Fort Belvoir
Fort Belvoir /ˈbɛlvwɑːr/ is a United States Army installation and a census-designated place (CDP) in Fairfax County, Virginia, United States. It was developed on the site of the former Belvoir plantation, seat of the prominent Fairfax family for whom Fairfax County was named. It was known as Camp A. A. Humphreys from 1917–1935 and Fort Belvoir afterward.
| Fort Belvoir | |
|---|---|
| Fairfax County, Virginia | |
          .png)    Emblems of units stationed at Ft. Belvoir | |
 Fort Belvoir  Fort Belvoir  Fort Belvoir | |
| Coordinates | 38°43′11″N 77°09′16″W |
| Site information | |
| Controlled by | U.S. Army |
| Site history | |
| Built | 1917 |
| Garrison information | |
| Current commander | COL Michael H. Greenberg (garrison commander) |
| Garrison | 29th Infantry Division (Light) 9th Theater Support Command 1st Information Operations Command (Land) 12th Aviation Battalion (MDW) 249th Engineer Battalion (Prime Power) 212th Military Police Detachment (MDW) 55th Ordnance Company (EOD) 75th MP Detachment (CID) Army Intelligence and Security Command Military Intelligence Readiness Command 902nd Military Intelligence Group Defense Logistics Agency Defense Contract Audit Agency Defense Threat Reduction Agency Missile Defense Agency National Geospatial-Intelligence Agency Aerospace Data Facility-East |
| Occupants | 51,000+ employees[1] (Fort Belvoir) 7,100 residents (Fort Belvoir CDP) |
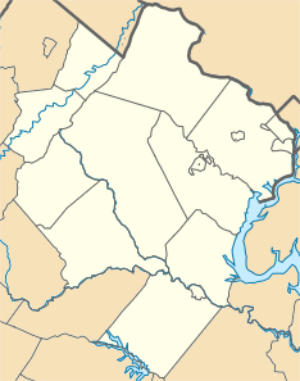
Fort Belvoir is home to a number of significant United States military organizations. With nearly twice as many workers as The Pentagon, Fort Belvoir is the largest employer in Fairfax County. Fort Belvoir comprises three geographically distinct areas: main base, Davison Army Airfield, and Fort Belvoir North.
History
Plantation
The Fort Belvoir site was originally the home of William Fairfax, the cousin and land agent of Thomas Fairfax, 6th Lord Fairfax of Cameron the proprietor of the Northern Neck, which stood on land now part of the base. William Fairfax purchased the property in 1738 when his cousin arranged for him to be appointed customs agent (tax collector) for the Potomac River, and William erected an elegant brick mansion overlooking the river, moving in with his family in 1740. Lord Fairfax came to America in 1747 and stayed less than a year at the Belvoir estate before moving to Greenway Court. The Fairfax family lived at Belvoir for over 30 years, but eldest son (and heir) George William Fairfax sailed to England on business in 1773, never to return. The manor home was destroyed by fire in 1783.
The ruins of the Belvoir Mansion and the nearby Fairfax family grave site are listed on the National Register of Historic Places.
Fort

The post was founded during World War I as Camp A. A. Humphreys, named for American Civil War Union Army general Andrew A. Humphreys, who was also Chief of Engineers. The post was renamed Fort Belvoir in the 1930s at the request of Howard W. Smith, a Congressman from Virginia, in recognition of the Belvoir plantation that once occupied the site.[2] The adjacent United States Army Corps of Engineers Humphreys Engineer Center retains part of the original name.
Camp Humphreys was established in World War I as the U.S. Army Engineers Training School. It served as the post-graduate institution for U.S. Military Academy engineers and a finishing school for engineering troops headed to war.[3] The school, which came to host the Engineer Officer Basic Course, relocated in 1988 from Fort Belvoir to Fort Leonard Wood, in Missouri.[4]
As a result of the 2005 Base Realignment and Closure Commission, a substantial number of personnel were transferred to Fort Belvoir, and others were civilians employed there. All major Washington, D.C.-area National Geospatial-Intelligence Agency (NGA) facilities, including those in Bethesda, MD, Reston, VA, and Washington, D.C. were consolidated at a new facility, the NGA Campus East, situated on the former Engineer Proving Ground site.[5] The cost of the new center was $2.4 billion.[6]
The Army Historical Foundation announced in March 2017, its intent to begin the construction of the National Museum of the United States Army at Fort Belvoir. The museum, set on 84 acres (34 ha), will tell the story of the army since 1775. The 185,000-square-foot (17,200 m2) museum will feature historical galleries, an "interactive Experiential Learning Center" and the Army Theater. There will also be outdoor venues including a Memorial Garden, Amphitheater, Parade Ground, and Army Trail. It is expected to open in late 2019.[7]
Units and agencies
Fort Belvoir serves as the headquarters for the Defense Logistics Agency, the Defense Acquisition University, the Defense Contract Audit Agency, the Defense Technical Information Center, the United States Army Intelligence and Security Command, the United States Army Military Intelligence Readiness Command, the Missile Defense Agency, the Defense Threat Reduction Agency, and the National Geospatial-Intelligence Agency.
Fort Belvoir is home to the Virginia National Guard's 29th Infantry Division (Light) and elements of ten Army Major Commands; nineteen different agencies and direct reporting units of the Department of Army; eight elements of the United States Army Reserve and the Army National Guard; and twenty-six Department of Defense agencies. Also located here are the 249th Engineer Battalion (Prime Power), the Military District of Washington's 12th Aviation Battalion which provides rotary-wing movement to the DoD and Congress, a Marine Corps detachment, a United States Air Force activity, United States Army Audit Agency, and an agency from the Department of the Treasury. In addition, Fort Belvoir is home to National Reconnaissance Office's (NRO) Aerospace Data Facility-East (ADF-E).[8][9]
 Defense Acquisition University Headquarters
Defense Acquisition University Headquarters Senior Officer housing
Senior Officer housing Enlisted housing
Enlisted housing McRee Barracks complex
McRee Barracks complex DeWitt Army Hospital (1957–2011)
DeWitt Army Hospital (1957–2011) Community Hospital
Community Hospital DLA Headquarters
DLA Headquarters Post Chapel
Post Chapel NGA Campus East
NGA Campus East
Demographics

Fort Belvoir is a census-designated place, consisting of the South Post and North Post and excluding Davison Army Airfield, the North Area, and the Southwest Area. Neighboring CDPs are Mount Vernon to the east, Woodlawn and Groveton to the northeast, Hayfield and Kingstowne to the north, and Franconia and Newington to the northwest. As of the census of 2010, there were 7,100 people, 1,777 households, and 1,700 families residing in the CDP. The population density was 809.9 people per square mile (312.7/km²). There were 2,018 housing units at an average density of 230.2/sq mi (88.9/km²). The racial makeup of the CDP was 64.9% White, 21.7% African American, 0.6% Native American, 2.5% Asian, 0.5% Pacific Islander, 2.5% some other race, and 7.3% from two or more races. Hispanic or Latino of any race were 13.2% of the population.[10]
There were 1,777 households, out of which 80.4% had children under the age of 18 living with them, 82.2% were headed by married couples living together, 11.0% had a female householder with no husband present, and 4.3% were non-families. 4.1% of all households were made up of individuals, and 0.1% were someone living alone who was 65 years of age or older. The average household size was 3.80, and the average family size was 3.90.[10]
In the CDP, the population was spread out with 44.7% under the age of 18, 9.4% from 18 to 24, 38.0% from 25 to 44, 7.6% from 45 to 64, and 0.3% who were 65 years of age or older. The median age was 22.6 years. For every 100 females, there were 99.5 males. For every 100 females age 18 and over, there were 96.8 males.[10]
For the period 2010 through 2014, the estimated median annual income for a household in the CDP was $73,942, and the median income for a family was $75,436. Male full-time workers had a median income of $47,188 versus $63,214 for females. The per capita income for the CDP was $22,956. About 2.0% of families and 2.6% of the population were below the poverty line, including 2.9% of those under age 18.[11]
Climate
The climate in this area is characterized by hot, humid summers and generally mild to cool winters. According to the Köppen Climate Classification system, Fort Belvoir has a humid subtropical climate, abbreviated "Cfa" on climate maps.[12]
Name controversy
In 2020, in the wake of the George Floyd protests and petitions to rename U. S. army bases with names related to the Confederacy, it was proposed that the fort be renamed as well. While not named after a Confederate officer, it was renamed after a slave plantation run by a British loyalist. Representative Howard W. Smith, who requested the renaming, was an old-school Southern Democrat who was sympathetic to the then-popular Dunning school of history that revered the Confederacy, and resented a base in Virginia being named after a Union general (A. A. Humphrey). Thus, the name of the base has been criticized as improperly nostalgic for slavery and the antebellum era.[2]
Notable people
- Jackson Miles Abbott, United States Army officer, birdwatcher, painter
- Jesse Burch, actor
- Robert T. Connor, former Borough president of Staten Island
- Wayne Cordeiro, minister
- John Driscoll, actor
- John Ebersole, educator
- Timothy Flanigan, businessman and politician
- Gregory D. Gadson, Soldier, actor, and motivational speaker
- Lauri Hendler, actress
- Larry Izzo, football player and coach
- Kenneth Kronholm, soccer player
- Hal Linden, actor
- Leslie Marx, Olympic fencer
- Patrick Ness, author
- William Oefelein, astronaut
- John Lynch Phillips, astronaut
- David Rabe, playwright
- Ahtyba Rubin, football player
- Rolf Saxon, actor
- John Wasdin, baseball player
- Randy Wiles, baseball player
- Bill Willingham, comic book writer and artist
- Christopher Evan Welch, actor
See also

- Army Gas School
- Accotink Bay Wildlife Refuge
- 911th Engineer Company (Technical Rescue)
- Military District of Washington
- Intelligence and Security Command
- National Geospatial-Intelligence Agency
- DeWitt Army Community Hospital
- Belvoir Federal Credit Union
- SM-1 (former nuclear reactor)
- Tysons Corner Communications Tower
References
- "Fort Belvoir thinks outside the gates for better relations with neighbors (especially drivers)". The Washington Post.
- Seidule, Ty (16 June 2020). "What to rename the Army bases that honor Confederate soldiers". The Washington Post. Retrieved 1 July 2020.
- "At Camp Humphreys, Va". The Sunday Star, Washington, DC, pg 68. 23 June 1918. Newspapers.com. https://www.newspapers.com/image/332637670
- "Engineer School Opens at Fort Leonard Wood". St. Louis Post-Dispatch. 1 June 1988. ProQuest 1492711189.
- NGA Campus East Archived 1 April 2011 at the Wayback Machine, nga.mil
- Davenport, Christian, "Projects' Costs Are Rising", Washington Post, 31 March 2009, p. B4
- Sweeney, Heather. "Construction to Begin on National Army Museum". Military.com. Retrieved 16 March 2017.
- Mission Ground Station Declassification memo, 2008 Archived 16 October 2011 at the Wayback Machine
- "NRO Mission Ground Station Declassification" (PDF). National Reconnaissance Office. 15 October 2008.
- "Profile of General Population and Housing Characteristics: 2010 Demographic Profile Data (DP-1): Fort Belvoir CDP, Virginia". U.S. Census Bureau, American Factfinder. Archived from the original on 13 February 2020. Retrieved 4 October 2016.
- "Selected Economic Characteristics: 2010-2014 American Community Survey 5-Year Estimates (DP03): Fort Belvoir CDP, Virginia". U.S. Census Bureau, American Factfinder. Archived from the original on 13 February 2020. Retrieved 4 October 2016.
- Climate Summary for Fort Belvoir
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Fort Belvoir, Virginia. |
- Fort Belvoir official home page
- Fort Belvoir Installation Overview from ArmyUSA.org