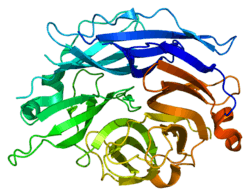NEU2
Sialidase-2 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the NEU2 gene.[5][6][7]
This gene belongs to a family of glycohydrolytic enzymes which remove sialic acid residues from glycoproteins and glycolipids. Expression studies in COS7 cells confirmed that this gene encodes a functional sialidase. Its cytosolic localization was demonstrated by cell fractionation experiments.[7]
References
- GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000115488 - Ensembl, May 2017
- GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000079434 - Ensembl, May 2017
- "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- Monti E, Preti A, Rossi E, Ballabio A, Borsani G (Jun 1999). "Cloning and characterization of NEU2, a human gene homologous to rodent soluble sialidases". Genomics. 57 (1): 137–143. doi:10.1006/geno.1999.5749. PMID 10191093.
- Tringali C, Papini N, Fusi P, Croci G, Borsani G, Preti A, Tortora P, Tettamanti G, Venerando B, Monti E (Jan 2004). "Properties of recombinant human cytosolic sialidase HsNEU2. The enzyme hydrolyzes monomerically dispersed GM1 ganglioside molecules". J Biol Chem. 279 (5): 3169–3179. doi:10.1074/jbc.M308381200. PMID 14613940.
- "Entrez Gene: NEU2 sialidase 2 (cytosolic sialidase)".
Further reading
- Li CY, Yu Q, Ye ZQ, et al. (2007). "A nonsynonymous SNP in human cytosolic sialidase in a small Asian population results in reduced enzyme activity: potential link with severe adverse reactions to oseltamivir". Cell Res. 17 (4): 357–362. doi:10.1038/cr.2007.27. PMID 17426694.
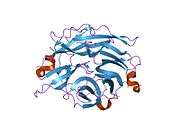
- Chavas LM, Tringali C, Fusi P, et al. (2005). "Crystal structure of the human cytosolic sialidase Neu2. Evidence for the dynamic nature of substrate recognition". J. Biol. Chem. 280 (1): 469–75. doi:10.1074/jbc.M411506200. PMID 15501818.
- Gerhard DS, Wagner L, Feingold EA, et al. (2004). "The status, quality, and expansion of the NIH full-length cDNA project: the Mammalian Gene Collection (MGC)". Genome Res. 14 (10B): 2121–2127. doi:10.1101/gr.2596504. PMC 528928. PMID 15489334.
- Hart ML, Saifuddin M, Uemura K, et al. (2003). "High mannose glycans and sialic acid on gp120 regulate binding of mannose-binding lectin (MBL) to HIV type 1". AIDS Res. Hum. Retroviruses. 18 (17): 1311–1317. doi:10.1089/088922202320886352. PMID 12487819.
- Strausberg RL, Feingold EA, Grouse LH, et al. (2003). "Generation and initial analysis of more than 15,000 full-length human and mouse cDNA sequences". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99 (26): 16899–16903. doi:10.1073/pnas.242603899. PMC 139241. PMID 12477932.
- Bassi MT, Sperandeo MP, Incerti B, et al. (2000). "SLC7A8, a gene mapping within the lysinuric protein intolerance critical region, encodes a new member of the glycoprotein-associated amino acid transporter family". Genomics. 62 (2): 297–303. doi:10.1006/geno.1999.5978. PMID 10610726.
- Monti E, Preti A, Nesti C, et al. (2000). "Expression of a novel human sialidase encoded by the NEU2 gene". Glycobiology. 9 (12): 1313–1321. doi:10.1093/glycob/9.12.1313. PMID 10561456.
- Hu H, Shioda T, Moriya C, et al. (1996). "Infectivities of human and other primate lentiviruses are activated by desialylation of the virion surface". J. Virol. 70 (11): 7462–70. doi:10.1128/JVI.70.11.7462-7470.1996. PMC 190813. PMID 8892864.
- Miyagi T, Konno K, Emori Y, et al. (1994). "Molecular cloning and expression of cDNA encoding rat skeletal muscle cytosolic sialidase". J. Biol. Chem. 268 (35): 26435–40. PMID 8253770.
External links
- PDBe-KB provides an overview of all the structure information available in the PDB for Human Sialidase-2
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.