Hurricane Bob
Hurricane Bob was one of the costliest hurricanes in New England history. The second named storm and first hurricane of the 1991 Atlantic hurricane season, Bob developed from an area of low pressure near The Bahamas on August 16. The depression steadily intensified, and became Tropical Storm Bob late on August 16. Bob curved north-northwestward as a tropical storm, but re-curved to the north-northeast after becoming a hurricane on August 17. As such, it brushed the Outer Banks of North Carolina on August 18 and August 19, and subsequently intensified into a major hurricane (Category 3 or greater on the Saffir-Simpson Hurricane Scale). After peaking in intensity with maximum sustained winds of 115 mph (185 km/h), Bob weakened slightly as it approached the coast of New England. Some sources say the winds of Bob might have gone as high as 125 mph sustained.[1][2]
| Category 3 major hurricane (SSHWS/NWS) | |
 Hurricane Bob approaching New England near peak intensity on August 19 | |
| Formed | August 16, 1991 |
|---|---|
| Dissipated | August 29, 1991 |
| (Extratropical after August 20) | |
| Highest winds | 1-minute sustained: 115 mph (185 km/h) |
| Lowest pressure | 950 mbar (hPa); 28.05 inHg |
| Fatalities | 15 direct, 2 indirect |
| Damage | $1.5 billion (1991 USD) |
| Areas affected | North Carolina, Mid-Atlantic states, New England, Atlantic Canada, and Iberian Peninsula |
| Part of the 1991 Atlantic hurricane season | |
Bob made landfall twice in Rhode Island as a Category 2 hurricane on August 19, first on Block Island and then in Newport. Upon doing so, it became the only hurricane to make landfall in the contiguous United States during the 1991 season. Moving further inland, Bob rapidly weakened, and deteriorated to a tropical storm while emerging into the Gulf of Maine. Shortly thereafter, Bob made landfall in Maine as a strong tropical storm early on August 20. Bob entered the Canadian province of New Brunswick a few hours later, where it transitioned into an extratropical cyclone. By August 21, the remnants of Bob crossed Newfoundland and re-emerged into the open Atlantic Ocean. The remnants traveled a long distance across the northern Atlantic Ocean, and finally dissipated west of Portugal on August 29.
Bob left extensive damage throughout New England in its wake, totaling approximately $1.5 billion (1991 USD, $2.82 billion 2020 USD). This made it one of the costliest United States hurricanes at the time; as of 2013, it ranked thirty-second in the category. But some sources say that Bob might have caused as much as $3 billion (1991 USD, $5.63 billion 2020 USD) in damage.[3][4] In addition, eighteen fatalities were reported in association with Bob.[5][6] The loss of life and most of the damage occurred as a result of high winds and rough seas. There were six confirmed tornadoes during its passage. Bob is the most recent hurricane to hit the New England states directly as a hurricane.[7]
Meteorological history
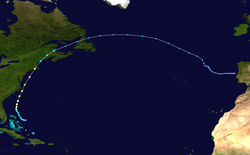
Hurricane Bob originated from the remnants of a frontal trough to the southeast of Bermuda on August 12. The system tracked towards the southwest and later west towards the Bahamas. By August 15th, satellite analysis of the system found a weak low pressure area a couple hundred miles east of the Bahamas.[8] Operationally, the system was not declared a tropical depression until 0600 UTC on August 16 after a reconnaissance mission into the storm found a closed circulation and flight level winds of 37 mph (60 km/h).[9] After post-storm analysis, it was determined that the low had developed into a depression around 0000 UTC. Several hours after being designated, the system began to develop convective banding features. Roughly 18 hours after being declared a depression, the National Hurricane Center (NHC) upgraded it to a tropical storm, giving it the name Bob. At this time, Bob was situated roughly 140 mi (225 km) northeast of Nassau, Bahamas. The storm tracked slowly towards the northwest in response to the deep layer mean flow it was embedded within.[8]
A deepening trough over the eastern United States was forecast to turn the storm toward the north on August 16. This turn took place earlier than forecasters anticipated.[10] The storm slowly intensified as convection was displaced from the center of circulation; however, upper-level outflow was well-defined and intensification of the storm was expected as it tracked over the Gulf Stream.[11] Later that day, Bob began to consolidate and a reconnaissance plane recorded hurricane-force winds at 1719 UTC, following this reading, the NHC upgraded the storm to a Category 1 hurricane on the Saffir–Simpson Hurricane Scale.[8] Shortly after, the hurricane began to turn towards the north-northeast in response to a subtropical ridge over the Atlantic and the trough over the southeastern United States.[12]
By August 18, the NHC noted that the hurricane was asymmetrical, having uneven distribution of the wind radii.[13] Later that day, deep convection continued to form and an eye later appeared on satellite imagery. Early the next day, the eye became increasingly defined as the center of Bob passed roughly 35 mi (55 km) from the North Carolina coastline. By 0600 UTC, Hurricane Hunters recorded flight level winds of 140 mph (225 km/h), corresponding to surface winds of 115 mph (185 km/h). At this time, the barometric pressure of the storm also decreased to 950 mbar (hPa; 28.05 inHg), the lowest pressure recorded during the storm. After attaining this intensity, the hurricane tracked quickly northeast at 25 mph (35 km/h), steered by the trough over the southeastern United States, an upper-level cutoff low over the Great Lakes Region and the subtropical ridge over the Atlantic.[12]
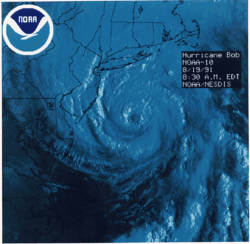
The track of Hurricane Bob by late August 18/early August 19 was similar to that of Hurricane Carol in 1954, another major hurricane that impacted New England.[12] Significantly cooler sea surface temperatures in the path of the hurricane resulted in weakening, leading to the eye becoming cloud-filled. Later on August 19, the western portion of the eyewall brushed the eastern tip of Long Island. Around 1800 UTC, the center of Bob made landfall near Newport, Rhode Island with winds of 100 mph (155 km/h), making it a Category 2 hurricane. The storm quickly weakened as it tracked through Rhode Island and Massachusetts before entering the Gulf of Maine. Around 0130 UTC on August 20, the now weakened Tropical Storm Bob made another landfall near Rockland, Maine.[12]
Later that day, Bob had crossed through Maine and part of New Brunswick, Canada and entered the Gulf of St. Lawrence. Around 1800 UTC, the former hurricane transitioned into an extratropical cyclone. Early the next day, the storm passed over northern Newfoundland before re-entering the Atlantic Ocean. Rapidly tracking eastward, the storm briefly weakened to the equivalent of a tropical depression on August 22. After restrengthening to tropical storm-force winds, the remnants of Bob turned towards the southeast and slowed. Once more, the extratropical system weakened to the equivalent of a tropical depression; however, it did not re-intensify. The storm slowly tracked towards the east before dissipating off the coast of Portugal on August 29.[12]
Preparations
Watches and warnings
Several hours after the declaration of Tropical Storm Bob on August 16, the Government of the Bahamas issued a tropical storm warning for the northwestern Bahamas, between the islands of Andros and Eleuthera. After the storm turned northward, this warning was discontinued as tropical storm-force winds were no longer expected to affect the islands. Shortly before Bob was upgraded to a hurricane on August 17, the NHC issued a hurricane watch for coastal areas of North Carolina between Little River Inlet northward to Virginia Beach, Virginia. Roughly four hours after this watch, it was upgraded to a hurricane warning. A new hurricane watch was issued late on August 17, encompassing areas between Virginia Beach northward to Cape Henlopen, Delaware. This watch was also upgraded to a warning on August 18 as Bob paralleled the Mid-Atlantic coastline. During the afternoon hours, a tropical storm warning was declared for areas in the lower Chesapeake Bay area, including Norfolk, Virginia.[14]
A new, extensive hurricane warning was issued late on August 18 when forecasts showed Bob moving directly over southern New England. The warning covered areas between Cape Henlopen, Delaware to Plymouth, Massachusetts, including Long Island and Long Island Sound. Early on August 19, all watches and warnings south of Cape Lookout, North Carolina were discontinued and the hurricane warning was extended northward to encompass areas south of Eastport, Maine. The Canadian Hurricane Centre began issuing warnings for Atlantic Canada later that day. Nova Scotia, Prince Edward Island and New Brunswick were placed under wind and heavy rain warnings.[14] By the morning of August 20, all watches and warnings in the United States were discontinued; however, a brief tropical storm warning was declared for coastal Maine between Rockland and Eastport before the remnants of Bob moved through eastern Canada. The advisories for Atlantic Canada were later discontinued after the system moved out of the region.[15]
Mid-Atlantic states and the Carolinas
Following the issuance of a hurricane warning in North Carolina on August 17,[14] mandatory evacuation orders were declared for the outermost islands in the state. Local police assisted significant traffic as an estimated 50,000 to 100,000 people left the region. At the height of the evacuations, delays in some places exceeded three hours. Despite the large number of evacuees, an additional 50,000 people were estimated to have stayed home and wait out the storm. Several bridges in the area were shut down prior to Bob's arrival as hurricane-force winds were likely to create life-threatening conditions on them. The National Park Service in the state also shut down campgrounds across the Outer Banks.[16] An evacuation shelter was also opened in Carteret County.[17]
In Virginia, 125 planes were relocated from Langley Air Force Base to Wright-Patterson Air Force Base in Dayton, Ohio. Roughly 400 people evacuated from coastal areas in Maryland, and stores in Ocean City reported a substantial increase in sales related to storm preparation. Further north in New Jersey, casinos prepared sandbags to protect the structures and tape to cover windows.[17]
In Suffolk County, New York, emergency officials were unsure of whether or not to issue evacuation orders for residents along coastal areas. This contemplation led to "mixed messages" on the ability of the government being sent to the public. By the evening of August 19, the evacuation order was not issued; however, the county was placed under a state of emergency and disaster centers were opened.[18] The American Red Cross opened four shelters on Long Island that housed 800 people during the storm.[19]
New England and Canada
Prior to Bob's arrival in New England, officials in Connecticut and Rhode Island declared a state of emergency in anticipation of significant damage. All state workers in the area were told to go home early and prepare for the storm. The Connecticut Legislature canceled a session on the state's budget and Governor Lowell P. Weicker, Jr. activated the emergency operations center. Submarines stationed in Groton left port and waited out the storm under water. Airplane and train service was disrupted throughout the Mid-Atlantic states and New England in relation to Bob.[20] The American Red Cross opened 23 shelters in 16 communities in Connecticut. In neighboring Rhode Island, the agency set up 40 shelters,[19] and there were an additional 25 shelters unaffiliated with the agency.[21] About 3,500 people statewide evacuated, including 2,000 on Block Island. Several people injured themselves while preparing for the storm.[22]
In Massachusetts, thousands of residents evacuated Cape Cod, leading to an 11 mi (18 km) backup on the Sagamore Bridge.[23] There were nine shelters set up in the region,[21] which became overcrowded with evacuees.[23] There were about 50,000 people who left their homes statewide, of which 6,500 went to shelters.[24] On Martha's Vineyard, electronic stores reported their best business sales in years, with supplies of D-batteries being cleaned off the shelves. Many residents purchased these as well as battery-powered radios and flashlights. President George H. W. Bush, staying at his home in Kennebunkport, Maine, evacuated to Pease Air Force Base in New Hampshire. To avoid possible risks by using helicopter, he drove by motorcade to the base. During this time, portions of Interstate 95 were closed to allow him direct access to the Air Force base; however, this created many miles of backup as thousands of residents moved inland.[23] Eight shelters were opened in New Hampshire,[21] and about 5,200 people – mostly tourists – evacuated the coastline.[25] There were 49 shelters opened in neighboring Maine,[21] and about 8,600 people evacuated along the coastline in York County.[26]
In the Bay of Fundy, fishermen were urged to return to port in fears of large swells from Hurricane Bob.[27]
Impact
| Location | Deaths | Damage(USD) |
| South Carolina | 1 | – |
| North Carolina | 1 | $8 million |
| New York | 2 | $150 million |
| Connecticut | 6 | $40 million [28] |
| Massachusetts | 1 | $1 billion |
| Rhode Island | 0 | $230 million |
| New Hampshire | 2 | $4 million |
| Maine | 3 | $42 million |
| Canada | 2 | – |
| Total | 18 | $1.4 billion |
Throughout the east coast of the United States, Hurricane Bob produced moderate rainfall and substantial damage. Damage totaled about $1.5 billion (1991 USD). That included about $700 million through cleanup costs, uninsured losses, and food claims.[29] That made it, at the time, one of the costliest United States hurricanes, although the total was due to the storm passing through a densely populated region.[30] As of 2010, Hurricane Bob ranked as the 22nd costliest tropical cyclone in the United States mainland.[31] Across its track, the hurricane left 2.1 million people without power.[32] There were six confirmed tornadoes, along with thirteen unconfirmed tornadoes.[33]
Carolinas and Mid-Atlantic

The center of Hurricane Bob passed several hundred miles east of South Carolina with only slight effects on the state.[12] However, the storm produced large swells that caught a swimmer in Myrtle Beach in strong undertow; this swimmer drowned to death.[20][29]
A crew of three sailed from Little River (Horry County, South Carolina) en route to Rhode Island. The hurricane destroyed the mast, leaving the crew stranded over the open ocean in shark-infested waters. After 12 days, the United States Coast Guard rescued the three.[34]
On 18 August 1991, Hurricane Bob brushed the Outer Banks of North Carolina, bringing strong winds and heavy rains. Although a maximum of 5.30 inches (135 mm) of rain fell at the National Weather Service office building at Cape Hatteras, little heavy rain fell inland of the Outer Banks. One person was killed in the state in relation to Bob, and damage from the storm was estimated at $8 million (1991 USD).[29] The community of Duck, North Carolina, received the highest recorded onshore sustained winds in the state, 62 miles per hour (100 km/h), whereas the highest gusts reached 74 miles per hour (119 km/h) at Cape Hatteras.[35] Diamond Shoal Light recorded a sustained wind of 85.0 knots (157.4 km/h; 97.8 mph) with a gust of 106.7 knots (197.6 km/h; 122.8 mph) and a minimum pressure of 962.1 millibars (962.1 hPa) on the evening of 18/19 August 1991.[36] Cape Hatteras also recorded a storm surge of 2.6 to 4.6 ft (0.79 to 1.40 m).[35]
Flooding was reported throughout the Outer Banks in relation to the heavy rains and storm surge of the storm. The storm required the shutdown of North Carolina Highway 12, the only highway connecting the area to the mainland, isolating those who decided to stay behind. Many residents lost power as numerous power lines fell from strong winds.[16] Six brief tornadoes, ranging between F0 and F1 on the Fujita scale, struck the state within squall lines in the outer rainbands of Hurricane Bob.[29] Four tornadoes in Dare County, North Carolina, caused $256,000 in damage.[37] Near Cape Hatteras, wind severely damaged one structure, which lost its roof and some siding.[20]
As the hurricane passed east of Virginia, it produced minimal rainfall and wind gusts of up to 40 miles per hour (64 km/h). No one reported damage beyond some minor beach erosion in Sandbridge, Virginia Beach, Virginia.[38]
In Ocean City, Maryland, a brief period of heavy rainfall caused street flooding. High waves caused minimal beach erosion and overwash along the coastline.[39]
High tides to 5.9 feet (1.8 m) occurred along the Delaware coastline.[40]
Farther north, the storm caused widespread beach erosion along the Jersey Shore, while heavy rains caused street flooding.[41]
The heaviest rains outside New England fell in Bridgehampton, New York, where 7.18 inches (182 mm) fell during the passage of the storm.[42] Two reported tornadoes struck Long Island.[33] High winds destroyed apple, corn, and peach fields along Long Island.[43] After a dry summer, the sudden deluge wrecked potato crops, resulting in $20 million in crop damage;[44] about one-sixth of the agricultural output of the region. High winds caused power outages for 477,765 Long Island Lighting Company customers for a period of nearly five days. Most power outages occurred in the East End. One person died in a car accident while a traffic light was offline,[45] and another person died when a falling tree struck a train conductor.[19] The high waves destroyed fish nets offshore [44] and caused beach erosion and the widespread destruction of boats along the coast.[45] Statewide damage totaled over $75 million.[33]
New England

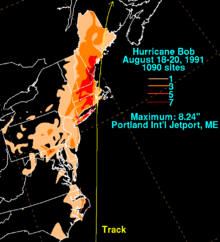
Before Bob made landfall in the New England mainland, it passed directly over Block Island, Rhode Island. Stations on the island recorded gusts to 105 mph (169 km/h) near the upper end of their range, indicating that the winds were likely stronger.[33] On the mainland, winds peaked at 90 mph (144 km/h) in Narragansett. In the state, the storm surge—the rise of water above the normal tide—was 6.6 ft (2.0 m) in the capital city of Providence, while the peak storm tide—the rise of water including the normal high tide—was 16.5 ft (5.0 m) at the mouth of the Sakonnet River.[46] At the latter location, the estimate was based on high-water marks, which included wave effects.[33] The high waves resulted in extensive beach erosion along the state's coastline. Roads were washed out in Coventry, and there was flooding reported along the Pocasset River.[22] Rainfall in the state peaked at 7.13 in (181 mm) in North Foster.[47] In Rhode Island, where the hurricane made landfall, Bob caused about 200,000 power outages;[21] about 60% of residents in the state and southeastern Massachusetts were left without power.[48] During the storm, treatment plants spilled over 100 million tons of sewage due to overflow into Narragansett Bay.[49] Damage totaled over $115 million.[33]
While moving over Rhode Island, the strong winds of Bob extended westward into Connecticut, peaking at 75 mph (120 km/h) near Groton; there, a gust of 100 mph (160 km/h) was reported.[46] High winds downed trees in every county in the state, although wind damage was heaviest in the southeastern portion near the coast.[50] Overall there were about 315,000 people left without power in Connecticut.[19] A man in Sterling died after being struck by a falling tree limb.[51] The highest storm surge was 5 ft (1.5 m) in New London.[46] Coastal flooding was limited to New London County, although coastal damage was minimal. One woman died while on a capsized sailboat.[51] In Norwich, a rainfall total of 6.22 in (158 mm) was reported, which was the statewide peak.[47] Flooding was minor, limited to streams and small rivers.[50] Total damage in the state was estimated around $49 million, including $4.5 million in crop damage. There was one death due to a fire that occurred during the storm's passage,[50][52] and there were five other deaths across the state.[29]
The most significant area affected by Bob was Massachusetts, where over $1 billion in damage occurred.[53] A C-MAN station in Buzzards Bay recorded winds every hour and observed peak sustained winds of 77 mph (124 km/h), along with gusts to 89 mph (143 km/h).[33] Sustained winds in the state peaked at 100 mph (161 km/h) in Provincetown,[54] and there was an unofficial report of a gust of 125 mph (201 km/h) in Brewster.[55] Cape Cod, which was mostly east of the eye, received very little precipitation, but some of the strongest winds. The highest rainfall total in the state was 7.06 in (179 mm) in Westfield.[47] Storm surges in the state were most significant along Buzzards Bay, peaking at 5.8 ft (1.8 m) in New Bedford and Woods Hole.[54] High waves eroded the beach around Chatham Light, leaving behind a 5 ft (1.5 m) cliff.[24] Other locations, including southward-facing shores along Martha's Vineyard and Nantucket, lost 50 ft (15 m) of beach from erosion. Boat damage was significant in the region.[48] The hurricane left over 500,000 people without power, including all of Cape Cod.[21] Damage was heaviest from Buzzards Bay eastward to Cape Cod, and at least 61 houses were destroyed. Damage was also extensive to apple and peach orchards across these areas,[48] and agricultural damage was estimated around $10 million. The state also suffered $69 million in damage to public property.[49]
Although it remained offshore of the state, Bob produced strong winds in New Hampshire, with gusts reaching 60 mph (97 km/h) at Pease Air National Guard Base.[56] Mount Washington experienced 7.46 in (189 mm) of precipitation during the storm's passage.[47] Both the Lovell and Contoocook rivers experienced flooding due to the storm, and widespread flooding occurred in urban areas in the south and central portions of the state.[25] There were two deaths in the state, one from an automobile accident and the other due to a capsized boat. High winds downed widespread trees and power lines,[25] causing 30,000 people to lose power statewide.[21] Damage was estimated around $2 million.[33] In neighboring Vermont, the highest rainfall report was 4.27 in (108 mm) in Vernon.[47]
Although moving across Maine as a tropical storm, Bob still maintained strong winds, producing gusts to 70 mph (110 km/h) in Portland.[57] A station in Wiscasset reported a gust of 92 mph (148 km/h) before it was blown away, and another station recorded a gust of 93 mph (150 km/h).[58] A total of 169,200 customers lost power during the hurricane, some of whom remaining without electricity for a week.[57] There was a tornado reported in St. Albans, which downed multiple trees, damaged a few houses, and moved a boathouse three blocks away;[58] its status as a tornado was not confirmed.[33] As it passed the region, the storm produced a 2.77 ft (0.84 m) storm tide.[57] The heaviest rainfall nationwide from the hurricane fell at the Portland International Jetport, where 8.24 in (209 mm) fell during its passage.[59] This contributed to August 1991 being the wettest month on record in Portland.[60] At the time, its 24‑hour rainfall total of 7.83 in (199 mm) was the highest on record, although it was surpassed in October 1996 by an extratropical system fueled by Hurricane Lili. The rains from Bob led to a record flow rate along the Presumpscot River, although that record was also surpassed by the 1996 system.[61] River flooding washed out five bridges and roads across southwestern Maine. One man died due to being swept away by floodwaters, and another died in the ocean while on a life raft.[26] A total of 700 houses were affected by the storm, including one that was destroyed and three that sustained major damage.[62] Damage in the area around Portland totaled over $25.7 million, and there were three deaths.[57]
Atlantic Canada
After causing severe damage in the United States, the remnants of Hurricane Bob moved into Atlantic Canada.[29] The highest rainfall amount in the country was 4.37 in (111 mm) in northern New Brunswick. St. John's, Newfoundland and Labrador recorded a record 1 inch (26 mm) of rainfall during the storm's passage. Gusty winds were observed across the region, and winds reached 68 mph (109 km/h) in Digby, Nova Scotia.[63] In Nova Scotia, two 17-year-old girls were washed out to sea near Cape Forchu after being caught in rough swells produced by the storm.[64] Rescue officials quickly began searching operations;[65] however, it was later confirmed that the two had drowned.[29] In Fredericton, New Brunswick, tropical storm-force winds downed trees and power lines, resulting in scattered power outages. Lightning associated with strong storms also reportedly struck some trees in the area.[65] A two-story home in Pointe-Verte collapsed due to high winds. In Petit-Rocher, five fishing boats sank after being overwhelmed by large swells at port. Firefighters in the area were surveying the town all night on August 20, checking for downed power lines and trees.[66] Power outages were also reported on Prince Edward Island. The storm left about $1 million in damage (1991 CAD) on Grand Manan Island in the Bay of Fundy.[63]
Aftermath and retirement
Following the storm's passage, the Long Island Lighting Company used 165 workers to restore the power outages on Long Island. In Connecticut, state officials deployed about 200 trucks to remove debris on roads. The Massachusetts National Guard was activated to assist in relief efforts.[19] In Rhode Island, a man was killed while repairing damage caused by Bob.[67] Beaches in the state re-opened by five days after the storm.[68] The hurricane mixed the waters in Long Island Sound and prevented the algae bloom that happened in previous summers.[69] In the days after Bob, the Commonwealth Electric Company brought electricians from outside the company and put their own workers on 16‑hour shifts to restore power across Massachusetts.[49] Most Massachusetts residents, excluding those living on Cape Cod and Martha's Vineyard, had their power restored within five days. Parts of Cape Cod had no power or running water for over two weeks.[68] The hurricane struck toward the end of the summer, which significantly impacted the tourism season already in the midst of a recession.[49] The New England coast was affected by a powerful nor'easter known as the Perfect Storm about two months after the hurricane struck the region. Some locations experienced worse damage from the October storm than from Bob.[70]
Due to the high damage from Hurricane Bob, President George H. W. Bush declared the following states as disaster (in order): Rhode Island, Massachusetts, Maine, Connecticut, New Hampshire, and New York.[71] Damage in Maine was insufficient to qualify for individual family assistance.[62] Instead, the declaration allocated federal funding to reimburse cities for debris removal, repairing damaged public buildings, and other municipal expenses for each of the states. Despite the declaration, the federal government did not immediately provide aid to the affected region. This was partially due to President Bush considering the storm a "disaster but not an emergency", which therefore required cuts from other budgets to offset the relief aid. This was in opposition to the Democratic-controlled Congress, who requested an expedited process.[72]
Due to its effects in the United States, the name Bob was subsequently retired by the World Meteorological Organization's hurricane committee in the spring of 1992, and will never be used again for an Atlantic hurricane.[73] It was replaced with Bill for the 1997 season.
See also
- List of Atlantic hurricanes
- List of New England hurricanes
- List of retired Atlantic hurricane names
- List of wettest tropical cyclones in Massachusetts
- Hurricane Carol - a storm with a similar track and also caused severe damage to New England in 1954
- Hurricane Earl (2010) - a storm with a similar track that also caused damage to New England and Canada
- Hurricane Sandy - killed many people along the Mid-Atlantic states and New England
References
- "The East Coast Storm". New York Times. Retrieved February 16, 2019.
- "Hurricane Bob Barrels into New England". UPI. Retrieved February 18, 2019.
- "Storm Preparation-Hurricane Bob". The Hour. September 2010. Retrieved June 5, 2018.
- "Hurricane Bob". Hurricanes, Blizzards and Noreasters. Retrieved June 5, 2018.
- "The Hunt for Hurricanes". Scholastic. Retrieved June 5, 2018.
- "What Lessons Did New England Learn". NECN. Retrieved June 5, 2018.
- The 23rd Anniversary of Hurricane Bob (Report). WPRI Providence. Archived from the original on August 24, 2014. Retrieved September 1, 2014.
- Max Mayfield (August 10, 1992). "Hurricane Bob Preliminary Report Page One". National Hurricane Center. Retrieved August 22, 2009.
- Miles B. Lawrence (August 16, 1991). "Tropical Depression Three Discussion One". National Hurricane Center. Retrieved August 22, 2009.
- Harold P. Gerrish (August 16, 1991). "Tropical Storm Bob Discussion Four". National Hurricane Center. Retrieved August 23, 2009.
- Lixion A. Avila (August 17, 1991). "Tropical Storm Bob Discussion Five". National Hurricane Center. Retrieved August 23, 2009.
- Max Mayfield (August 10, 1992). "Hurricane Bob Preliminary Report Page Two". National Hurricane Center. Retrieved August 23, 2009.
- Richard Pasch (August 18, 1991). "Hurricane Bob Discussion Ten". National Hurricane Center. Retrieved August 23, 2009.
- Max Mayfield (August 10, 1992). "Hurricane Bob Preliminary Report Page Seventeen". National Hurricane Center. Retrieved April 23, 2010.
- Max Mayfield (August 10, 1992). "Hurricane Bob Preliminary Report Page Eighteen". National Hurricane Center. Retrieved April 23, 2010.
- "Hurricane Bob Lashes North Carolina". Gettysburg Times. Associated Press. August 19, 1991. Retrieved April 23, 2010.
- Anita Snow (Associated Press) (August 20, 1991). "New England bracing for strike by Hurricane Bob". Kingman Daily Miner. Retrieved April 23, 2010.
- Charles V. Zehren (August 20, 1991). "Hurricane Bob: Officials Unclear on Evacuation". Newsday. Retrieved April 23, 2010.
- FEMA Headquarters (1991). "Situation Report — Hurricane Bob" (GIF). National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Retrieved 2011-07-12.
- "Hurricane Bob lashes North Carolina; Long Island braces for a direct hit". The Daily Reporter. Associated Press. August 21, 1991. Retrieved April 23, 2010.
- FEMA Headquarters (1991). "Situation Report — Hurricane Bob" (GIF). National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Retrieved 2011-07-12.
- Valley/Sisson, Providence, Rhode Island National Weather Service (1991-08-23). "Preliminary Survey on Hurricane Bob... First Issue" (GIF). National Hurricane Center. Retrieved 2011-09-18.CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
- Michael Specter (August 20, 1991). "Hurricane Rakes New England". the Washington Post. Retrieved April 23, 2010.
- Seeley, Boston Weather Forecast Office (1991-08-27). "Post-Storm Hurricane Report for Chatham, Massachusetts" (GIF). National Hurricane Center. Retrieved 2011-09-17.
- Concord, New Hampshire National Weather Service (1991-08-21). "Hurricane Bob Preliminary Report". National Hurricane Center. Retrieved 2011-09-18.
- Wayne Cotterly (2002-10-21). "Hurricane Bob". Archived from the original on 2016-04-01. Retrieved 2011-09-18.
- Staff Writer (August 19, 1991). "Bob warnings : Hurricane lashes U.S. coast on way to Maritimes". Kitchener – Waterloo Record. p. A2. Retrieved April 24, 2010.
- http://www.nhc.noaa.gov/archive/storm_wallets/atlantic/atl1991-prelim/bob/prelim04.gif. Missing or empty
|title=(help) - Max Mayfield (August 10, 1992). "Hurricane Bob Preliminary Report Page Four". National Hurricane Center. Retrieved April 23, 2010.
- Staff Writer. "Hurricane Bob ranks no. 2 most expensive storm". Harlan Daily Enterprise. Associated Press. Retrieved 2011-09-19.
- Landsea, Christopher W.; Blake, Eric S.; Gibney, Ethan J. (2011-08-31). "The deadliest, costliest, and most intense United States tropical cyclones from 1851 to 2010 (and other frequently requested hurricane facts)" (PDF). NOAA Technical Memorandum NWS-NHC-6. National Oceanic Atmospheric Administration: 19. Retrieved 2011-09-16.
- Max Mayfield (August 10, 1992). "Hurricane Bob Preliminary Report Page Five". National Hurricane Center. Retrieved 2011-09-17.
- Max Mayfield (August 10, 1992). "Hurricane Bob Preliminary Report Page Three" (GIF). National Hurricane Center. Retrieved September 17, 2011.
- Staff Writer (1991-09-01). "Hurricane Bob Strands Three in Atlantic for 12 Days". Associated Press. Retrieved 2011-09-19.
- Max Mayfield (August 10, 1992). "Hurricane Bob Preliminary Report Page Nine". National Hurricane Center. Retrieved April 23, 2010.
- http://www.ndbc.noaa.gov/data/climatic/DSLN7.txt. Missing or empty
|title=(help) - "NCDC Storm Events Database". National Climatic Data Center. 2010. Archived from the original on September 15, 1999. Retrieved April 23, 2010.
- Norfolk, VA National Weather Service (1991-08-19). "Preliminary Report Hurricane Bob" (GIF). National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Retrieved 2011-07-21.
- Davis, Baltimore MD National Weather Service (1991-08-23). "Preliminary Report Hurricane Bob" (GIF). National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Retrieved 2011-07-21.
- Smelgus, Wilmington Delaware National Weather Service (1991-08-20). "Preliminary Report Hurricane Bob" (GIF). National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Retrieved 2011-07-21.
- "Preliminary Report Hurricane Bob... Corrected" (GIF). Atlantic City National Weather Service. 1991-08-23. Retrieved 2011-07-29.
- Tropical Cyclone Rainfall in the Mid Atlantic United States
- Staff Writer (1991-08-26). "Costs still climbing from Hurricane Bob". Bangor Daily News. Associated Press. Retrieved 2011-07-29.
- Sarah Bartlett (1991-09-02). "Between Heat and Hurricane, Summer Weather Is Weird". New York Times. Retrieved 2011-07-29.
- "Section 5.4.4: Risk Assessment – Hurricane" (PDF). Suffolk County, New York Government. October 2008. Retrieved 2011-08-19.
- Max Mayfield (August 10, 1992). "Wind reports on Hurricane Bob in Connecticut and Rhode Island, August 1991" (GIF). National Hurricane Center. Retrieved 2011-09-17.
- Roth, David M; Hydrometeorological Prediction Center (2012). "Tropical Cyclone Rainfall for the New England United States". Tropical Cyclone Rainfall Point Maxima. United States National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration's National Weather Service. Retrieved June 23, 2012.
- David R. Vallee; Michael R. Dion (2005-12-05). "Hurricane Bob". Boston, MA National Weather Service. Retrieved 2011-07-12.
- Staff Writer (1991-08-26). "Costs Still Climbing from Hurricane Bob". Bangor Daily news. Retrieved 2011-09-19.
- Hartford, Connecticut National Weather Service (1991-08-23). "Preliminary Survey... Hurricane Bob" (GIF). National Hurricane Center. Retrieved 2011-09-17.
- Hartford, Connecticut National Weather Service (1991-08-23). "Preliminary Survey... Hurricane Bob (page 2)" (GIF). National Hurricane Center. Retrieved 2011-09-17.
- Bruce Budd, Hartford Weather Service Office (1991-08-28). "Hurricane Bob Additional Information" (GIF). National Hurricane Center. Retrieved 2011-09-15.
- Staff Writer (1991-11-30). "Storm season is over". Reading Eagle. Associated Press. Retrieved 2011-07-13.
- Max Mayfield (August 10, 1992). "Wind reports on Hurricane Bob in Rhode Island and Massachusetts, August 1991" (GIF). National Hurricane Center. Retrieved 2011-09-17.
- Max Mayfield (August 10, 1992). "Wind reports on Hurricane Bob in New England and Canada, August 1991" (GIF). National Hurricane Center. Retrieved 2011-09-17.
- Max Mayfield (August 10, 1992). "Hurricane Bob selected surface observations, August 1991" (GIF). National Hurricane Center. Retrieved 2011-09-17.
- Joseph A. Ronco (1991-09-18). "Hurricane Report: Bob" (GIF). Portland National Weather Service. National Hurricane Center. Retrieved 2011-09-16.
- Joseph A. Ronco (1991-09-18). "Hurricane Report: Bob (page 2)" (GIF). Portland National Weather Service. National Hurricane Center. Retrieved 2011-09-16.
- Roth, David M; Hydrometeorological Prediction Center (2007-04-30). "Hurricane Bob — August 18–21, 1991". United States National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration's National Weather Service. Retrieved 2011-07-12.
- Gray, Maine National Weather Service (2011-09-09). "The Portland ME Climate Summary for the Month of August 2011". Archived from the original on December 30, 2005. Retrieved 2011-09-18.
- John W. Cannon (September 2000). "A Hydrometeorological Assessment of the October 1996 Record Rainstorm in Maine" (PDF). Eastern Region Headquarters. Retrieved 2011-09-18.
- Staff Writer (1991-09-16). "No aid for storm damage to Maine private property". Bangor Daily News. Associated Press. Retrieved 2011-09-19.
- Canadian Hurricane Centre (2010-09-14). "1991-Bob". Retrieved 2011-09-19.
- "Storm sweeps 2 teens to sea 'The wave just sucked them away . . . The ocean was wild'". Toronto Star. Associated Press. August 20, 1991. p. A3. Retrieved April 24, 2010.
- "Hurricane Bob lashes coast 2 swept out to sea as storm hits Nova Scotia". Toronto Star. Associated Press. August 20, 1991. p. A3. Retrieved April 24, 2010.
- Staff Writer (August 21, 1991). "Hurricane blows out after leaving trail of destruction". Kitchener – Waterloo Record. p. A12. Retrieved April 24, 2010.
- David Crombie (1991-09-17). "Worker electrocuted in Westport 3 others hurt while moving house damaged in hurricane". Journal-Bulletin Staff Writer. Retrieved 2011-09-19.
- Staff Writer (1991-08-25). "Massachusetts fights to recover from Hurricane Bob". Record-Journal. Associated Press. Retrieved 2011-09-19.
- Elsa Brenner (1991-10-06). "Shore Communities Assess Implications Of L.I. Sound Study". New York Times. Retrieved 2011-09-19.
- William C. Hidlay (1991-11-01). "Maine hit hard by storm". Bangor Daily News. Associated Press. Retrieved 2011-07-03.
- "1991 Federal Disaster Declarations". Federal Emergency Management Agency. 2005-05-23. Retrieved 2011-09-18.
- John Diamond (1991-10-18). "Congress Attempting to Speed Up Disaster Funds". The Hour. Associated Press. Retrieved 2011-09-19.
- "Tropical Cyclone Naming History and Retired Names". United States National Hurricane Center. April 17, 2015. Archived from the original on February 12, 2006. Retrieved July 19, 2015.
