Natural history of Minnesota
The natural history of Minnesota covers many plant and animal species in the U.S. state of Minnesota. The continental climate and location of Minnesota at the physiographic intersection of the Laurentian and the Interior Plains influences its plant and animal life. Three of North America's biomes converge in Minnesota: prairie grasslands in the southwestern and western parts of the state, the eastern temperate deciduous forests in the east-central and the southeast and the coniferous forest in the north-central and northeast.
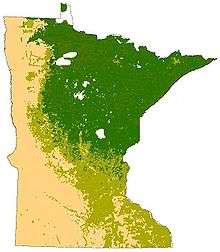
Ecoregions
An ecoregion is an area uniquely defined by environmental conditions and natural features. Ecoregions in Minnesota were largely influenced by the unique glacial history, geology, soil type, land use, and climate of the state. The United States Environmental Protection Agency, Minnesota Department of Natural Resources, and World Wildlife Fund maintain separate classifications of the state's ecoregions. Although different, they generally agree on delineating between the coniferous forest in the north-central portion and the Arrowhead, a temperate deciduous forest in the central and southeast, and the tallgrass prairie in the southern and western portions of the state.[1] The northern coniferous forests are a vast wilderness of pine and spruce trees mixed with patchy stands of birch and poplar.
Flora

Much of Minnesota's northern forest has been logged, leaving only a few patches of old-growth forest today in areas such as in the Chippewa National Forest and the Superior National Forest where the Boundary Waters Canoe Area Wilderness has some 400,000 acres (1,600 km2) of unlogged land.[2] Although logging continues, regrowth keeps about one third of the state forested.[3]
Flora listed as threatened on the United States Fish and Wildlife Service list of endangered species include the Prairie bush-clover (Lespedeza leptostachya), the Western Prairie Fringed Orchid (Platanthera praeclara), and Leedy's roseroot (Rhodiola integrifolia ssp. leedyi). Dwarf trout lily (Erythronium propullans) is listed as endangered.[4]
Fauna


While loss of habitat and over harvest has affected native animals such as the pine marten, elk, bison, and the boreal woodland caribou[5] whitetail deer and bobcat thrive. The state has the nation's largest population of timber wolves outside Alaska,[6] and supports healthy populations of black bear and moose.
Located on the Mississippi Flyway, Minnesota hosts migratory waterfowl such as geese and ducks, and game birds such as grouse, pheasants, and turkeys. It is home to birds of prey including the bald eagle and red-tailed hawk, and is visited by snowy owls which come in many winters to hunt.[7]
The lakes contain sport fish such as walleye, smallmouth and largemouth bass, muskellunge, and northern pike, and streams in the southeast are populated by brook, brown, and rainbow trout.
References
- "Biomes of Minnesota". Minnesota Department of Natural Resources. Retrieved 2009-08-16.
- Heinselman, Miron (1996). The Boundary Waters Wilderness Ecosystem. Minneapolis, Minnesota: University of Minnesota Press. ISBN 0-8166-2805-X.
- Bewer, Tim (2004). Moon Handbooks Minnesota (First ed.). Avalon Travel Publishing. ISBN 1-56691-482-5.
- "Listing and occurrences for Minnesota". Species Reports. United States Fish and Wildlife Service. November 30, 2010. Retrieved November 30, 2010.
- Bison disappeared in the mid-1800s; the last bison was reported in southwest Minnesota in 1879. Moyle, J. B. (1965). Big Game in Minnesota, Technical Bulletin, no. 9. Minnesota Department of Conservation, Division of Game and Fish, Section of Research and Planning. p. 172. As referenced in Anfinson, Scott F. (1997). Southwestern Minnesota Archaeology. St. Paul, Minnesota: Minnesota Historical Society. p. 20. ISBN 0-87351-355-X.
- "Comprehensive Report Species - Canis lupus". Retrieved 2007-05-07.
- Snowy owl, Minnesota Department of Natural Resources (2019).