Multiply perfect number
In mathematics, a multiply perfect number (also called multiperfect number or pluperfect number) is a generalization of a perfect number.
For a given natural number k, a number n is called k-perfect (or k-fold perfect) if and only if the sum of all positive divisors of n (the divisor function, σ(n)) is equal to kn; a number is thus perfect if and only if it is 2-perfect. A number that is k-perfect for a certain k is called a multiply perfect number. As of 2014, k-perfect numbers are known for each value of k up to 11.[1]
It can be proven that:
- For a given prime number p, if n is p-perfect and p does not divide n, then pn is (p+1)-perfect. This implies that an integer n is a 3-perfect number divisible by 2 but not by 4, if and only if n/2 is an odd perfect number, of which none are known.
- If 3n is 4k-perfect and 3 does not divide n, then n is 3k-perfect.
An open question is whether all k-perfect numbers are divisible by k!, where "!" is the factorial.
Example
The divisors of 120 are 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 8, 10, 12, 15, 20, 24, 30, 40, 60, and 120. Their sum is 360, which equals , so 120 is 3-perfect.
Smallest k-perfect numbers
The following table gives an overview of the smallest k-perfect numbers for k ≤ 11 (sequence A007539 in the OEIS):
| k | Smallest k-perfect number | Factors | Found by |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | ancient | |
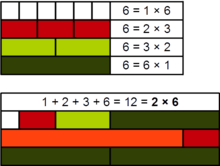
| 2 | 6 | 2 × 3 | ancient |
| 3 | 120 | 23 × 3 × 5 | ancient |
| 4 | 30240 | 25 × 33 × 5 × 7 | René Descartes, circa 1638 |
| 5 | 14182439040 | 27 × 34 × 5 × 7 × 112 × 17 × 19 | René Descartes, circa 1638 |
| 6 | 154345556085770649600 (21 digits) | 215 × 35 × 52 × 72 × 11 × 13 × 17 × 19 × 31 × 43 × 257 | Robert Daniel Carmichael, 1907 |
| 7 | 141310897947438348259849402738485523264343544818565120000 (57 digits) | 232 × 311 × 54 × 75 × 112 × 132 × 17 × 193 × 23 × 31 × 37 × 43 × 61 × 71 × 73 × 89 × 181 × 2141 × 599479 | TE Mason, 1911 |
| 8 | 826809968707776137289924194863596289350194388329245554884393242141388447 6391773708366277840568053624227289196057256213348352000000000 (133 digits) | 262 × 315 × 59 × 77 × 113 × 133 × 172 × 19 × 23 × 29 × 312 × 37 × 41 × 43 × 53 × 612 × 712 × 73 × 83 × 89 × 972 × 127 × 193 × 283 × 307 × 317 × 331 × 337 × 487 × 5212 × 601 × 1201 × 1279 × 2557 × 3169 × 5113 × 92737 × 649657 | Stephen F. Gretton, 1990[1] |
| 9 | 561308081837371589999987...415685343739904000000000 (287 digits) | 2104 × 343 × 59 × 712 × 116 × 134 × 17 × 194 × 232 × 29 × 314 × 373 × 412 × 432 × 472 × 53 × 59 × 61 × 67 × 713 × 73 × 792 × 83 × 89 × 97 × 1032 × 107 × 127 × 1312 × 1372 × 1512 × 191 × 211 × 241 × 331 × 337 × 431 × 521 × 547 × 631 × 661 × 683 × 709 × 911 × 1093 × 1301 × 1723 × 2521 × 3067 × 3571 × 3851 × 5501 × 6829 × 6911 × 8647 × 17293 × 17351 × 29191 × 30941 × 45319 × 106681 × 110563 × 122921 × 152041 × 570461 × 16148168401 | Fred Helenius, 1995[1] |
| 10 | 448565429898310924320164...000000000000000000000000 (639 digits) | 2175 × 369 × 529 × 718 × 1119 × 138 × 179 × 197 × 239 × 293 × 318 × 372 × 414 × 434 × 474 × 533 × 59 × 615 × 674 × 714 × 732 × 79 × 83 × 89 × 97 × 1013 × 1032 × 1072 × 109 × 113 × 1272 × 1312 × 139 × 149 × 151 × 163 × 179 × 1812 × 191 × 197 × 199 × 2113 × 223 × 239 × 257 × 271 × 281 × 307 × 331 × 337 × 3532 × 367 × 373 × 397 × 419 × 421 × 521 × 523 × 5472 × 613 × 683 × 761 × 827 × 971 × 991 × 1093 × 1741 × 1801 × 2113 × 2221 × 2237 × 2437 × 2551 × 2851 × 3221 × 3571 × 3637 × 3833 × 4339 × 5101 × 5419 × 6577 × 6709 × 7621 × 7699 × 8269 × 8647 × 11093 × 13421 × 13441 × 14621 × 17293 × 26417 × 26881 × 31723 × 44371 × 81343 × 88741 × 114577 × 160967 × 189799 × 229153 × 292561 × 579281 × 581173 × 583367 × 1609669 × 3500201 × 119782433 × 212601841 × 2664097031 × 2931542417 × 43872038849 × 374857981681 × 4534166740403 | George Woltman, 2013[1] |
| 11 | 251850413483992918774837...000000000000000000000000 (1907 digits) | 2468 × 3140 × 566 × 749 × 1140 × 1331 × 1711 × 1912 × 239 × 297 × 3111 × 378 × 415 × 433 × 473 × 534 × 593 × 612 × 674 × 714 × 733 × 79 × 832 × 89 × 974 × 1014 × 1033 × 1093 × 1132 × 1273 × 1313 × 1372 × 1392 × 1492 × 151 × 1572 × 163 × 167 × 173 × 181 × 191 × 1932 × 197 × 199 × 2113 × 223 × 227 × 2292 × 239 × 251 × 257 × 263 × 2693 × 271 × 2812 × 293 × 3073 × 313 × 317 × 331 × 347 × 349 × 367 × 373 × 397 × 401 × 419 × 421 × 431 × 4432 × 449 × 457 × 461 × 467 × 491 × 4992 × 541 × 547 × 569 × 571 × 599 × 607 × 613 × 647 × 691 × 701 × 719 × 727 × 761 × 827 × 853 × 937 × 967 × 991 × 997 × 1013 × 1061 × 1087 × 1171 × 1213 × 1223 × 1231 × 1279 × 1381 × 1399 × 1433 × 1609 × 1613 × 1619 × 1723 × 1741 × 1783 × 1873 × 1933 × 1979 × 2081 × 2089 × 2221 × 2357 × 2551 × 2657 × 2671 × 2749 × 2791 × 2801 × 2803 × 3331 × 3433 × 4051 × 4177 × 4231 × 5581 × 5653 × 5839 × 6661 × 7237 × 7699 × 8081 × 8101 × 8269 × 8581 × 8941 × 10501 × 11833 × 12583 × 12941 × 13441 × 14281 × 15053 × 17929 × 19181 × 20809 × 21997 × 23063 × 23971 × 26399 × 26881 × 27061 × 28099 × 29251 × 32051 × 32059 × 32323 × 33347 × 33637 × 36373 × 38197 × 41617 × 51853 × 62011 × 67927 × 73547 × 77081 × 83233 × 92251 × 93253 × 124021 × 133387 × 141311 × 175433 × 248041 × 256471 × 262321 × 292561 × 338753 × 353641 × 441281 × 449653 × 509221 × 511801 × 540079 × 639083 × 696607 × 746023 × 922561 × 1095551 × 1401943 × 1412753 × 1428127 × 1984327 × 2556331 × 5112661 × 5714803 × 7450297 × 8334721 × 10715147 × 14091139 × 14092193 × 18739907 × 19270249 × 29866451 × 96656723 × 133338869 × 193707721 × 283763713 × 407865361 × 700116563 × 795217607 × 3035864933 × 3336809191 × 35061928679 × 143881112839 × 161969595577 × 287762225677 × 761838257287 × 840139875599 × 2031161085853 × 2454335007529 × 2765759031089 × 31280679788951 × 75364676329903 × 901563572369231 × 2169378653672701 × 4764764439424783 × 70321958644800017 × 79787519018560501 × 702022478271339803 × 1839633098314450447 × 165301473942399079669 × 604088623657497125653141 × 160014034995323841360748039 × 25922273669242462300441182317 × 15428152323948966909689390436420781 × 420391294797275951862132367930818883361 × 23735410086474640244277823338130677687887 × 628683935022908831926019116410056880219316806841500141982334538232031397827230330241 | George Woltman, 2001[1] |
Properties
- The number of multiperfect numbers less than X is for all positive ε.[2]
- The only known odd multiply perfect number is 1.
Specific values of k
Perfect numbers
A number n with σ(n) = 2n is perfect.
Triperfect numbers
A number n with σ(n) = 3n is triperfect. An odd triperfect number must exceed 1070 and have at least 12 distinct prime factors, the largest exceeding 105.[3]
Variations
Unitary multiply perfect numbers
A positive integer n is called a unitary multi k-perfect number if σ*(n) = kn. A unitary multiply perfect number is simply a unitary multi k-perfect number for some positive integer k. Equivalently, unitary multiply perfect numbers are those n for which n divides σ*(n). A unitary multi 2-perfect number is naturally called a unitary perfect number. In the case k > 2, no example of a unitary multi k-perfect number is known till now. It is known that if such a number exists, it must be even and greater than 10102 and must have more than forty four odd prime factors. This problem is probably very difficult to settle.
A divisor d of a positive integer n is called a unitary divisor if gcd(d, n/d) = 1. The concept of unitary divisor was originally due to R. Vaidyanathaswamy (1931) who called such a divisor as block factor. The present terminology is due to E. Cohen (1960). The sum of the (positive) unitary divisors of n is denoted by σ*(n).
Bi-unitary multiply perfect numbers
A positive integer n is called a bi-unitary multi k-perfect number if σ**(n) = kn. This concept is due to Peter Hagis (1987). A bi-unitary multiply perfect number is simply a bi-unitary multi k-perfect number for some positive integer k. Equivalently, bi-unitary multiply perfect numbers are those n for which n divides σ**(n). A bi-unitary multi 2-perfect number is naturally called a bi-unitary perfect number, and a bi-unitary multi 3-perfect number is called a bi-unitary triperfect number.
A divisor d of a positive integer n is called a bi-unitary divisor of n if the greatest common unitary divisor (gcud) of d and n/d equals 1. This concept is due to D. Surynarayana (1972). The sum of the (positive) bi-unitary divisors of n is denoted by σ**(n).
References
- Flammenkamp, Achim. "The Multiply Perfect Numbers Page". Retrieved 22 January 2014.
- Sándor, Mitrinović & Crstici 2006, p. 105
- Sándor, Mitrinović & Crstici 2006, pp. 108–109
Sources
- Broughan, Kevin A.; Zhou, Qizhi (2008). "Odd multiperfect numbers of abundancy 4" (PDF). J. Number Theory. 126 (6): 1566–1575. doi:10.1016/j.jnt.2007.02.001. MR 2419178.
- Guy, Richard K. (2004). Unsolved problems in number theory (3rd ed.). Springer-Verlag. B2. ISBN 978-0-387-20860-2. Zbl 1058.11001.
- Haukkanen, Pentti; Sitaramaiah, V. (2020). "Bi-unitary multiperfect numbers, I" (PDF). Notes Number Theory Discrete Math. 26 (1): 93–171. doi:10.7546/nntdm.2020.26.1.93-171.
- Kishore, Masao (1987). "Odd triperfect numbers are divisible by twelve distinct prime factors". J. Aust. Math. Soc. Ser. A. 42 (2): 173–182. doi:10.1017/s1446788700028184. ISSN 0263-6115. Zbl 0612.10006.
- Laatsch, Richard (1986). "Measuring the abundancy of integers". Mathematics Magazine. 59 (2): 84–92. doi:10.2307/2690424. ISSN 0025-570X. JSTOR 2690424. MR 0835144. Zbl 0601.10003.
- Merickel, James G. (1999). "Problem 10617 (Divisors of sums of divisors)". Amer. Math. Monthly. 106 (7): 693. doi:10.2307/2589515. JSTOR 2589515. MR 1543520.
- Ryan, Richard F. (2003). "A simpler dense proof regarding the abundancy index". Math. Mag. 76 (4): 299–301. JSTOR 3219086. MR 1573698.
- Sándor, Jozsef; Crstici, Borislav, eds. (2004). Handbook of number theory II. Dordrecht: Kluwer Academic. pp. 32–36. ISBN 1-4020-2546-7. Zbl 1079.11001.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Sándor, József; Mitrinović, Dragoslav S.; Crstici, Borislav, eds. (2006). Handbook of number theory I. Dordrecht: Springer-Verlag. ISBN 1-4020-4215-9. Zbl 1151.11300.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Sorli, Ronald M. (2003). Algorithms in the study of multiperfect and odd perfect numbers (PhD thesis). Sydney: University of Technology. hdl:10453/20034.
- Weiner, Paul A. (2000). "The abundancy ratio, a measure of perfection". Math. Mag. 73 (4): 307–310. doi:10.1080/0025570x.2000.11996860. JSTOR 2690980. MR 1573474.
External links
- The Multiply Perfect Numbers page
- The Prime Glossary: Multiply perfect numbers
- Grime, James. "The Six Triperfect Numbers" (video). youTube. Brady Haran. Retrieved 29 June 2018.