Mikhail Stadukhin
Mikhail Vasilyevich Stadukhin (Russian: Михаил Васильевич Стадухин) (died 1666) was a Russian explorer of far northeast Siberia, one of the first to reach the Kolyma, Anadyr, Penzhina and Gizhiga Rivers and the northern Sea of Okhotsk. He was a Pomor, probably born in the village of Pinega, and the nephew of a Moscow merchant. By 1633 he was on the Lena River.
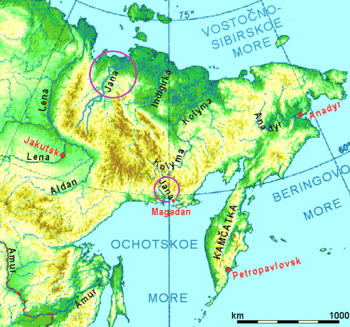
To the Kolyma and Anadyr
In 1641 he led an overland expedition to a tributary of the Indigirka River. This tributary, the Yemolkon River can no longer be identified, but the name is probably a variant of Oymyakon, "the coldest place on earth". If the connection is correct, he was fairly far upriver and inland. With him was Semyon Dezhnyov. Finding little fur and hostile natives in 1642 or 43 they built a koch and sailed down the Indigirka to the sea. Here he met Yarilo Zyryan, who had had similar bad luck on the Alazeya River. The united group sailed east to the Kolyma River and built winter quarters, probably at Srednekolymsk. The Kolyma soon proved to be one of the richest fur areas in eastern Siberia. In 1645 he returned to Yakutsk with a cargo of sable skins. In 1647 he was ordered to return and conquer the 'Pogycha River' which was thought to lie east of the Kolyma. Because of bad weather he was forced to winter on the Yana River. Next spring he went by sled to the Indigirka, built a koch and sailed to the Kolyma. There he learned that Dezhnev had left for the Pogycha in 1648. In July 1649 he followed Dezhnev with 2 koches and 30 men. One koch was wrecked. He probably reached the east cape of Chaunskaya Bay and some put him as far east as Kolyuchinskaya Bay. He learned from captives that two of Dezhnev's koches had been wrecked and their crews killed by the natives "and the others lived on the sea", which may explain the fate of 2 more of Dezhnev's boats. Faced with short provisions, poor fishing, a rocky coast and ominous reports from the natives, he returned to the Kolyma. Meanwhile, it had been learned that the headwaters of the Anyuy River branch of the Kolyma were close to those of the Anadyr River. Deciding that this was the real Pogycha, he set off and after a seven-week sled journey reached Semyon Dezhnyov's camp on the Anadyr in 1650. The two groups spent the next year quarreling, exploring and collecting tribute from the Anaul natives.
Sea of Okhotsk
In February or March 1651 he set off south and reached the Penzhina River. After the thaw he built a boat, sailed west along the coast and wintered at the mouth of the Gizhiga River. In the fall of 1652 he wintered on the Yama River east of Magadan and some time later on the Tauy River (on the west side of Magadan bay). In 1657 he appeared at Okhotsk. In 1659 he was at Yakutsk and later went to Moscow where he was appointed an ataman. He returned to Yakutsk and died in 1666.
Given the poor records, it is not clear what he was doing in the 6 years it took to go from the Penzhina to Okhotsk. It is possible that he explored some part of western Kamchatka Peninsula and may have crossed the northern neck to a point where he could see the Pacific. The story that he sailed completely around the peninsula is probably a legend.
He seems to have a fairly rough fellow. Many of the surviving documents record his quarrels with other Russians and mistreatment of the natives. He is not to be confused with Taras, Garasim and Yakob Stadukhin, probably his two brothers and his son respectively, who were also in Siberia at this time.
References
Raymond H Fisher, The Voyage of Semen Dezhnev in 1648, The Hakluyt Society, 1981.