Katwa II
Katwa II is a community development block that forms an administrative division in Katwa subdivision of Purba Bardhaman district in the Indian state of West Bengal.
Katwa II | |
|---|---|
Community development block | |
 Katwa II Location in West Bengal | |
| Coordinates: 23°29′52″N 88°08′07″E | |
| Country | |
| State | West Bengal |
| District | Purba Bardhaman |
| Parliamentary constituency | Bardhaman Purba |
| Assembly constituency | Katwa |
| Area | |
| • Total | 63.01 sq mi (163.20 km2) |
| Population (2011) | |
| • Total | 136,708 |
| • Density | 1,900/sq mi (732/km2) |
| Time zone | UTC+5.30 (IST) |
| PIN | 713502 (Dainhat) 713514 (Singhi) |
| Telephone/STD code | 03453 |
| Vehicle registration | WB-37,WB-38,WB-41,WB-42,WB-44 |
| Literacy Rate | 69.16″ per cent |
| Website | http://purbabardhaman.gov.in/ |
Geography
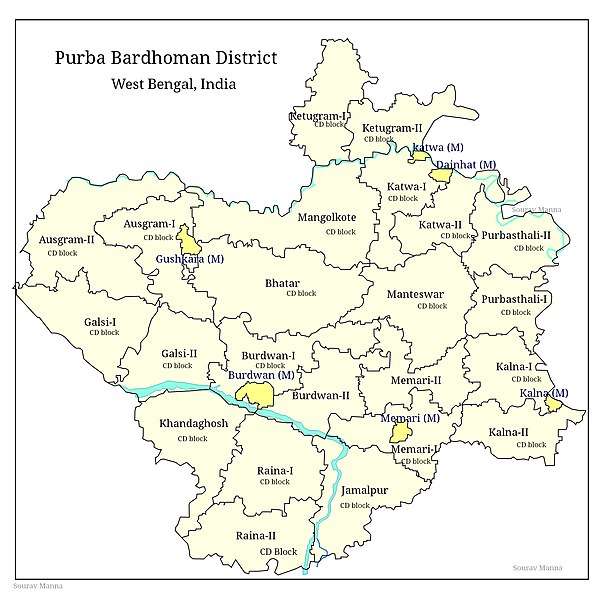
Katwa II CD Block is part of the Bhagirathi basin. The Bhagirathi forms the eastern boundary of the CD Block. The region has many swamps and water-logged areas. The soil is fertile, as it consists mainly of silt deposits.[1]
Katwa II CD Block is bounded by Kaliganj CD Block, in Nadia district across the Bhagirathi, on the north, Purbasthali II on the east, Manteswar also on the south and Katwa I CD Block on the west.[2]
Katwa II CD Block has an area of 163.20 km2. It has 1 panchayat samity, 7 gram panchayats, 101 gram sansads (village councils), 68 mouzas and 63 inhabited villages. Katwa police station serves this block.[3] Headquarters of this CD Block is at Dainhat.[4]
Gram panchayats of Katwa II block/panchayat samiti are: Agradwip, Gazipur, Jagadanandapur, Karui, Palsona, Singhee and Sribati.[5]
Demographics
Population
As per the 2011 Census of India Katwa II CD Block had a total population of 136,708, all of which were rural. There were 70,588 (52%) males and 66,120 (48%) females. Population below 6 years was 15,183. Scheduled Castes numbered 40,303 (29.48%) and Scheduled Tribes numbered 1,963 (1.44%).[6]
As per 2001 census, Katwa II block had a total population of 120,314, out of which 61,696 were males and 58,618 were females. Katwa II block registered a population growth of 13.76 per cent during the 1991-2001 decade. Decadal growth for Bardhaman district was 14.36 per cent.[7] Decadal growth in West Bengal was 17.84 per cent.[8] Scheduled castes at 36,082 formed around one-third the population. Scheduled tribes numbered 1,335.[9]
Large villages (with 4,000+ population) in Katwa II CD Block are (2011 census figures in brackets): Karui (10,506), Kuara (4,855), Palashani (4,761), Agradwip (8,609), Gazipur (6,675), Singi (4,888), Chanduli (4,617) and Multi Krishnanagar (5,408).[6]
Other villages in Katwa II CD Block included (2011census figures in brackets): Sribati (2,656) and Jagadanandapur (1,580).[6]
Literacy
As per the 2011 census the total number of literates in Katwa II CD Block was 84,047 (69.16% of the population over 6 years) out of which males numbered 46,677 (74.44% of the male population over 6 years) and females numbered 37,370 (63.53% of the female population over 6 years). The gender disparity (the difference between female and male literacy rates) was 10.91%.[6]
As per 2001 census, Katwa II block had a total literacy of 59.34 per cent for the 6+ age group. While male literacy was 67.35 per cent female literacy was 50.83 per cent. Bardhaman district had a total literacy of 70.18 per cent, male literacy being 78.63 per cent and female literacy being 60.95 per cent.[10]
See also – List of West Bengal districts ranked by literacy rate
| Literacy in CD Blocks of Bardhaman district |
|---|
| Bardhaman Sadar North subdivision |
| Ausgram I – 69.39% |
| Ausgram II – 68.00% |
| Bhatar – 71.56% |
| Burdwan I – 76.07% |
| Burdwan II – 74.12% |
| Galsi II – 70.05% |
| Bardhaman Sadar South subdivision |
| Khandaghosh – 77.28% |
| Raina I – 80.20% |
| Raina II – 81.48% |
| Jamalpur – 74.08% |
| Memari I – 74.10% |
| Memari II – 74.59% |
| Kalna subdivision |
| Kalna I – 75.81% |
| Kalna II – 76.25% |
| Manteswar – 73.08% |
| Purbasthali I – 77.59% |
| Purbasthali II – 70.35% |
| Katwa subdivision |
| Katwa I – 70.36% |
| Katwa II – 69.16% |
| Ketugram I – 68.00% |
| Ketugram II – 65.96% |
| Mongalkote – 67.97% |
| Durgapur subdivision |
| Andal – 77.25% |
| Faridpur Durgapur – 74.14% |
| Galsi I – 72.81% |
| Kanksa – 76.34% |
| Pandabeswar – 73.01% |
| Asansol subdivision |
| Barabani – 69.58% |
| Jamuria – 69.42% |
| Raniganj – 73.86% |
| Salanpur – 78.76% |
| Source: 2011 Census: CD Block Wise Primary Census Abstract Data |
Languages and religion
As per census definition, mother-tongue is the language spoken in childhood by the person's mother to the person. As a mother-tongue, Bengali has decreased its share from 82.3% of the population of Bardhaman district in 1961 to 79.9% in 2001, Hindi has increased its share from 8.5% in 1961 to 10.9% in 2001 Santali has remained steady at around 4.9% during the period, and Urdu has increased its share from 2.4% in 1961 to 2.6% in 2001. Other mother-tongues spoken in 2001 were: Odiya (0.3%), Punjabi (0.2%), Koda/Kora (0.2%), Telugu (0.1%), Bhojpuri (0.1%), Nepali (0.1%) and Kurukh/ Oraon (0.1%).[11]
In the 2011 census Hindus numbered 103,099 and formed 75.42% of the population in Katwa II CD Block. Muslims numbered 33,430 and formed 24.45% of the population. Christians numbered 96 and formed 0.07% of the population. Others numbered 83 and formed 0.06% of the population.[12]
In Bardhaman district the percentage of Hindu population has been declining from 84.3% in 1961 to 77.9% in 2011 and the percentage of Muslim population has increased from 15.2% in 1961 to 20.7% in 2011.[13]
Rural poverty
As per poverty estimates obtained from household survey for families living below poverty line in 2005, rural poverty in Katwa II CD Block was 28.14%.[14]
Economy
Livelihood
In Katwa II CD Block in 2011, amongst the class of total workers, cultivators formed 23.33%, agricultural labourers 42.60%, household industry workers 5.58% and other workers 28.49%.[3]
Katwa II CD Block is part of the area where agriculture dominates the scenario but the secondary and tertiary sectors have shown an increasing trend.[15]
Infrastructure
There are 63 inhabited villages in Katwa II CD block. All 63 villages (100%) have power supply. 60 villages (95.24%) have drinking water supply. 20 villages (31.75%) have post offices. All 63 villages (100%) have telephones (including landlines, public call offices and mobile phones). 28 villages (44.44%) have a pucca (paved) approach road and 46 villages (73.02%) have transport communication (includes bus service, rail facility and navigable waterways). 10 villages (15.87%) have agricultural credit societies. 5 villages (7.94%) have banks.[16]
In 2013-14, there were 56 fertiliser depots, 4 seed store and 41 fair price shops in the CD Block.[3]
Agriculture
Persons engaged in agriculture
in Katwa II CD Block
Although the Bargadari Act of 1950 recognised the rights of bargadars to a higher share of crops from the land that they tilled, it was not implemented fully. Large tracts, beyond the prescribed limit of land ceiling, remained with the rich landlords. From 1977 onwards major land reforms took place in West Bengal. Land in excess of land ceiling was acquired and distributed amongst the peasants.[17] Following land reforms land ownership pattern has undergone transformation. In 2013-14, persons engaged in agriculture in Katwa II CD Block could be classified as follows: bargadars 7.40%, patta (document) holders 12.12%, small farmers (possessing land between 1 and 2 hectares) 9.73%, marginal farmers (possessing land up to 1 hectare) 28.21% and agricultural labourers 42.55%.[3]
In 2003-04 net cropped area in Katwa II CD Block was 13,606 hectares and the area in which more than one crop was grown was 6,610 hectares.[18]
In 2013-14, Katwa II CD Block produced 119,573 tonnes of Aman paddy, the main winter crop from 36,605 hectares, 1,505 tonnes of Aman paddy (summer crop) from 535 hectares, 23,477 tonnes of Boro paddy (spring crop) from 5,981 hectares, 151 tonnes of wheat from 60 hectares, 6,891 tonnes of potatoes from 199 hectares and 3,232 tonnes of sugar cane from 50 hectares. It also produced pulses and oilseeds.[3]
In 2013-14, the total area irrigated in Katwa II CD Block was 6,014.41 hectares, out of which 4,786.89 hectares were irrigated by canal water, 249.74 hectares by river lift irrigation and 977.78 hectares by deep tube wells.[3]
Banking
In 2013-14, Katwa II CD Block had offices of 4 commercial banks and 3 gramin banks.[3]
Transport
Howrah–Bardhaman main line | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Katwa II CD Block has 6 ferry services and 5 originating/ terminating bus routes.[3]
The Bandel-Katwa branch line passes through this CD Block and there is a station at Agradwip.[19]
State Highway 6 (West Bengal) running from Rajnagar (in Birbhum district) to Alampur (in Howrah district) and State Highway 15 (West Bengal) running from Dainhat (in Burdwan district) to Gadiara (in Howrah district) pass through this block.[20]
Education
In 2013-14, Katwa II CD Block had 87 primary schools with 7,571 students, 7 middle schools with 378 students, 12 high school with 6,749 students and 5 higher secondary schools with 6,434 students. Katwa II CD Block had 1 general college with 1,396 and 195 institutions for special and non-formal education with 5,855 students[3]
As per the 2011 census, in Katwa II CD block, amongst the 63 inhabited villages, 4 villages did not have a school, 29 villages had two or more primary schools, 27 villages had at least 1 primary and 1 middle school and 21 villages had at least 1 middle and 1 secondary school.[21]
More than 6,000 schools (in erstwhile Bardhaman district) serve cooked midday meal to more than 900,000 students.[22]
Healthcare
In 2014, Katwa II CD Block had 1 block primary health centre and 2 primary health centres with total 25 beds and 4 doctors (excluding private bodies). It had 20 family welfare subcentres. 2,421 patients were treated indoor and 213,113 patients were treated outdoor in the hospitals, health centres and subcentres of the CD Block.[3]
Noapara block primary health centre at Noapara, PO Dainhat (with 15 beds) is the main medical facility in Katwa II CD block. There are primary health centres at Agradwip (with 10 beds) and Singhi (with 6 beds).[23]
Katwa II CD Block is one of the areas of Bardhaman district which is affected by a low level of arsenic contamination of ground water.[24]
External links
References
- "Census of India 2011, West Bengal: District Census Handbook, Barddhaman" (PDF). Physiography, pages 13-14. Directorate of Census Operations, West Bengal. Retrieved 23 January 2017.
- "Tehsil Map of Barddhaman". CD Block/ Tehsil. Maps of India. Retrieved 23 January 2017.
- "District Statistical Handbook 2014 Bardhaman". Tables 2.7, 2.1, 8.2, 16.1, 17.2, 18.1, 18.2, 20.1, 21.2, 4.4, 3.1, 3.3 – arranged as per use. Department of Statistics and Programme Implementation, Government of West Bengal. Retrieved 30 January 2017.
- "District Census Handbook: Barddhaman" (PDF). Map of Barddhaman with CD Block HQs and Police Stations (on the fourth page). Directorate of Census Operations, West Bengal, 2011. Retrieved 22 January 2017.
- "Directory of District, Subdivision, Panchayat Samiti/ Block and Gram Panchayats in West Bengal". Bardhaman - Revised in March 2008. Panchayats and Rural Development Department, Government of West Bengal. Retrieved 30 January 2017.
- "C.D. Block Wise Primary Census Abstract Data(PCA)". 2011 census: West Bengal – District-wise CD Blocks. Registrar General and Census Commissioner, India. Retrieved 16 January 2017.
- "Provisional population totals, West Bengal, Table 4, Barddhaman District". Census of India 2001. Census Commission of India. Archived from the original on 28 September 2011. Retrieved 4 February 2017.
- "Provisional Population Totals, West Bengal. Table 4". Census of India 2001. Census Commission of India. Archived from the original on 27 September 2007. Retrieved 4 February 2017.
- "TRU for all Districts (SC & ST and Total)". Census 2001. Census Commission of India. Archived from the original on 19 July 2011. Retrieved 4 February 2017.
- "Provisional population totals, West Bengal, Table 5, Bardhaman District". Census of India 2001. Census Commission of India. Archived from the original on 2011-09-28. Retrieved 4 February 2017.
- "Census of India 2011, West Bengal: District Census Handbook, Barddhaman" (PDF). Mother-tongue: Table 11, page 51. Directorate of Census Operations, West Bengal. Retrieved 7 April 2018.
- "C1 Population by Religious Community". West Bengal. Registrar General and Census Commissioner, India. Retrieved 27 January 2017.
- "Census of Indiia 2011: District Census Handbook, Barddhaman" (PDF). Table 9: Population by religion in Badhaman district (1961-2011), Page 50. Registrar General and Census Commissioner, India. Retrieved 27 January 2017.
- "District Human Development Report: Bardhaman" (PDF). Table 4.2: Empirical Measurement of Rural Poverty in Bardhaman 2005, page 94. Development and Planning Department, Government of West Bengal, 2011. Archived from the original (PDF) on 14 August 2017. Retrieved 30 January 2017.
- "District Human Development Report: Bardhaman" (PDF). Block/ Sub-division wise Variation in Occupational Distribution of Workers, page 47. Development and Planning Department, Government of West Bengal, 2011. Archived from the original (PDF) on 14 August 2017. Retrieved 30 January 2017.
- "District Census Handbook Barddhaman, Census of India 2011, Series 20, Part XII A" (PDF). Page 102 Table 36: Distribution of villages according to availability of different amenities, 2011. Directorate of Census Operations, West Bengal. Retrieved 9 February 2019.
- "District Human Development Report: South 24 Parganas". (1) Chapter 1.2, South 24 Parganas in Historical Perspective, pages 7-9 (2) Chapter 3.4, Land reforms, pages 32-33. Development & Planning Department, Government of West Bengal, 2009. Archived from the original on 5 October 2016. Retrieved 7 August 2016.
- "District Human Development Report, Bardhaman" (PDF). Table 3.10, Gross Cropped Area, Net Cropped Area and Cropping Intensity of different blocks of Bardhaman district 2003-04, Page 53. Development and Planning Department, Government of West Bengal, May 2011. Archived from the original (PDF) on 14 August 2017. Retrieved 30 January 2017.
- "37913 Howrah-Katwa local". Time Table. indiarailinfo. Retrieved 13 February 2017.
- "List of State Highways in West Bengal". West Bengal Traffic Police. Retrieved 5 February 2017.
- "District Census Handbook, Barddhaman, 2011, Series 20, Part XII A" (PDF). Page 1082, Appendix I A: Villages by number of Primary Schools and Appendix I B: Villages by Primary, Middle and Secondary Schools. Directorate of Census Operations, West Bengal. Retrieved 9 February 2019.
- "Midday Meal – Burdwan, WB". District Authorities. Retrieved 12 February 2019.
- "Health & Family Welfare Department". Health Statistics. Government of West Bengal. Retrieved 19 January 2019.
- "Groundwater Arsenic contamination in West Bengal-India (20 years study )". Bardhaman. SOES. Retrieved 9 September 2011.