Halaf culture
The Halaf culture is a prehistoric period which lasted between about 6100 BC and 5100 BC.[1] The period is a continuous development out of the earlier Pottery Neolithic and is located primarily in the fertile valley of the Khabur River (Nahr al-Khabur), of south-eastern Turkey, Syria, and northern Iraq, although Halaf-influenced material is found throughout Greater Mesopotamia.
 | |
| Geographical range | Mesopotamia |
|---|---|
| Period | Neolithic 3 – Pottery Neolithic (PN) |
| Dates | c. 6,100–5,100 BC |
| Type site | Tell Halaf |
| Major sites | Tell Brak |
| Preceded by | Pre-Pottery Neolithic B, Yarmukian culture |
| Followed by | Halaf-Ubaid Transitional period, Hassuna culture, Samarra culture |
While the period is named after the site of Tell Halaf in north Syria, excavated by Max von Oppenheim between 1911 and 1927, the earliest Halaf period material was excavated by John Garstang in 1908 at the site of Sakce Gözü, then in Syria but now part of Turkey.[2] Small amounts of Halaf material were also excavated in 1913 by Leonard Woolley at Carchemish, on the Turkish/Syrian border.[3] However, the most important site for the Halaf tradition was the site of Tell Arpachiyah, now located in the suburbs of Mosul, Iraq.[4]
The Halaf period was succeeded by the Halaf-Ubaid Transitional period which comprised the late Halaf (c. 5400–5000 BC), and then by the Ubaid period.
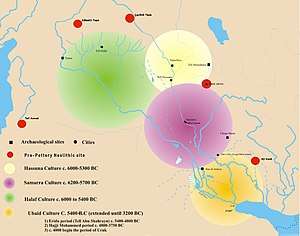
Origin
Previously, the Syrian plains were not considered as the homeland of Halaf culture, and the Halafians were seen either as hill people who descended from the nearby mountains of southeastern Anatolia, or herdsmen from northern Iraq.[5] However, those views changed with the recent archaeology conducted since 1986 by Peter Akkermans, which have produced new insights and perspectives about the rise of Halaf culture.[6] A formerly unknown transitional culture between the pre-Halaf Neolithic's era and Halaf's era was uncovered in the Balikh valley, at Tell Sabi Abyad (the Mound of the White Boy).
Currently, eleven occupational layers have been unearthed in Sabi Abyad. Levels from 11 to 7 are considered pre-Halaf; from 6 to 4, transitional; and from 3 to 1, early Halaf. No hiatus in occupation is observed except between levels 11 and 10.[5] The new archaeology demonstrated that Halaf culture was not sudden and was not the result of foreign people, but rather a continuous process of indigenous cultural changes in northern Syria,[7] that spread to the other regions.[1]
Culture
Architecture
Although no Halaf settlement has been extensively excavated some buildings have been excavated: the tholoi of Tell Arpachiyah, circular domed structures approached through long rectangular anterooms. Only a few of these structures were ever excavated. They were constructed of mud-brick sometimes on stone foundations and may have been for ritual use (one contained a large number of female figurines). Other circular buildings were probably just houses.
Halaf pottery
The best known, most characteristic pottery of Tell Halaf, called Halaf ware, produced by specialist potters, can be painted, sometimes using more than two colors (called polychrome) with geometric and animal motifs. Other types of Halaf pottery are known, including unpainted, cooking ware and ware with burnished surfaces. There are many theories about why the distinctive pottery style developed.
The theory is that the pottery came about due to regional copying and that it was exchanged as a prestige item between local elites is now disputed. The polychrome painted Halaf pottery has been proposed to be a "trade pottery"—pottery produced for export—however, the predominance of locally produced painted pottery in all areas of Halaf sites including potters settlement questions that theory.
Halaf pottery has been found in other parts of northern Mesopotamia, such as at Nineveh and Tepe Gawra, Chagar Bazar, Tell Amarna[8] and at many sites in Anatolia (Turkey) suggesting that it was widely used in the region. In addition, the Halaf communities made female figurines of partially baked clay and stone and stamp seals of stone, (see also Impression seal). The seals are thought to mark the development of concepts of personal property, as similar seals were used for this purpose in later times. The Halaf people used tools made of stone and clay. Copper was also known, but was not used for tools.
 Fragment of a bowl; 5600–5000 BC; cermaic; 8.2 cm; Metropolitan Museum of Art (New York City)
Fragment of a bowl; 5600–5000 BC; cermaic; 8.2 cm; Metropolitan Museum of Art (New York City) Halafian ware
Halafian ware Fertility figurine (maybe a goddess?); 5000–4000 BC; terracotta with traces of pigment; 8.1 × 5 × 5.4 cm; by Halaf culture; Walters Art Museum (Baltimore, US)
Fertility figurine (maybe a goddess?); 5000–4000 BC; terracotta with traces of pigment; 8.1 × 5 × 5.4 cm; by Halaf culture; Walters Art Museum (Baltimore, US)
Stamp seals
The Halaf culture saw the earliest known appearance of stamp seals in the Near East.[9] They featured essentially geometric patterns.[9]
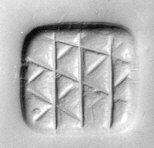 Loop-handled rectangular seal, Halaf culture.
Loop-handled rectangular seal, Halaf culture. Loop-handled circular seal.
Loop-handled circular seal. Stamp seal and modern impression – geometric pattern. Halaf culture
Stamp seal and modern impression – geometric pattern. Halaf culture
Economy
Dryland farming was practiced by the population. This type of farming was based on exploiting natural rainfall without the help of irrigation, in a similar practice to that still practiced today by the Hopi people of Arizona. Emmer wheat, two-rowed barley and flax were grown. They kept cattle, sheep and goats.
Halaf's end (Northern Ubaid)
Halaf culture ended by 5000 BC after entering the so-called Halaf-Ubaid Transitional period.[10] Many Halafians settlements were abandoned, and the remaining ones showed Ubaidian characters.[11] The new period is named Northern Ubaid to distinguish it from the proper Ubaid in southern Mesopotamia,[12] and two explanations were presented for the transformation. The first maintain an invasion and a replacement of the Halafians by the Ubaidians, however, there is no hiatus between the Halaf and northern Ubaid which exclude the invasion theory.[11][13] The most plausible theory is a Halafian adoption of the Ubaid culture,[11] which is supported by most scholars including Oates, Breniquet and Akkermans.[12][13][14]
Chronological context
See also
References
Citations
- Mario Liverani (2013). The Ancient Near East: History, Society and Economy. p. 48. ISBN 9781134750849.
- Castro Gessner, G. 2011. "A Brief Overview of the Halaf Tradition" in Steadman, S and McMahon, G (eds.) The Oxford Handbook of Ancient anatolia. Oxford: Oxford University Press. p. 780
- Castro Gessner, G. 2011. "A Brief Overview of the Halaf Tradition" in Steadman, S and McMahon, G (eds.) The Oxford Handbook of Ancient anatolia. Oxford: Oxford University Press. p. 781
- Campbell, S. 2000. "The Burnt House at Arpachiyah: A Reexamination" Bulletin of the American Schools of Oriental Research no. 318. p. 1
- Maria Grazia Masetti-Rouault; Olivier Rouault; M. Wafler (2000). La Djéziré et l'Euphrate syriens de la protohistoire à la fin du second millénaire av. J.C, Tendances dans l'interprétation historique des données nouvelles, (Subartu) – Chapter : Old and New Perspectives on the Origins of the Halaf Culture by Peter Akkermans. pp. 43–44.
- Peter M.M.G. Akkermans, Glenn M. Schwartz (2003). The Archaeology of Syria: From Complex Hunter-Gatherers to Early Urban Societies (c. 16,000–300 BC). p. 101. ISBN 9780521796668.
- Peter M.M.G. Akkermans, Glenn M. Schwartz (2003). The Archaeology of Syria: From Complex Hunter-Gatherers to Early Urban Societies (c. 16,000–300 BC). p. 116. ISBN 9780521796668.
- Clop Garcia, X.; Alvarez Perez, A.; Hatert, Frédéric (2004). "Characterization study of Halaf ceramic production at Tell Amarna (Euphrates Valley, Syria)". Cite journal requires
|journal=(help) - Brown, Brian A.; Feldman, Marian H. (2013). Critical Approaches to Ancient Near Eastern Art. Walter de Gruyter. p. 304. ISBN 978-1614510352.
- John L. Brooke (2014). Climate Change and the Course of Global History: A Rough Journey. p. 204. ISBN 9780521871648.
- Georges Roux (1992). Ancient Iraq. p. 101. ISBN 9780141938257.
- Susan Pollock; Reinhard Bernbeck (2009). Archaeologies of the Middle East: Critical Perspectives. p. 190. ISBN 9781405137232.
- Peter M.M.G. Akkermans, Glenn M. Schwartz (2003). The Archaeology of Syria: From Complex Hunter-Gatherers to Early Urban Societies (c. 16,000–300 BC). p. 157. ISBN 9780521796668.
- Robert J. Speakman; Hector Neff (2005). Laser Ablation ICP-MS in Archaeological Research. p. 128. ISBN 9780826332547.
- Liverani, Mario (2013). The Ancient Near East: History, Society and Economy. Routledge. p. 13, Table 1.1 "Chronology of the Ancient Near East". ISBN 9781134750917.
- Shukurov, Anvar; Sarson, Graeme R.; Gangal, Kavita (7 May 2014). "The Near-Eastern Roots of the Neolithic in South Asia". PLOS ONE. 9 (5): e95714. Bibcode:2014PLoSO...995714G. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0095714. ISSN 1932-6203. PMC 4012948. PMID 24806472.
- Bar-Yosef, Ofer; Arpin, Trina; Pan, Yan; Cohen, David; Goldberg, Paul; Zhang, Chi; Wu, Xiaohong (29 June 2012). "Early Pottery at 20,000 Years Ago in Xianrendong Cave, China". Science. 336 (6089): 1696–1700. Bibcode:2012Sci...336.1696W. doi:10.1126/science.1218643. ISSN 0036-8075. PMID 22745428.
- Thorpe, I. J. (2003). The Origins of Agriculture in Europe. Routledge. p. 14. ISBN 9781134620104.
- Price, T. Douglas (2000). Europe's First Farmers. Cambridge University Press. p. 3. ISBN 9780521665728.
- Jr, William H. Stiebing; Helft, Susan N. (2017). Ancient Near Eastern History and Culture. Routledge. p. 25. ISBN 9781134880836.
Bibliography
- Akkermans, Peter M.M.G.; Schwartz, Glenn M. (2003). The Archaeology of Syria: From Complex Hunter-Gatherers to Early Urban Societies (c. 16,000–300 BC). Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-52179-666-8.
- Liverani, Mario (2013). The Ancient Near East: History, Society and Economy. Routledge. ISBN 978-1-134-75091-7.
- Masetti-Rouault, Maria Grazia; Rouault, Olivier; Wafler, Markus (2000). La Djéziré et l'Euphrate syriens de la protohistoire à la fin du second millénaire av. J.C, Tendances dans l'interprétation historique des données nouvelles, (Subartu). Brepols. ISBN 978-2-50351-063-7.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Halaf culture. |
- Halaf culture The Metropolitan Museum of Art
- Halaf Bowl from Arpachiyah - British Museum