Coțofeni culture
The Coţofeni culture (Serbian: Kocofeni), generally associated with the Usatovo culture,[1][2] was an Early Bronze Age archaeological culture that existed between 3500 and 2500 BC in the mid-Danube area of south-eastern Central Europe.
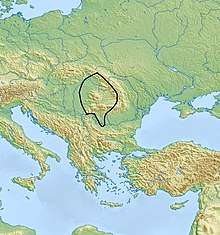 | |
| Geographical range | Romania, Bulgaria, Serbia |
|---|---|
| Period | Chalcolithic to Early Bronze Age |
| Dates | between c. 3500 and 2500 BC |
| Preceded by | Cernavoda culture |
| Followed by | Wietenberg culture |
The first report of a Coţofeni find was made by Fr. Schuster[3] in 1865 from the Râpa Roşie site in Sebeş (present-day Alba County, Romania). Since then this culture has been studied by a number of people to varying degrees. Some of the more prominent contributors to the study of this culture include C. Gooss, K. Benkő, B. Orbán, G. Téglas, K. Herepey, S. Fenichel, Julius Teutsch, Cezar Bolliac, V. Christescu, Teohari Antonescu, and Cristian Popa.
Geographic area
The Coţofeni culture area can be seen from two perspectives, as a fluctuation zone, or in its maximum area of extent. This covers present day Maramureş, some areas in Sătmar, the mountainous and hilly areas of Crişana, Transylvania,[4][5] Banat,[6] Oltenia,[7] Muntenia (not including the North-East), and across the Danube in present-day eastern Serbia and northwestern Bulgaria.[8]
Chronology
Absolute chronology
Bronze Age in Romania Unfortunately, most of the Coţofeni culture chronology is based on just three samples collected at three different Coţofeni sites. Based on these radiocarbon dates, this culture can be placed between roughly 3500 and 2500 BC.[9]
Relative chronology
Cultural synchronisms have been established based on mutual trade relations (visible as imported items) as well as stratigraphic observations. There is an evident synchronicity between:
Coţofeni I - Cernavoda III - Baden A - Spherical Amphorae;
Coţofeni II - Baden B-C Kostolac;[10][11]
Coţofeni III - Kostolac-Vučedol A-B.
Relations with contemporary neighbouring cultures
During the evolution of the Coţofeni culture, there were clearly relationships with other neighbouring cultures. The influence between the Coţofeni and their neighbours the Baden, Kostolac,[12] Vučedol, Globular Amphora culture as well as the Ochre Burial populations was reciprocal. The areas bordering these cultures show cultural traits that have mixed aspects, for example Coţofeni-Baden[13][14] and Coţofeni-Kostolac finds. These finds of mixed aspects suggest a cohabitation between related populations.[15] It also supports the idea of well established trade between cultures.
See also
- Bronze Age in Romania
- Basarabi culture
- Otomani culture
- Pecica culture
- Wietenberg culture
- Prehistory of Transylvania
- Prehistoric Romania
Notes
- Chernykh, Evgenil Nikolaevich (1992-12-03). Ancient Metallurgy in the USSR: The Early Metal Age. CUP Archive. p. 95. ISBN 9780521252577.
- Anthony, David W. (2010-07-26). The Horse, the Wheel, and Language: How Bronze-Age Riders from the Eurasian Steppes Shaped the Modern World. Princeton University Press. p. 361. ISBN 9781400831104.
- Fr. W. Schuster, 1867, Ueber alte Begräbnißstätten bei Mühlbach, în Programm des evangelischen Untergymnasiums zu Mühlbach und die damit verbundenen Lehranstalten Mühlbachs, 1866-1867, p. 3-16.
- H. Ciugudean, 1996, Perioada timpurie a epocii bronzului în centrul şi sud-vestul Transilvaniei, Bibliotheca Thracologica, XIII, Bucharest, 1996.
- Z. Kalmar, 1983, Descoperiri Coţofeni în bazinul someşan (Someşuri, Crasna, Almaş), in ActaMP, VII, 1983, p. 61-68.
- H. Ciugudean, 2000, Eneoliticul final în Transilvania şi Banat: cultura Coţofeni, Bibliotheca Historica et Archaeologica Banatica, Timişoara, 2000.
- D. Berciu, 1939, Arheologia preistorică a Olteniei, Craiova, 1939.
- S. Alexandrov, 1990, Cultura Coţofeni în Bulgaria (Doctoral thesis, advisor. D. Berciu), Bucharest, 1990 (mss.).
- P. Raczky, 1995, New data on the absolute chronology of the Copper Age in the Carpathian Basin, în Neure Daten zur Siedlungsgeschichte und Chronologie der Kupferzeit des Karpatenbeckens, Inventaria Praehistorica Hungarie, Budapest, 1995, p. 51-60.
- P. I. Roman, 1977, Noţiunea de “cultura Kostolac”, in SCIVA, 28, 1977, 3, p. 419-429.
- P. I. Roman, 1980, Der “Kostolac-Kultur”-Begriff nach 35 Jahren, in PZ, 55, 1980, 2, p. 220-227.
- D. Nikolić, 2000, Kostolačka kultura na teritoriji Srbje, Centre for Archaeological Research, 19, Beograd, 2000.
- I. Emödi, 1984, Descoperiri ale culturilor Coţofeni şi Baden în peşterile Igriţa şi Izbândiş, in ActaMN, XXI, 1984, p. 405-431.
- S. Morintz, P. Roman, 1973, Über die Übergangsperiode vom Äneolithikum zur Bronzezeit in Rumänien, in Symposium Badener Kultur, Bratislava, 1973, p.259-295.
- P. I. Roman, 1982, Constituirea noilor grupe etnoculturale de la începutul epocii bronzului, in Carpica, XIV, 1982, p. 39-49.
References
- J. P. Mallory, "Usatavo Culture", Encyclopedia of Indo-European Culture, Fitzroy Dearborn, 1997.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Coțofeni culture. |