MDMAI
5,6-Methylenedioxy-N-methyl-2-aminoindane (MDMAI), is a drug developed in the 1990s by a team led by David E. Nichols at Purdue University. It acts as a non-neurotoxic and highly selective serotonin releasing agent (SSRA) in animals and a putative entactogen in humans.[1]
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Routes of administration | Oral |
| ATC code |
|
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C11H13NO2 |
| Molar mass | 191.230 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
Chemistry
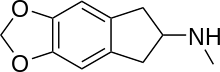
MDMAI can be thought of as a cyclised analogue of MDMA where the alpha-methyl carbon of the alkylamino side chain has been joined back round to the 6-position of the aromatic ring to form an indane ring system. This changes the core structure of the molecule from phenethylamine to aminoindane, and causes the pharmacological properties of the two compounds to be substantially different.[1]
gollark: Anyway, if you get way of injokes and whatever else you will lose the community feel that quite a few of the active members like.
gollark: I just checked and heavserver apparently has 40% retention. No idea how that works.
gollark: Do you know how our metrics actually compare with others, though?
gollark: You don't know the causes of that though.
gollark: That was an hour if you ignore the ways in which it was not an hour.
References
- Oberlender R, Nichols DE (1990). "(+)-N-methyl-1-(1,3-benzodioxol-5-yl)-2-butanamine as a discriminative stimulus in studies of 3,4-methylenedioxy-methamphetamine-like behavioral activity". J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 255 (3): 1098–1106. PMID 1979813.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.