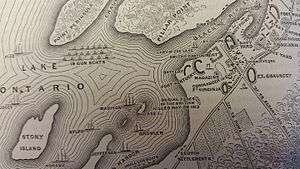
Second Battle of Sacket's Harbor
The Second Battle of Sacket's Harbor or simply the Battle of Sacket's Harbor, took place on 29 May 1813, during the War of 1812. A British force was transported across Lake Ontario and attempted to capture the town, which was the principal dockyard and base for the American naval squadron on the lake. Twelve warships were built here. The British were repulsed by American regulars, militia, marines and sailors.
Background
In the early weeks of the War, the British had seized control of the Great Lakes. In September 1812 U.S. Navy Captain Isaac Chauncey was ordered to assume command of naval forces on Lakes Ontario and Erie with the directive to "...use every exertion to obtain control of them this fall." Within three weeks he had directed and brought 149 ships' carpenters, 700 Seamen and Marines, and some 100 cannon, along with a good quantity of muskets and other supplies, to Sacket's Harbor on Lake Ontario[8] where there was already a small navy yard.
At the start of the campaigning season of 1813, the main American forces on the border between the United States and Canada had been concentrated at Sacket's Harbor. The naval squadron which Chauncey had created was superior to the opposing British and Canadian-manned squadron at Kingston, and the troops under Major General Henry Dearborn could outnumber the British at any point on their extended front. The Americans had a chance to storm Kingston, which would have eliminated the British squadron and perhaps allowed the Americans to secure almost all of Upper Canada.
However, Dearborn and Chauncey exaggerated the number of British regulars they believed to be stationed at Kingston, and instead proceeded to attack York, the Provincial capital of Upper Canada, at the other end of the lake. On 27 April, the Americans won the Battle of York, temporarily occupying and looting the town. They withdrew to Fort Niagara near the mouth of the Niagara River, preparing to attack the British position at Fort George on the opposite side of the river.
Late in 1812, Captain James Lucas Yeo had been appointed by the Admiralty to command the British naval force on the Great Lakes. He arrived at Quebec on 5 May 1813, and proceeded up the Saint Lawrence River to Kingston with a party of 150 naval officers and sailors.[9] On the way, he overtook and joined the Governor General of Canada, Lieutenant General Sir George Prevost, who was also proceeding to Kingston. This was Prevost's second visit to Upper Canada in four months, as he thought it would probably prove necessary to replace Major General Roger Hale Sheaffe, who had lost the confidence of the Provincial Assembly after his defeat at York.
Prevost and Yeo arrived at Kingston on 15 May. While Prevost reorganised his command and attempted to raise the morale of the militia and civil authorities, Yeo hastened the completion of the new sloop-of-war Wolfe and the refitting of several other armed vessels. (Much of the work had already been accomplished by three officers, Commanders Robert Heriot Barclay, Robert Finnis and Daniel Pring, who had been detached from the naval establishment at Halifax, Nova Scotia). Prevost and Yeo knew that when the Wolfe was completed, Yeo's squadron would be slightly superior to Chauncey's, but also that the Americans were building the 28-gun heavy sloop-of-war General Pike at Sackett's Harbor, which would return the advantage to Chauncey.[10]
On 25 May, Chauncey's squadron was sighted off Fort George. The British commander there, Brigadier General John Vincent, immediately sent a dispatch vessel to Kingston with the information. (Two days later, he was driven from his position with heavy losses at the Battle of Fort George.) On learning of Chauncey's presence off Fort George, Yeo and Prevost realised that the American squadron and Dearborn's army would probably be occupied there for several days.[11] They had an opportunity to capture Sacket's Harbor, and deliver a decisive blow to the shipyard to ensure that the British gained naval supremacy on the lake.
Battle
British forces
The available British troops at Kingston, consisting of the grenadier company of the 100th Regiment, two companies of the 8th (The King's) Regiment of Foot, four companies of the 104th Regiment, one company of the Glengarry Light Infantry, two companies of the Canadian Voltigeurs and a detachment of Royal Artillery with two 6-pounder guns, were hastily assembled and embarked on Yeo's vessels. As no General officer was immediately available to command them, Prevost himself led the expedition, although he delegated command of the troops once they were ashore to his Adjutant General, Colonel Edward Baynes.[12]
Battle of Henderson Bay
The British force set out late on 27 May and arrived off Sacket's Harbor early the next morning. The wind was very light, which made it difficult for Yeo to manoeuvre close to the shore. He was also unfamiliar with the local conditions and depths of water. Shortly before midday on 28 May, the troops began rowing ashore, but unknown sails were sighted in the distance. In case they might be Chauncey's fleet, the attack was called off, and the troops returned to the ships. The distant sails proved to belong to twelve bateaux carrying troops from the 9th and 21st U.S. Regiments of Infantry from Oswego to Sackets Harbor.[1][13] The British sent out three large canoes full of Native American warriors and a gunboat carrying a detachment of the Glengarry Light Infantry to intercept them.[1]
The British force caught up with the convoy off Stoney Point on Henderson Bay. As the British opened fire, the Americans, who were mostly raw recruits, landed their bateaux at Stoney Point and fled into the woods. The Natives pursued them through the trees and hunted them down. After about half an hour, during which they lost 35 men killed, the surviving United States troops regained their vessels and raised a white flag. The senior officer rowed out to Yeo's fleet and surrendered his remaining force of 115 officers and men.[1] Only seven of the American troops escaped and reached Sacket's Harbor.[13]
American defenses
This delay gave the Americans time to reinforce their defences. Some 400 regulars were then stationed at Sacket's Harbor, mainly the small detachments manning Fort Volunteer and Fort Tompkins at the harbour entrance, and various parties of reinforcements and invalids. The senior regular officer was Lieutenant Colonel Electus Backus of the 1st Regiment of Light Dragoons. There were 250 volunteers from the New York militia, and an additional 500 militia were hastily called up from the surrounding area. Under arrangements made by Henry Dearborn before he departed for York, Brigadier General Jacob Brown of the New York state militia took command of all troops at Sacket's Harbor.[14]
In addition to Fort Volunteer and Fort Tompkins, the Americans had built several strong blockhouses south of the village, and partially completed a line of earthworks and abatis (defence works made from felled trees and branches) surrounding the town and shipyard. These defences had been planned and laid out the previous year by Lieutenant Colonel Alexander Macomb.
Most of the American flotilla was at Fort George with Chauncey, but two armed schooners, Fair American and Pert, were anchored in Blackwater Creek, off Sacket's Harbor. The senior naval officer present was Lieutenant Woolcott Chauncey, younger brother of the Commodore.
Order of Battle
| British/Native American order of battle | American order of battle |
|---|---|
|
British Army: Lieutenant General Sir George Prévost[15]
|
Sackets Harbor: Brigadier General Jacob Brown[17][18]
|
British attack
The next morning, 29 May, Prevost resumed the attack. The British troops landed on Horse Island, south of the town, under fire from two 6-pounder field guns belonging to the militia and a naval 32-pounder firing at long range from Fort Tompkins. They also faced musket fire from the Albany Volunteers defending the island.[20] Although the British lost several men in the boats, they succeeded in landing, and the Volunteers withdrew. Once the landing force was fully assembled, they charged across the flooded causeway linking the island to the shore. Although the British should have been an easy target at this point, the American militia fled, abandoning their guns. Brigadier General Brown eventually rallied about 100 of them.[3]
The British swung to their left, hoping to take the town and dockyard from the landward side, but the American regulars with some field guns gave ground only slowly. They fell back behind their blockhouses and defences, from where they repulsed every British attempt to storm their fortifications.
Yeo had gone ashore to accompany the troops, and none of the larger British vessels was brought into a range at which to support the attack. The small British gunboats, which could approach very close to the shore, were armed only with small, short-range carronades, which were ineffective against the American defences. Eventually one British ship, Beresford, mounting 16 guns, worked close in using sweeps (long oars). When its crew opened fire, they quickly drove the American artillerymen from Fort Tompkins. Some of Beresford's shot went over the fort and landed in and around the dockyard. Under the mistaken impression that the fort had surrendered, a young American naval officer, Acting Lieutenant John Drury, ordered the sloop-of-war General Pike, which was under construction, and large quantities of stores to be set on fire. Lieutenant Woolcott Chauncey had orders to defend the yard rather than the schooners, but had instead gone aboard one of the schooners, which were engaging the British vessels at long and ineffective range.[21]
By this time, Prevost was convinced that success was impossible to attain. His own field guns did not come into action and without them he was unable to batter breaches in the American defences, while the militia which Brown had rallied were attacking his own right flank and rear. He gave the order to retreat. Prevost later wrote that the enemy had been beaten and that the retreat was carried out in perfect order, but other accounts by British soldiers stated that the re-embarkation took place in disorder, and each unit acrimoniously blamed the others for the repulse.[22]
The Americans for their part claimed that had Prevost not retreated hastily when he did, he would never have returned to Kingston. The U.S. 9th Infantry had been force-marching to the sounds of battle, but the British had departed before they could intervene.[23]
Casualties

The British Army casualty return for the engagement detailed 1 officer and 47 men killed, 12 officers and 183 men wounded, and 3 officers and 13 men "wounded and missing" (i.e. left behind).[4] The separate Royal Navy casualty list gave 1 killed and 5 wounded.[5] This added up to a total British loss of 49 killed and 216 wounded, of whom 16 were left behind on the field.
However, Patrick Wilder says "three captured British officers and 32 British soldiers were placed in the care of the American military surgeons.[6] This would indicate that 19 of the British enlisted men who were assumed to have been killed when the official return of casualties was made out were in fact wounded and captured. This gives a revised British casualty total of 30 killed, 200 wounded, and 35 wounded prisoners. One notable British casualty was Captain Andrew Gray, Prevost's Deputy Assistant Adjutant General, who was killed.
Major William Swan's casualty report for the American force detailed 22 killed, 84 wounded, and 26 missing for the U.S. regulars and the federal volunteer units. Swan gave no detailed report of the militia loss, stating only that it did not "exceed twenty-five".[2] This would give an American loss in the battle of May 29 of about 157 killed, wounded and missing, including Lieutenant Colonel Electus Backus, who was killed.
Including the 35 men killed and 115 captured at Henderson Bay on May 28, the American loss came to 307 officers and enlisted men killed, wounded or captured. The British captured three 6-pounder guns and 154 prisoners on May 28 and May 29,[3] which indicates that 39 prisoners were taken on May 29. Since only 26 of the regular and volunteer troops were reported as "missing", this would suggest that about half of the 25 or so militia casualties were captured. This gives a grand total American loss for May 28–29 of 153 killed and wounded and 154 taken prisoner.
Results
Although General Pike had been set on fire, since it was constructed from green wood it did not burn well, and the Americans were able to salvage the ship. The fires set by Acting Lieutenant Drury consumed $500,000 worth of stores and construction materials, which was to prove a handicap later in the year. The brig Duke of Gloucester, which had earlier been brought back as a prize from York, was also destroyed but was no great loss as it was in poor repair.
The news of the British assault caused Commodore Chauncey to recall his entire squadron to Sacket's Harbor until General Pike was completed, leaving the American Army on the Niagara peninsula without support. They had already been checked at the Battle of Stoney Creek, and Yeo attacked their vulnerable lakeside flank, capturing provision boats, tents and large quantities of supplies and forcing them to withdraw to Fort George.
Yeo made another attempt to destroy General Pike after it had been launched but while it was still fitting out at Sackett's Harbor and waiting for replacements for the materials destroyed on 29 May. He intended to launch a surprise attack from boats at dawn on 1 July, but day broke while he was still short of his objective and his force took refuge on the north shore of Blackwater Creek. During the day, some seamen and marines deserted and Yeo called off the attack, fearing (correctly) that the deserters would have alerted the Americans.[24]
For several months, the fighting on and around Lake Ontario was stalemated, until General Pike heavily damaged Yeo's flagship, Wolfe, in an engagement off York on 28 September. Yeo withdrew into Burlington Bay, and conceded control of the lake for the remainder of the year.
Jacob Brown was rewarded for his part in the victory at Sacket's Harbor with a regular commission as Brigadier General in the United States Army. On the British side, Prevost's prestige was badly damaged by the repulse, although he remained in command in Canada for another year and a half before another defeat at the Battle of Plattsburgh finally ruined his reputation.
Four active regular infantry battalions of the United States Army (1-2 Inf, 2-2 Inf, 1-5 Inf and 2-5 Inf) perpetuate the lineages of American infantry units (the old 9th, 21st and 23rd Infantry Regiments) that were at the Battle of Sackett's Harbor.
Within the British Army, the 1st (Royal Scots) Foot is perpetuated by the Royal Regiment of Scotland while the 8th (King's) Foot is perpetuated by the Duke of Lancaster's Regiment.
The Canadian Army commemorates the 104th Regiment of Foot through the North Shore (New Brunswick) Regiment and the Glengarry Light Infantry through the Stormont, Dundas and Glengarry Highlanders. The Royal Newfoundland Fencibles are perpetuated by the Royal Newfoundland Regiment while the Canadian Voltigeurs are perpetuated by Les Voltigeurs de Quebec.

Brigadier and Quartermaster General Robert Swartwout dispatched a letter on 23 June to Major General William Henry Harrison announcing the American victory. Dispatch from Quartermaster General Robert Swartwout to General William Henry Harrison via Postmaster Erastus Granger of Buffalo, New York, 1p, at Headquarters, Fort George, 2 June 1813, 10 o'clock a.m. Sir, The Dispatch for General Harrison which I have the honor to enclose. You will be pleased to forward to that office by Express. The British under Sir Gen Prevost and Sir Gen Yeo have been defeated with great loss in an attack which they made upon Sackets Harbor on the 2 Militia. Our loss in numbers was trifling. Signed by Swartwout as Brigadier Quarter Master General.
Analysis
The British defeat at Sacket's Harbor compared badly with Americans' victorious opposed landings at York and Fort George, even though the odds at Sackett's Harbor were slightly more favourable to the defenders. The chief reason was probably that the attack was launched without sufficient preparation, planning and rehearsal. The troops were an ad hoc collection of detachments, who had not been exercised together. This applied to the American regulars also, but since they were fighting from behind fixed defences, this mattered less.
Although Prevost had previously commanded troops in an opposed landing at Martinique in 1809, he had not directly led them, but as at Sacket's Harbor he had delegated command to another officer (in this instance, Brigadier General Daniel Hoghton). He was to be noted for his caution in later actions. Colonel Baynes, to whom Prevost delegated command at Sackett's Harbor, had had little opportunity to lead troops in battle during his career. Yeo had a reputation as a fighting captain, gained by leading landing parties, but was new to the command and conditions on the lake, and cautiously kept most of his warships in deep water on 28 May. When he went ashore on 29 May to be close to the fighting, the larger British vessels were apparently left without orders and only Beresford attempted to intervene decisively.
Battlefield preservation
The American Battlefield Trust and its partners have acquired and preserved 25 acres (0.10 km2) of the Sacket's Harbor battlefield.[25]
See also
- First Battle of Sacket's Harbor
- Bibliography of early American naval history, War of 1812
References
- Wilder, p.75
- Wilder, p. 122
- Hitsman, p.148
- Cruikshank, p. 278
- Cruikshank, p. 290
- Wilder, p. 119
- Lossing, Benson (1868). The Pictorial Field-Book of the War of 1812. Harper & Brothers, Publishers. p. 614.
- Paine, 1920 pp. 293-304
- Hitsman, p.142
- Hitsman, p.143
- Hitsman, p.144
- Hitsman, p.146
- Roosevelt, p.130
- Morris, p.17
- Glengarry Light Infantry site
- "The Gentleman's Magazine". 1865. p. 125. Retrieved 28 October 2015.
- Morris p.40
- Feltoe p.88
- Jefferson County War of 1812 officer's roll Archived 2013-12-15 at the Wayback Machine
- Malcolmson, p.133-134
- Malcolmson, pp.136-137
- Hitsman, pp.148-149
- Elting, p.131
- Malcolmson, pp.151-153
- American Battlefield Trust "Saved Land" webpage. Accessed May 23, 2018.
Bibliography
- Cruikshank, Ernest (1971). The Documentary History of the Campaign upon the Niagara Frontier in the Year 1813. Part I: January to June, 1813. New York: Arno Press (reprint edition). ISBN 0-405-02838-5.
- Paine, Ralph Delahaye (2010) [1920]. The fight for a free sea: a chronicle of the War of 1812.
Yale University Press, New Haven, 1920. p. 235. ISBN 1-59114-362-4. Url - Elting, John R. (1995). Amateurs to Arms:A military history of the War of 1812. New York: Da Capo Press. ISBN 0-306-80653-3.
- Feltoe, Richard. (2013). The Pendulum of War: The Fight for Upper Canada, January-June 1813. Toronto: Dundurn. ISBN 978-1459706996.
- Hitsman, J. Mackay; Donald E. Graves (1999). The Incredible War of 1812. Toronto: Robin Brass Studio. ISBN 1-896941-13-3.
- Latimer, Jon (2007). 1812: War with America. Harvard University Press. ISBN 0-674-02584-9.
- Malcomson, Robert (1998). Lords of the Lake:The Naval War on Lake Ontario 1812-1814. Toronto: Robin Brass Studio. ISBN 1-896941-08-7.
- Morris, J.D. (2000). Sword of the Border: Major General Jacob Jennings Brown, 1775-1828. Kent. Ohio: The Kent State University Press. ISBN 0-87338-659-0.
- Roosevelt, Theodore. The Naval War of 1812. New York: Modern Library. ISBN 0-375-75419-9.
- Wilder, Patrick A. (1994). The Battle of Sackett's Harbour. Baltimore, MD: The Nautical & Aviation Company of America. ISBN 1-877853-27-5.
Further reading
- Homans, Benjamin (1833). The Military and Naval Magazine of the United States, Volumes 1-2. Thompson and Homans, Washington. pp. 393.
