (PDT) |
| Congressional districts | 1st, 2nd |
| Website | www |
Skagit County comprises the Mount Vernon-Anacortes, WA Metropolitan Statistical Area, and is included in the Seattle-Tacoma, WA Combined Statistical Area. It is located in the Puget Sound region.
Geography
According to the U.S. Census Bureau, the county has a total area of 1,920 square miles (5,000 km2), of which 1,731 square miles (4,480 km2) is land and 189 square miles (490 km2) (9.8%) is water.[4] It is noted for its broad, fertile valley of the Skagit River, a center for cultivation of tulips and strawberries.
Geographic features


- Allan Island
- Burrows Island
- Cascade Mountains
- Cypress Island
- Fir Island
- Fidalgo Island
- Guemes Island
- Hart Island
- Hope Island
- Kiket Island
- Pass Island
- Samish Island
- Sauk River
- Sinclair Island
- Skagit Island
- Skagit River
- Vendovi Island
- Mount Buckner, highest point in Skagit County
Adjacent counties
- Whatcom County – north
- Okanogan County – east
- Chelan County – southeast
- Snohomish County – south
- Island County – southwest
- San Juan County – west
National protected areas
- Mount Baker-Snoqualmie National Forest (part)
- North Cascades National Park (part)
- Ross Lake National Recreation Area (part)
- Pacific Northwest National Scenic Trail (part)
Demographics
| Historical population | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Census | Pop. | %± | |
| 1890 | 8,747 | — | |
| 1900 | 14,272 | 63.2% | |
| 1910 | 29,241 | 104.9% | |
| 1920 | 33,373 | 14.1% | |
| 1930 | 35,142 | 5.3% | |
| 1940 | 37,650 | 7.1% | |
| 1950 | 43,273 | 14.9% | |
| 1960 | 51,350 | 18.7% | |
| 1970 | 52,381 | 2.0% | |
| 1980 | 64,138 | 22.4% | |
| 1990 | 79,555 | 24.0% | |
| 2000 | 102,979 | 29.4% | |
| 2010 | 116,901 | 13.5% | |
| Est. 2019 | 129,205 | [5] | 10.5% |
| U.S. Decennial Census[6] 1790–1960[7] 1900–1990[8] 1990–2000[9] 2010–2019[1] | |||
2000 census
As of the census[10] of 2000, there were 102,979 people, 38,852 households, and 27,351 families living in the county. The population density was 59 people per square mile (23/km²). There were 42,681 housing units at an average density of 25 per square mile (10/km²). The racial makeup of the county was 86.49% White, 0.44% Black or African American, 1.85% Native American, 1.49% Asian, 0.16% Pacific Islander, 7.17% from other races, and 2.40% from two or more races. 11.20% of the population were Hispanic or Latino of any race. 13.9% were of German, 11.2% English, 9.2% Norwegian, 8.2% Irish and 6.7% United States or American ancestry.
Three Salish Native American tribes have reservations in the county: the Swinomish, Upper Skagit, and Samish.
There were 38,852 households out of which 32.80% had children under the age of 18 living with them, 56.60% were married couples living together, 9.70% had a female householder with no husband present, and 29.60% were non-families. 23.30% of all households were made up of individuals and 10.00% had someone living alone who was 65 years of age or older. The average household size was 2.60 and the average family size was 3.06.
In the county, the population was spread out with 26.30% under the age of 18, 8.60% from 18 to 24, 26.90% from 25 to 44, 23.60% from 45 to 64, and 14.60% who were 65 years of age or older. The median age was 37 years. For every 100 females there were 98.00 males. For every 100 females age 18 and over, there were 95.70 males.
The median income for a household in the county was $42,381, and the median income for a family was $48,347. Males had a median income of $37,207 versus $26,123 for females. The per capita income for the county was $21,256. About 7.90% of families and 11.10% of the population were below the poverty line, including 13.50% of those under age 18 and 6.80% of those age 65 or over.
2010 census
As of the 2010 United States Census, there were 116,901 people, 45,557 households, and 30,656 families living in the county.[11] The population density was 67.5 inhabitants per square mile (26.1/km2). There were 51,473 housing units at an average density of 29.7 per square mile (11.5/km2).[12] The racial makeup of the county was 83.4% white, 2.2% American Indian, 1.8% Asian, 0.7% black or African American, 0.2% Pacific islander, 8.7% from other races, and 3.2% from two or more races. Those of Hispanic or Latino origin made up 16.9% of the population.[11] The largest ancestry groups were: 17.8% German, 14.9% Mexican, 13.7% English, 11.4% Irish, 8.3% Norwegian, 4.8% Swedish, and 4.3% Dutch.[13]
Of the 45,557 households, 30.8% had children under the age of 18 living with them, 52.1% were married couples living together, 10.1% had a female householder with no husband present, 32.7% were non-families, and 25.6% of all households were made up of individuals. The average household size was 2.53 and the average family size was 3.01. The median age was 40.1 years.[11]
The median income for a household in the county was $54,811 and the median income for a family was $63,468. Males had a median income of $48,979 versus $34,628 for females. The per capita income for the county was $26,925. About 7.4% of families and 11.7% of the population were below the poverty line, including 16.0% of those under age 18 and 6.2% of those age 65 or over.[14]
Government
Skagit County's government is headed by three commissioners, in the system laid out in the state constitution for all counties without charters. Commissioners are "nominated" in the primary by their district, but then are elected in the general by a county-wide vote. Commissioners are therefore said to represent the entire county, and not just their district.
The current Skagit County commissioners include Lisa Janicki, a Democrat from District 3, which encompasses Burlington east of Interstate 5, Sedro-Woolley, and the rest of eastern Skagit County; Ken Dahlstedt, a Democrat from District 2, which covers Mount Vernon, Conway, and south county; and Ron Wesen, a Republican from District 1, which includes Anacortes, La Conner, and that area of the county west of Interstate 5 and north of McLean Road.
Politics
| Year | Republican | Democratic | Third parties |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2016 | 42.6% 24,736 | 46.0% 26,690 | 11.4% 6,633 |
| 2012 | 45.0% 25,071 | 51.5% 28,688 | 3.5% 1,938 |
| 2008 | 43.9% 24,687 | 53.4% 30,053 | 2.7% 1,513 |
| 2004 | 50.0% 26,139 | 48.1% 25,131 | 2.0% 1,029 |
| 2000 | 49.0% 22,163 | 45.2% 20,432 | 5.8% 2,626 |
| 1996 | 39.9% 16,397 | 44.5% 18,295 | 15.6% 6,426 |
| 1992 | 32.9% 13,388 | 39.1% 15,936 | 28.0% 11,404 |
| 1988 | 51.1% 16,550 | 46.8% 15,159 | 2.1% 692 |
| 1984 | 56.5% 18,840 | 41.9% 13,947 | 1.6% 539 |
| 1980 | 50.7% 15,520 | 36.9% 11,299 | 12.4% 3,804 |
| 1976 | 48.7% 13,060 | 47.4% 12,718 | 4.0% 1,059 |
| 1972 | 58.1% 14,212 | 37.8% 9,233 | 4.1% 1,003 |
| 1968 | 45.8% 10,354 | 46.6% 10,529 | 7.6% 1,711 |
| 1964 | 36.2% 8,138 | 63.7% 14,344 | 0.1% 28 |
| 1960 | 52.4% 12,168 | 47.4% 11,003 | 0.2% 49 |
| 1956 | 56.7% 12,149 | 43.1% 9,243 | 0.2% 48 |
| 1952 | 57.4% 11,446 | 41.7% 8,321 | 0.9% 185 |
| 1948 | 44.9% 8,176 | 49.9% 9,080 | 5.2% 936 |
| 1944 | 45.0% 7,805 | 54.3% 9,409 | 0.7% 118 |
| 1940 | 44.4% 7,985 | 54.5% 9,796 | 1.1% 189 |
| 1936 | 33.4% 5,222 | 61.7% 9,639 | 4.8% 754 |
| 1932 | 30.6% 4,246 | 60.5% 8,395 | 9.0% 1,247 |
| 1928 | 73.6% 8,336 | 25.1% 2,848 | 1.3% 145 |
| 1924 | 48.0% 5,071 | 6.6% 699 | 45.4% 4,806 |
| 1920 | 51.6% 5,320 | 17.9% 1,840 | 30.5% 3,146 |
| 1916 | 40.2% 4,142 | 47.9% 4,936 | 12.0% 1,232 |
| 1912 | 26.0% 2,399 | 21.2% 1,962 | 52.8% 4,876 |
| 1908 | 56.4% 2,924 | 28.0% 1,449 | 15.6% 810 |
| 1904 | 69.9% 3,051 | 20.2% 880 | 9.9% 432 |
| 1900 | 55.9% 1,814 | 37.6% 1,220 | 6.5% 211 |
| 1896 | 43.4% 1,268 | 55.6% 1,623 | 1.0% 30 |
| 1892 | 42.9% 1,246 | 31.8% 923 | 25.3% 734 |
County conservation efforts
In 2006, the Skagit County Marine Resources Committee commissioned a study to evaluate establishing one or more no-take marine reserves to protect rockfish and other groundfish from overfishing.[16]
Transportation
Skagit Transit provides bus service in Skagit County. It also provides connections to Everett, Bellingham, Whidbey Island and Camano Island. Skagit Transit also operates the Guemes Island ferry linking Anacortes, Washington to Guemes Island.
Major highways
Communities


Census-designated places
Unincorporated communities
Reservations
- Swinomish Indian Reservation
- Upper Skagit Indian Reservation
- Samish Indian Reservation
Ghost Towns
Footnotes
- "State & County QuickFacts". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved January 7, 2014.
- "Find a County". National Association of Counties. Retrieved June 7, 2011.
- "Milestones for Washington State History — Part 2: 1851 to 1900". HistoryLink.org. March 6, 2003.
- "2010 Census Gazetteer Files". United States Census Bureau. August 22, 2012. Retrieved July 16, 2015.
- "Population and Housing Unit Estimates". Retrieved April 11, 2020.
- "U.S. Decennial Census". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved January 7, 2014.
- "Historical Census Browser". University of Virginia Library. Retrieved January 7, 2014.
- "Population of Counties by Decennial Census: 1900 to 1990". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved January 7, 2014.
- "Census 2000 PHC-T-4. Ranking Tables for Counties: 1990 and 2000" (PDF). United States Census Bureau. Retrieved January 7, 2014.
- "U.S. Census website". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved May 14, 2011.
- "DP-1 Profile of General Population and Housing Characteristics: 2010 Demographic Profile Data". United States Census Bureau. Archived from the original on February 13, 2020. Retrieved March 6, 2016.
- "Population, Housing Units, Area, and Density: 2010 – County". United States Census Bureau. Archived from the original on February 13, 2020. Retrieved March 6, 2016.
- "DP02 SELECTED SOCIAL CHARACTERISTICS IN THE UNITED STATES – 2006–2010 American Community Survey 5-Year Estimates". United States Census Bureau. Archived from the original on February 13, 2020. Retrieved March 6, 2016.
- "DP03 SELECTED ECONOMIC CHARACTERISTICS – 2006–2010 American Community Survey 5-Year Estimates". United States Census Bureau. Archived from the original on February 13, 2020. Retrieved March 6, 2016.
- Leip, David. "Dave Leip's Atlas of U.S. Presidential Elections". uselectionatlas.org. Retrieved 18 March 2018.
- Valz, JH; Dinnel, PA (2007). "Bottomfish Variability in the Proposed Marine Reserves of Skagit County, Washington". In: NW Pollock and JM Godfrey (Eds.) The Diving for Science…2007, Proceedings of the American Academy of Underwater Sciences, Twenty-sixth annual Scientific Diving Symposium, University of Miami, Miami, FL. Retrieved 2009-03-24.
Further reading
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Skagit County, Washington. |
