Shenandoah National Park
Shenandoah National Park /ˈʃɛnənˌdoʊə/ (often /ˈʃænənˌdoʊə/) is an American national park that encompasses part of the Blue Ridge Mountains in the state of Virginia. The park is long and narrow, with the Shenandoah River and its broad valley to the west, and the rolling hills of the Virginia Piedmont to the east. Skyline Drive is the main park road, generally traversing near the ridgeline of the mountains. Almost 40% of the land area—79,579 acres (124.3 sq mi; 322.0 km2)—has been designated as wilderness and is protected as part of the National Wilderness Preservation System. The highest peak is Hawksbill Mountain at 4,051 feet (1,235 m).
| Shenandoah National Park | |
|---|---|
IUCN category II (national park) | |
.jpg) Skyline Drive | |
 Location in the United States  Location in Virginia  Location in the Shenandoah Valley | |
| Location | Virginia, United States |
| Nearest city | Front Royal |
| Coordinates | 38°32′N 78°21′W |
| Area | 199,173 acres (311.208 sq mi; 806.02 km2)[1] |
| Established | December 26, 1935 |
| Visitors | 1,264,880 (in 2018)[2] |
| Governing body | National Park Service |
| Website | Official website |
Geography
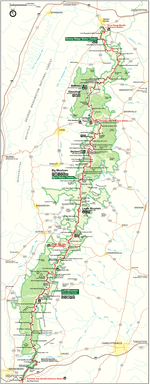
The park encompasses parts of eight counties. On the west side of Skyline Drive they are, from northeast to southwest, Warren, Page, Rockingham, and Augusta counties. On the east side of Skyline Drive they are Rappahannock, Madison, Greene, and Albemarle counties. The park stretches for 105 miles (169 km) along Skyline Drive from near the town of Front Royal in the northeast to near the city of Waynesboro in the southwest. The park headquarters are located in Luray.
Geology
Shenandoah National Park lies along the Blue Ridge Mountains in north-central Virginia. These mountains form a distinct highland rising to elevations above 4,000 feet (1,200 m). Local topographic relief between the Blue Ridge Mountains and Shenandoah Valley exceeds 3,000 feet (910 m) at some locations. The crest of the range divides the Shenandoah River drainage basin, part of the Potomac River drainage, on the west side, from the James and Rappahannock River drainage basins on the east side.[3]
Some of the rocks exposed in the park date to over one billion years in age, making them among the oldest in Virginia. Bedrock in the park includes Grenville-age granitic basement rocks (1.2–1.0 billion years old) and a cover sequence of metamorphosed Neoproterozoic (570–550 million years old) sedimentary and volcanic rocks of the Swift Run and Catoctin formations. Columns of Catoctin Formation metamorphosed basalt can be seen at Compton Peak.[4] Clastic rocks of the Chilhowee Group are of early Cambrian age (542–520 million years old). Quaternary surficial deposits are common and cover much of the bedrock throughout the park.[5][6]
The park is located along the western part of the Blue Ridge anticlinorium, a regional-scale Paleozoic structure at the eastern margin of the Appalachian fold and thrust belt. Rocks within the park were folded, faulted, distorted, and metamorphosed during the late Paleozoic Alleghanian orogeny (325 to 260 million years ago).[7] The rugged topography of Blue Ridge Mountains is a result of differential erosion during the Cenozoic, although some post-Paleozoic tectonic activity occurred in the region.[8][9]
History

Creation of the park
Legislation to create a national park in the Appalachian mountains was first introduced by freshman Virginia congressman Henry D. Flood in 1901, but despite the support of President Theodore Roosevelt, failed to pass. The first national park was Yellowstone, in Wyoming, Montana, and Idaho. It was signed into law in 1872. Yosemite National Park was created in 1890. When Congress created the National Park Service (NPS) in 1916, additional parks had maintained the western pattern (Crater Lake in 1902, Wind Cave in 1903, Mesa Verde in 1906, then Denali in 1917). Grand Canyon, Zion and Acadia were all created in 1919 during the administration of Virginia-born president Woodrow Wilson. Acadia finally broke the western mold, becoming the first eastern national park. It was also based on donations from wealthy private landowners. Stephen Mather, the first NPS director, saw a need for a national park in the southern states, and solicited proposals in his 1923 year-end report. In May 1925, Congress and President Calvin Coolidge authorized the NPS to acquire a minimum of 250,000 acres (390.6 sq mi; 1,011.7 km2) and a maximum of 521,000 acres (814.1 sq mi; 2,108.4 km2) to form Shenandoah National Park, and also authorized creation of Great Smoky Mountains National Park. However, the legislation also required that no federal funds would be used to acquire the land. Thus, Virginia needed to raise private funds, and could also authorize state funds and use its eminent domain (condemnation) power to acquire the land to create Shenandoah National Park.
Virginia's Democratic gubernatorial candidate (and the late Congressman Flood's nephew), Harry F. Byrd supported creation of Shenandoah National Park, as did his friend William E. Carson, a businessman who had become Virginia's first chairman of the Commission on Conservation and Development.[10][11] Development of the western national parks had assisted tourism, which produced jobs, which Byrd and local politicians supported. The land that became Shenandoah park was scenic, mountainous, and had also lost about half of its trees to the Chestnut blight (which was incurable and affected trees as they reached maturity). However, it had been held as private property for over a century, so many farms and orchards existed. After Byrd became governor and convinced the legislature to appropriate $1 million for land acquisition and other work, Carson and his teams (including surveyors and his brother Kit who was Byrd's law partner) tried to figure out who owned the land. They found that it consisted of more than 5,000 parcels, some of them inhabited by tenant farmers or squatters (who were ineligible to receive compensation). Some landowners, including wealthy resort owner George Freeman Pollock and Luray Realtor and developer L. Ferdinand Zerkel, had long wanted the park created and had formed the Northern Virginia Park Association to win over the national park selection committee.[12][13] However, many local families who had lived in the area for generations (especially people over 60 years old) did not want to sell their land, and some refused to sell at any price. Carson promised that if they sold to the state, they could still live on their homesteads for the rest of their lives. Carson also lobbied the new president, Herbert Hoover, who bought land to establish a vacation fishing camp near the headwaters of the Rapidan River (and would ultimately donate it to the park as he left office; it remains as Rapidan Camp).

The commonwealth of Virginia slowly acquired the land through eminent domain, and then gave it to the U.S. federal government to establish the national park. Carson's brother suggested that Virginia's legislature authorize condemnation by counties (followed by arbitration for individual parcels) rather than condemn each parcel. Some families accepted the payments because they needed the money and wanted to escape the subsistence lifestyle. Nearly 90 percent of the inhabitants worked the land for a living: selling timber, charcoal or crops. They had previously been able to earn money to buy supplies by harvesting the now-rare chestnuts, by working during the apple and peach harvest season (but the drought of 1930 devastated those crops and killed many fruit trees), by selling handmade textiles and crafts (displaced by factories) and moonshine (illegal after Prohibition started).
However, Carson and the politicians did not seek citizen input early in the process, nor convince residents that they could live better in a tourist economy. Instead they started with an advertising campaign to raise the funds, and courthouse property evaluations and surveys. Upon Mather's death in 1929, the new NPS director, Horace M. Albright also decided that the federal agency would only accept vacant land, so even elderly residents would be forced to leave. Thus, many families and entire communities were forced to vacate portions of the Blue Ridge Mountains in eight Virginia counties. Although the Skyline Drive right-of-way was purchased from owners without condemnation, the costs of the acreage purchased trebled over initial estimates and the acreage decreased to what Carson called a "fish-bone" shape and others a "shoestring".[14] Although Byrd and Carson convinced Congress to reduce the minimum size of Shenandoah Park to just over 160,000 acres (250.0 sq mi; 647.5 km2) to eliminate some high-priced lands, in 1933 newly elected President Franklin D. Roosevelt decided to also create the Blue Ridge Parkway to connect to then-under-construction Skyline Drive on the Shenandoah National Park ridgeline, which required additional condemnations.
When many families continued to refuse to sell their land in 1932 and 1933, proponents changed tactics. Freeman hired social worker Miriam Sizer to teach at a summer school he had set up near one of his workers' communities, and asked her to write a report about the conditions in which they lived. Although later discredited, the report depicted the local population as very poor and inbred, and was soon used to support forcible evictions and burning of former cabins so residents would not sneak back. University of Chicago sociologists Fay-Cooper Cole and Mandel Sherman described how the small valley communities or hollows had existed "without contact with law or government" for centuries, which some analogized to a popular comic strip Li'l Abner and his fictional community, Dogpatch. In 1933, Sherman and journalist Thomas Henry published Hollow Folk[15] drawing pitying eyes to local conditions and "hillbillies."[16][17][18] As in many rural areas of the time, most remote homesteads in the Shenandoah lacked electricity and often running water, as well as access to schools and health facilities during many months. However, Hoover had hired experienced rural teacher Christine Vest to teach near his summer home (and who believed the other reports exaggerated, as did Episcopal missionary teachers in other Blue Ridge areas).[19]

Carson had had ambitions to become governor in 1929 and 1933, but Byrd instead selected George C. Peery of the state's southwest corner to succeed easterner Pollard.[20] After winning election, Peery and Carson's successor would establish Virginia's state park system, although plans to relocate reluctant residents kept changing and basically failed. Carson had hoped to head that new state agency, but was not selected because of his growing differences with Byrd, over fees owed his brother and especially over the evictions that began in late 1933 against his advice but pursuant to new federal policies and that garnered much negative publicity.
Most of the reluctant families came from the park's central counties (Madison, Page, and Rappahannock), not the northern counties nearest Byrd's and Carson's bases, or from the southern end where residents could see tourism's benefits at Thomas Jefferson's Monticello since the 1920s, as well as the jobs available in the Shenandoah and new Blue Ridge projects. In 1931 and 1932, residents were allowed to petition the state agency to stay another year to gather crops, etc. However, some refused to cooperate to any extent, others wanted to continue to use resources now protected (including timber or homes and gardens vacated by others), and many found the permit process arbitrary. Businessman Robert H. Via filed suit against the condemnations in 1934 but did not prevail (and ended up moving to Pennsylvania and never cashed his condemnation check).
Carson announced his resignation from his unpaid job effective in December 1934. As one of his final acts, Carson wrote the new NPS director, Arno B. Cammerer, urging that 60 people over 60 years of age whose plots were not visible from the new Skyline Drive not be evicted. When evictions kept creating negative publicity in 1935, photographer Arthur Rothstein coordinated with the Hollow Folk authors and then went to document the conditions they claimed.[16]

Creation of the park had immediate benefits to some Virginians. During the Great Depression, many young men received training and jobs through the Civilian Conservation Corps (CCC). The first CCC camp in Virginia was established in the George Washington National Forest near Luray, and Governor Pollard quickly filled his initial quota of 5,000 workers. About 1,000 men and boys worked on Skyline Drive, and about 100,000 worked in Virginia during the agency's existence.[21][22] In Shenandoah Park, CCC crews removed many of the dead chestnut trees whose skeletons marred views in the new park, as well as constructed trails and facilities. Tourism revenues also skyrocketed. On the other hand, CCC crews were assigned to burn and destroy some cabins in the park, to prevent residents from coming back. Also, U.S. Secretary of the Interior Harold Ickes who had jurisdiction over the NPS and partial jurisdiction over the CCC, tried to use his authority to force Byrd to cooperate on other New Deal projects.
Shenandoah National Park was finally established on December 26, 1935, and soon construction began on the Blue Ridge Parkway that Byrd wanted.[23] President Franklin Delano Roosevelt formally opened Shenandoah National Park on July 3, 1936. Eventually, about 40 people (on the "Ickes list") were allowed to live out their lives on land that became the park. One of them was George Freeman Pollock, whose residence Killahevlin was later listed on the National Register, and whose Skyland Resort reopened under a concessionaire in 1937. Carson also donated significant land; a mountain in the park is now named in his honor and signs acknowledge his contributions. The last grandmothered resident was Annie Lee Bradley Shenk. NPS employees had watched and cared for her since 1950; she died in 1979 at age 92. Most others left quietly. 85-year-old Hezekiah Lam explained, "I ain't so crazy about leavin' these hills but I never believed in bein' ag'in (against) the Government. I signed everythin' they asked me."[24]
Segregation and desegregation

In the early 1930s, the National Park Service began planning the park facilities and envisioned separate provisions for blacks and whites. At that time, in Jim Crow Virginia, racial segregation was the order of the day. In its transfer of the parkland to the federal government, Virginia initially attempted to ban African Americans entirely from the park, but settled for enforcing its segregation laws in the park's facilities.[25]
By the 1930s, there were several concessions operated by private firms within the area that would become the park, some going back to the late 19th century. These early private facilities at Skyland Resort, Panorama Resort, and Swift Run Gap were operated only for whites. By 1937, the Park Service accepted a bid from Virginia Sky-Line Company to take over the existing facilities and add new lodges, cabins, and other amenities, including Big Meadows Lodge. Under their plan, all the sites in the parks, save one, were for "whites only". Their plan included a separate facility for African Americans at Lewis Mountain—a picnic ground, a smaller lodge, cabins and a campground. The site opened in 1939, and it was substantially inferior to the other park facilities. By then, however, the Interior Department was increasingly anxious to eliminate segregation from all parks. Pinnacles picnic ground was selected to be the initial integrated site in the Shenandoah, but Virginia Sky-Line Company continued to balk, and distributed maps showing Lewis Mountain as the only site for African Americans. During World War II, concessions closed and park usage plunged. But once the War ended, in December 1945, the NPS mandated that all concessions in all national parks were to be desegregated. In October 1947 the dining rooms of Lewis Mountain and Panorama were integrated and by early 1950, the mandate was fully accomplished.[25]
Social history
Particularly after the 1960s, park operations broadened from nature-focused to include social history. The Potomac Appalachian Trail Club had restored some cabins beginning in the 1940s, and made them available to overnight hikers. Some displaced residents (and their descendants) created the Children of the Shenandoah to lobby for more balanced presentations.
In the 1990s, the park hired cultural resource specialists and conducted an archeological inventory of existing structures, the Survey of Rural Mountain Settlement. Eventually, the park's new focus on cultural resources coincided with agitation from a descendant's organization known as the Children of Shenandoah, which resulted in the removal of questionable interpretive displays. Hikes and tours that explained the social history of the displaced mountain people began.[17]
Attractions
Skyline Drive
The park is best known for Skyline Drive, a 105-mile (169 km) road that runs the length of the park along the ridge of the mountains. 101 miles (163 km) of the Appalachian Trail are also in the park. In total, there are over 500 miles (800 km) of trails within the park. There is also horseback riding, camping, bicycling, and a number of waterfalls. The Skyline Drive is the first National Park Service road east of the Mississippi River listed as a National Historic Landmark on the National Register of Historic Places. It is also designated as a National Scenic Byway.
Backcountry camping
Shenandoah National Park offers 196,000 acres (306.2 sq mi; 793.2 km2) of backcountry and wilderness camping. While in the backcountry, campers must use a "Leave No Trace" policy that includes burying excrement and not building campfires.[26]
Backcountry campers must also be careful of wildlife such as bears and venomous snakes. Campers must suspend their food from trees while not in use in "bear bags" or park-approved bear canisters to prevent unintentionally feeding the bears, who then become habituated to humans and their food and therefore dangerous. All animals are protected by federal law.
Lodging
Campgrounds and cabins
Most of the campgrounds are open from April to October–November. There are five major campgrounds:[27]
- Mathews Arm Campground
- Big Meadows Campground
- Lewis Mountain Campground
- Loft Mountain Campground
- Dundo Group Campground
Lodges
There are three lodges/cabins:[28]
- Skyland Resort
- Big Meadows
- Lewis Mountain Cabins

Lodges are located at Skyland and Big Meadows. The park's Harry F. Byrd Visitor Center is also located at Big Meadows. Another visitor center is located at Dickey Ridge. Campgrounds are located at Mathews Arm, Big Meadows, Lewis Mountain, and Loft Mountain.
Rapidan Camp, the restored presidential fishing retreat Herbert Hoover built on the Rapidan River in 1929, is accessed by a 4.1-mile (6.6 km) round-trip hike on Mill Prong Trail, which begins on the Skyline Drive at Milam Gap (Mile 52.8). The NPS also offers guided van trips that leave from the Byrd Center at Big Meadows.
Shenandoah National Park is one of the most dog-friendly in the national park system. The campgrounds all allow dogs, and dogs are allowed on almost all of the trails including the Appalachian Trail, if kept on leash (6 feet or shorter). Dogs are not allowed on ten trails: Fox Hollow Trail, Stony Man Trail, Limberlost Trail, Post Office Junction to Old Rag Shelter, Old Rag Ridge Trail, Old Rag Saddle Trail, Dark Hollow Falls Trail, Story of the Forest Trail, Bearfence Mountain Trail, Frazier Discovery Trail. These ten trails fall short of a total of 20 miles of the 500 miles of trails of the Shenandoah National Park.[29]
Streams and rivers in the park are very popular with fly fisherman for native brook trout.[30]
Waterfalls
Many waterfalls are located within the park boundaries. Below is a list of significant falls.[31]
| Falls | Height | Location | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Overall Run | 93 ft (28 m) | Mile 21.1, parking lot just south of Hogback Overlook | The tallest waterfall in the park. 6.5 mile (10 km) round trip hike. Go before June as this waterfall tends to dry up. |
| Whiteoak Canyon | 86 ft (26 m) | Mile 42.6, Whiteoak Canyon parking area | Whiteoak Canyon has a series of six waterfalls, the first (and tallest) is 86 feet (28 m). Not all the falls are easily accessible from the trail. Start at the lowest and work your way up to the tallest waterfall. |
| Cedar Run | 34 ft (10 m) | Mile 45.6, Hawksbill Gap parking area | Difficult 3.4 mile (5 km) round trip hike. Sights along the way include waterfalls, swimming holes, and natural rock slides of varying lengths. |
| Rose River | 67 ft (20 m) | Mile 49.4, parking at Fishers Gap Overlook | A 2.6 mile (4 km) round trip hike. Can also be done as a longer loop hike. |
| Dark Hollow Falls | 70 ft (21 m) | Mile 50.7, Dark Hollow Falls parking area | 1.4 mile (2 km) round trip hike. The closest waterfall to Skyline Drive and the most popular. No pets allowed on this trail. |
| Lewis Falls | 81 ft (25 m) | Mile 51.4, parking lot just south of Big Meadows, next to a service road | 2 mile (3 km) round trip hike. |
| South River Falls | 83 ft (25 m) | Mile 62.8, park at South River picnic area | 3.3 mile (5 km) loop hike to an overlook above the falls. There is also a rocky, 1 mile (2 km) round trip spur trail that goes to the base of the falls. The "shortcut" is before the overlook but watch out for water snakes as they're very common in this area. |
| Doyles River Falls | 28 and 63 ft (9 and 19 m) | Mile 81.1, Doyles River parking area | A 3-mile (4.8 km) round trip hike to see both the upper and lower falls. Be sure to go a little past the lower falls viewing spot for a better view. Can also be turned into a 7.8-mile (12.6 km) loop trail that also goes by Jones Run Falls |
| Jones Run Falls | 42 ft (13 m) | Mile 84.1, Jones Run parking area | A 3.6-mile (5.8 km) round trip hike. Can also be turned into a longer loop hike that goes by Doyles River upper and lower falls |
 Whiteoak Canyon
Whiteoak Canyon Rose River Falls
Rose River Falls South River Falls
South River Falls Jones Run Falls
Jones Run Falls
Hiking trails
Dark Hollow Falls Trail
.jpg)
Beginning at mile 50.7 of the Skyline Drive near the Byrd Visitor Center, Dark Hollow Falls Trail leads downhill beside Hogcamp Branch to Dark Hollow Falls, a 70-foot cascade. The distance from the trailhead to the base of the falls is 0.7 mile, although the trail continues beyond that point, crossing the creek and connecting with the Rose River fire road.[32] Various fauna can be viewed along the trail, including occasional sightings of black bears and timber rattlesnakes.[33] While the trail is relatively short, parts of it are steep and may prove challenging to some visitors. There is no view from the brink of the falls, and slippery rocks make it inadvisable to leave the trail.[32]
Climate
According to the Köppen climate classification system, Shenandoah National Park has a humid continental climate with warm summers and no dry season (Dfb). According to the United States Department of Agriculture, the plant hardiness zone at Big Meadows Visitor Center (3514 ft / 1071 m) is 6a with an average annual extreme minimum temperature of -7.1 °F (-21.7 °C).[34]
| Climate data for Big Meadows, Virginia (station elevation 3,540ft) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °F (°C) | 68 (20) |
66 (19) |
78 (26) |
87 (31) |
89 (32) |
88 (31) |
95 (35) |
92 (33) |
90 (32) |
84 (29) |
75 (24) |
68 (20) |
95 (35) |
| Mean maximum °F (°C) | 54.5 (12.5) |
57.6 (14.2) |
66.4 (19.1) |
75.8 (24.3) |
79.2 (26.2) |
83 (28) |
84.3 (29.1) |
83.4 (28.6) |
80.9 (27.2) |
73.6 (23.1) |
64.9 (18.3) |
57.8 (14.3) |
84.7 (29.3) |
| Average high °F (°C) | 36.1 (2.3) |
38.3 (3.5) |
45.9 (7.7) |
56.9 (13.8) |
65.5 (18.6) |
72.3 (22.4) |
75.4 (24.1) |
74.1 (23.4) |
68.1 (20.1) |
58.7 (14.8) |
48.0 (8.9) |
38.9 (3.8) |
56.5 (13.6) |
| Average low °F (°C) | 18.4 (−7.6) |
19.7 (−6.8) |
26.3 (−3.2) |
35.7 (2.1) |
45.5 (7.5) |
53.4 (11.9) |
57.2 (14.0) |
55.9 (13.3) |
49.8 (9.9) |
39.8 (4.3) |
30.4 (−0.9) |
21.4 (−5.9) |
37.8 (3.2) |
| Mean minimum °F (°C) | −2.2 (−19.0) |
−0.8 (−18.2) |
6.9 (−13.9) |
17.8 (−7.9) |
29.4 (−1.4) |
39.7 (4.3) |
46.2 (7.9) |
44 (7) |
34.2 (1.2) |
23.1 (−4.9) |
12.1 (−11.1) |
2 (−17) |
−6.4 (−21.3) |
| Record low °F (°C) | −29 (−34) |
−14 (−26) |
−6 (−21) |
7 (−14) |
18 (−8) |
31 (−1) |
34 (1) |
31 (−1) |
25 (−4) |
12 (−11) |
−1 (−18) |
−15 (−26) |
−29 (−34) |
| Average precipitation inches (mm) | 3.56 (90) |
3.06 (78) |
4.06 (103) |
4.03 (102) |
4.73 (120) |
4.71 (120) |
4.54 (115) |
4.88 (124) |
5.12 (130) |
4.86 (123) |
4.35 (110) |
3.61 (92) |
51.51 (1,308) |
| Average snowfall inches (cm) | 10.5 (27) |
9.5 (24) |
8.4 (21) |
1.7 (4.3) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0.7 (1.8) |
3.6 (9.1) |
6.6 (17) |
41.0 (104) |
| Average precipitation days | 9 | 8 | 10 | 10 | 12 | 11 | 12 | 11 | 10 | 9 | 8 | 8 | 118 |
| Average snowy days | 7 | 6 | 4 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 5 | 28 |
| Source: http://www.wrcc.dri.edu/cgi-bin/cliMAIN.pl?va0720 | |||||||||||||
Ecology

The climate of the park and its flora and fauna are typical for mountainous regions of the eastern Mid-Atlantic woodland, while a large portion of common species are also typical of ecosystems at lower altitudes. A. W. Kuchler's potential natural vegetation type for the park is Appalachian oak (104) within an eastern hardwood forest vegetation form (25), also known as a temperate broadleaf and mixed forest.[35]
Pines predominate on the southwestern faces of some of the southernmost hillsides, where an occasional prickly pear cactus may also grow naturally. In contrast, some of the northeastern aspects are most likely to have small but dense stands of moisture loving hemlocks and mosses in abundance. Other commonly found plants include oak, hickory, chestnut, maple, tulip poplar, mountain laurel, milkweed, daisies, and many species of ferns. The once predominant American chestnut tree was effectively brought to extinction by a fungus known as the chestnut blight during the 1930s; though the tree continues to grow in the park, it does not reach maturity and dies back before it can reproduce. Various species of oaks superseded the chestnuts and became the dominant tree species. Gypsy moth infestations beginning in the early 1990s began to erode the dominance of the oak forests as the moths would primarily consume the leaves of oak trees. Though the gypsy moths seem to have abated, they continue to affect the forest and have destroyed almost ten percent of the oak groves.[36]
Wildlife

Mammals include black bear, coyote,[37] striped skunk, spotted skunk, raccoon, beaver, river otter, opossum, woodchuck, two species of foxes, white-tailed deer, and eastern cottontail rabbit. Though unsubstantiated, there have been some reported sightings of cougar in remote areas of the park.[38] Over 200 species of birds make their home in the park for at least part of the year. About thirty live in the park year round, including the barred owl, Carolina chickadee, red-tailed hawk, and wild turkey. The peregrine falcon was reintroduced into the park in the mid-1990s and by the end of the 20th century there were numerous nesting pairs in the park.[39] Thirty-two species of fish have been documented in the park, including brook trout, longnose and eastern blacknose dace, and the bluehead chub.[40]
Ranger programs
Park rangers organize several programs from spring to fall. These include ranger-led hikes, as well as discussions of the history, flora, and fauna. Shenandoah Live is an online series where listeners may chat live with rangers and learn about some of the park's features. Rangers discuss a wide range of topics while answering questions and talking with experts from the field.[41]
Artist-in-Residence Program
In 2014, under the leadership of Superintendent Jim Northup, Shenandoah National Park established an Artist-in-Residence Program that is administered by the Shenandoah National Park Trust, the park's philanthropic partner.[42] Photographer Sandy Long was selected as the park's first artist-in-residence.[43][44] The results of Long's residency were featured in the photography exhibit "Wild Beauty: The Artful Nature of Shenandoah National Park"[45] held at the Looking Glass Art Gallery in the historic Hawley Silk Mill, in Hawley, Pennsylvania.
See also
References
- "Listing of acreage as of December 31, 2011". Land Resource Division, National Park Service. Retrieved 2012-03-07.
- "NPS Annual Recreation Visits Report". National Park Service. Retrieved 2019-03-11.
- "GOL 135: The geology of Shenandoah National Park, Virginia". nvcc.edu. Retrieved 17 June 2015.
- Callan Bentley (14 November 2011). "Compton Peak: superb columnar jointing". Callan Bentley's blog Mountain Beltway on American Geophysical Union Blogosphere. Retrieved 24 July 2015.
- "Archived copy" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2010-09-01. Retrieved 2010-08-31.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)
- Scott Southworth (17 June 2015). "Geologic Map of the Shenandoah National Park Region, Virginia". usgs.gov. Retrieved 17 June 2015.
- Hatcher, R.D. "Tracking Lower-to-Mid-to-Upper Crustal Deformation Processes through Time and Space through Three Paleozoic Orogenies in the Southern Appalachians Using Dated Metamorphic Assemblages and Faults". Geological Society of America Abstracts with Programs v. 40, p. 513. Geological Society of America. Retrieved 2012-01-23.
- "Google Earth Multimedia". wm.edu. Archived from the original on 2016-03-03. Retrieved 7 May 2015.
- "Geological Evolution of Virginia and the Mid-Atlantic Region". jmu.edu. Retrieved 7 May 2015.
- "Carson, William Edward (1870–1942)". www.encyclopediavirginia.org. Retrieved 14 September 2017.
- Ronald Heinemann, Harry Byrd (Charlottesville, University of Virginia Press 1996) pp. 76, 81, 87–89
- "Historical Overview - Shenandoah National Park (U.S. National Park Service)". www.nps.gov. Retrieved 14 September 2017.
- Darwin Lambert, the Undying Part of Shenandoah National Park (Shenandoah History Association, 1989, 2001) pp. 199–200
- Heinemann, Harry Byrd p. 89
- Sherman, Mandel; Henry, Thomas R. (14 September 2017). "Hollow folk". Thomas Y. Crowell Company. Retrieved 14 September 2017 – via Hathi Trust.
- "Shenandoah secrets: Pork, propaganda, and the creation of a COOL national park". www.readthehook.com. Retrieved 14 September 2017.
- "The Displaced - Shenandoah National Park (U.S. National Park Service)". www.nps.gov. Retrieved 14 September 2017.
- "Rejecting the hillfolk". xroads.virginia.edu. Retrieved 14 September 2017.
- "Creation and Dispossession: Shenandoah National Park and its Residents - Special Collections at Belk Library". collections.library.appstate.edu. Retrieved 14 September 2017.
- Heinemann, Harry Byrd, pp. 89–90
- Anne Frederick, Shenandoah, its National Park and Neighbors, (Arcadia Publishing, 2000) pp. 38–39
- Ronald L. Heinemann, Depression and New Deal in Virginia (Charlottesville: University of Virginia Press 1983) p. 65
- Heinemann, Harry Byrd pp. 174–175
- Shenandoah National Park Archived 2008-04-15 at the Wayback Machine. vahistory.org. Retrieved on September 22, 2007.
- Engle, Reed (January 1996). "Shenandoah National Park – Segregation / Desegregation". National Park Service. Retrieved 2007-09-10.
- "The Leave No Trace Seven Principles - Leave No Trace". lnt.org.
- "Campgrounds – Shenandoah National Park (U.S. National Park Service)". nps.gov. Retrieved 7 May 2015.
- "Ooops! Page Not Found – Aramark Leisure". visitshenandoah.com. Retrieved 7 May 2015.
- "Official SNP Pet Policy." National Park Service. Retrieved on September 22, 2007.
- Slone, Harry (1991). Virginia Trout Streams-A guide to fishing the Blue Ridge watershed. Woodstock, Vermont: Backcounty Publications. pp. 37–54. ISBN 0-88150-207-3.
- Nicole Blouin, Steve; Bordonaro, Marilou W (1996). Waterfalls of the Blue Ridge. Menasha Ridge Press. ISBN 0-89732-190-1.
- "Fishers Gap to Naked Creek Overlook". Guide to Shenandoah National Park and Skyline Drive. Retrieved 2012-06-26.
- "Virginia Birding and Wildlife Trail » Mountain Trail » Skyline Drive » Dark Hollow Falls Trail, Shenandoah National Park". Archived from the original on 20 March 2007. Retrieved 14 September 2017.
- "USDA Interactive Plant Hardiness Map". United States Department of Agriculture. Retrieved 2019-07-18.
- "U.S. Potential Natural Vegetation, Original Kuchler Types, v2.0 (Spatially Adjusted to Correct Geometric Distortions)". Data Basin. Retrieved 2019-07-18.
- "Shenandoah National Park – Forests". National Park Service. Retrieved 2007-09-10.
- "Coyote-Wolf Hybrids Have Spread Across U.S. East". 8 November 2011. Retrieved 14 September 2017.
- "Shenandoah National Park – Mammals". National Park Service. Retrieved 2007-09-01.
- "Shenandoah National Park – Birds". National Park Service. Retrieved 2007-09-01.
- "Shenandoah National Park – Fish". National Park Service. Retrieved 2007-09-01.
- "Ranger Programs – Shenandoah National Park (U.S. National Park Service)". nps.gov. Retrieved 7 May 2015.
- "Shenandoah National Park debuts artist-in-residence program for 2014". Augusta Free Press. Retrieved 2016-03-12.
- Brown, Cassandra (Winter 2015). "Making Art in the Park: Shenandoah National Park's First Artist-in-Residence Reflects on Her Experience" (PDF). Piedmont Virginian. Retrieved March 12, 2016.
- "Shenandoah National Park appoints artist-in-residence from Pike County". poconorecord.com. Retrieved 2016-03-12.
- ""Wild Beauty" images of Shenandoah National Park on exhibit". News Eagle. Retrieved 2016-03-12.
External links
- Official website

- Shenandoah National Park— When Past is Present: Archaeology of the Displaced in Shenandoah National Park
- NASA Earth Observatory Satellite images of Shenandoah National Park and park's vicinity
- United States Geological Survey: Geologic Map of the Shenandoah National Park Region, Virginia
- Henry Heatwole's Guide to Shenandoah National Park and Skyline Drive
- Interactive Virtual Tours of Shenandoah National Park
- The Ground Beneath Our Feet online exhibit of the Virginia Historical Society regarding creation of the Shenandoah National Park
- A Guide to the Shenandoah Valley Oral History Project, 2005–2006
