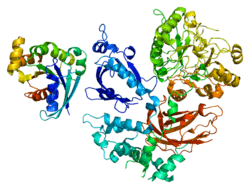
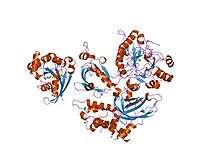
PLCB2
1-Phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate phosphodiesterase beta-2 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PLCB2 gene.[5][6][7]
Function
The gene codes for the enzyme phospholipase C β2. The enzyme catalyzes the formation of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate and diacylglycerol from phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate. This reaction uses calcium as a cofactor and plays an important role in the intracellular transduction of many extracellular signals. This gene is activated by two G-protein alpha subunits, alpha-q and alpha-11, as well as G-beta gamma subunits.
Interactions
PLCB2 has been shown to interact with MAP2K3[8] and TRPM7.[9]
gollark: Put in the hostnames (ns1.luadns.net etc.) and not the IPs.
gollark: Yes. For redundancy or something.
gollark: Yes, CONFIGURE them utterly as your domain's nameservers.
gollark: Then configure custom nameservers and put in the LuaDNS ones.
gollark: Go to "management tools" then "nameservers".
References
- GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000137841 - Ensembl, May 2017
- GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000040061 - Ensembl, May 2017
- "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- Park D, Jhon DY, Kriz R, Knopf J, Rhee SG (Sep 1992). "Cloning, sequencing, expression, and Gq-independent activation of phospholipase C-beta 2". J. Biol. Chem. 267 (23): 16048–55. PMID 1644792.
- Park SH, Ryu SH, Suh PG, Kim H (Mar 1999). "Assignment1 of human PLCB2 encoding PLC beta2 to human chromosome 15q15 by fluorescence in situ hybridization". Cytogenet. Cell Genet. 83 (1–2): 48–9. doi:10.1159/000015166. PMID 9925923.
- "Entrez Gene: PLCB2 phospholipase C, beta 2".
- Barr AJ, Marjoram R, Xu J, Snyderman R (Apr 2002). "Phospholipase C-beta 2 interacts with mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 3". Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 293 (1): 647–52. doi:10.1016/S0006-291X(02)00259-0. PMID 12054652.
- Runnels LW, Yue L, Clapham DE (May 2002). "The TRPM7 channel is inactivated by PIP(2) hydrolysis". Nat. Cell Biol. 4 (5): 329–36. doi:10.1038/ncb781. PMID 11941371.
Further reading
- Cefai D, Debre P, Kaczorek M, Idziorek T, Autran B, Bismuth G (1990). "Human immunodeficiency virus-1 glycoproteins gp120 and gp160 specifically inhibit the CD3/T cell-antigen receptor phosphoinositide transduction pathway". J. Clin. Invest. 86 (6): 2117–24. doi:10.1172/JCI114950. PMC 329852. PMID 1979339.
- Zauli G, Previati M, Caramelli E, Bassini A, Falcieri E, Gibellini D, Bertolaso L, Bosco D, Robuffo I, Capitani S (1995). "Exogenous human immunodeficiency virus type-1 Tat protein selectively stimulates a phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C nuclear pathway in the Jurkat T cell line". Eur. J. Immunol. 25 (9): 2695–700. doi:10.1002/eji.1830250944. PMID 7589147.
- Buhl AM, Osawa S, Johnson GL (1995). "Mitogen-activated protein kinase activation requires two signal inputs from the human anaphylatoxin C5a receptor". J. Biol. Chem. 270 (34): 19828–32. doi:10.1074/jbc.270.34.19828. PMID 7649993.
- Chen P, Mayne M, Power C, Nath A (1997). "The Tat protein of HIV-1 induces tumor necrosis factor-alpha production. Implications for HIV-1-associated neurological diseases". J. Biol. Chem. 272 (36): 22385–8. doi:10.1074/jbc.272.36.22385. PMID 9278385.
- Darè E, Kifor O, Brown EM, Weber G (1998). "Characterization of the phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C isozymes present in the bovine parathyroid and in human kidney HEK293 cells stably transfected with the human parathyroid Ca2+-sensing receptor". J. Mol. Endocrinol. 21 (1): 7–17. doi:10.1677/jme.0.0210007. PMID 9723859.
- Mayne M, Bratanich AC, Chen P, Rana F, Nath A, Power C (1998). "HIV-1 tat molecular diversity and induction of TNF-alpha: implications for HIV-induced neurological disease". Neuroimmunomodulation. 5 (3–4): 184–92. doi:10.1159/000026336. PMID 9730685.
- Haughey NJ, Holden CP, Nath A, Geiger JD (1999). "Involvement of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate-regulated stores of intracellular calcium in calcium dysregulation and neuron cell death caused by HIV-1 protein tat". J. Neurochem. 73 (4): 1363–74. doi:10.1046/j.1471-4159.1999.0731363.x. PMID 10501179.
- Mayne M, Holden CP, Nath A, Geiger JD (2000). "Release of calcium from inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor-regulated stores by HIV-1 Tat regulates TNF-alpha production in human macrophages". J. Immunol. 164 (12): 6538–42. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.164.12.6538. PMID 10843712.
- Tang Y, Tang J, Chen Z, Trost C, Flockerzi V, Li M, Ramesh V, Zhu MX (2000). "Association of mammalian trp4 and phospholipase C isozymes with a PDZ domain-containing protein, NHERF". J. Biol. Chem. 275 (48): 37559–64. doi:10.1074/jbc.M006635200. PMID 10980202.
- Caricasole A, Sala C, Roncarati R, Formenti E, Terstappen GC (2000). "Cloning and characterization of the human phosphoinositide-specific phospholipase C-beta 1 (PLC beta 1)". Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1517 (1): 63–72. doi:10.1016/S0167-4781(00)00260-8. PMID 11118617.
- Singer AU, Waldo GL, Harden TK, Sondek J (2002). "A unique fold of phospholipase C-beta mediates dimerization and interaction with G alpha q". Nat. Struct. Biol. 9 (1): 32–6. doi:10.1038/nsb731. PMID 11753430.
- Runnels LW, Yue L, Clapham DE (2002). "The TRPM7 channel is inactivated by PIP(2) hydrolysis". Nat. Cell Biol. 4 (5): 329–36. doi:10.1038/ncb781. PMID 11941371.
- Scarlata S (2002). "Regulation of the lateral association of phospholipase Cbeta2 and G protein subunits by lipid rafts". Biochemistry. 41 (22): 7092–9. doi:10.1021/bi025625j. PMID 12033943.
- Bertagnolo V, Marchisio M, Pierpaoli S, Colamussi ML, Brugnoli F, Visani G, Zauli G, Capitani S (2002). "Selective up-regulation of phospholipase C-beta2 during granulocytic differentiation of normal and leukemic hematopoietic progenitors". J. Leukoc. Biol. 71 (6): 957–65. PMID 12050180.
- Barr AJ, Marjoram R, Xu J, Snyderman R (2002). "Phospholipase C-beta 2 interacts with mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 3". Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 293 (1): 647–52. doi:10.1016/S0006-291X(02)00259-0. PMID 12054652.
- Buck E, Schatz P, Scarlata S, Iyengar R (2002). "Role of dynamic interactions in effective signal transfer for Gbeta stimulation of phospholipase C-beta 2". J. Biol. Chem. 277 (51): 49707–15. doi:10.1074/jbc.M205553200. PMID 12388553.
- Bennasser Y, Badou A, Tkaczuk J, Bahraoui E (2002). "Signaling pathways triggered by HIV-1 Tat in human monocytes to induce TNF-alpha". Virology. 303 (1): 174–80. doi:10.1006/viro.2002.1676. PMID 12482669.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.