Diagram
A diagram is a symbolic representation of information using visualization techniques. Diagrams have been used since ancient times on walls of caves , but became more prevalent during the Enlightenment.[1] Sometimes, the technique uses a three-dimensional visualization which is then projected onto a two-dimensional surface. The word graph is sometimes used as a synonym for diagram.
Overview
The term "diagram" in its commonly used sense can have a general or specific meaning:
- visual information device : Like the term "illustration", "diagram" is used as a collective term standing for the whole class of technical genres, including graphs, technical drawings and tables.[2]
- specific kind of visual display : This is the genre that shows qualitative data with shapes that are connected by lines, arrows, or other visual links.
In science the term is used in both ways. For example, Anderson (1997) stated more generally: "diagrams are pictorial, yet abstract, representations of information, and maps, line graphs, bar charts, engineering blueprints, and architects' sketches are all examples of diagrams, whereas photographs and video are not".[3] On the other hand, Lowe (1993) defined diagrams as specifically "abstract graphic portrayals of the subject matter they represent".[4]
In the specific sense diagrams and charts contrast with computer graphics, technical illustrations, infographics, maps, and technical drawings, by showing "abstract rather than literal representations of information".[2] The essence of a diagram can be seen as:[2]
- a form of visual formatting devices
- a display that does not show quantitative data (numerical data), but rather relationships and abstract information
- with building blocks such as geometrical shapes connected by lines, arrows, or other visual links.
Or in Hall's (1996) words "diagrams are simplified figures, caricatures in a way, intended to convey essential meaning".[5] These simplified figures are often based on a set of rules. The basic shape according to White (1984) can be characterized in terms of "elegance, clarity, ease, pattern, simplicity, and validity".[2] Elegance is basically determined by whether or not the diagram is "the simplest and most fitting solution to a problem".[6]
Gallery of diagram types
There are at least the following types of diagrams:
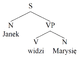
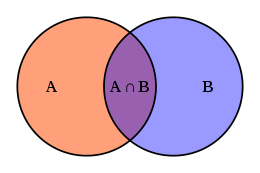
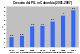
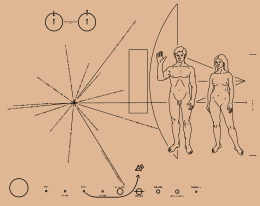
- Logical or conceptual diagrams, which take a collection of items and relationships between them, and express them by giving each item a 2D position, while the relationships are expressed as connections between the items or overlaps between the items, for example:
|
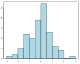
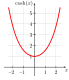
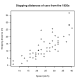
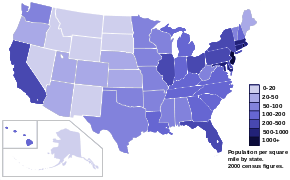
- Quantitative diagrams, which display a relationship between two variables that take either discrete or a continuous ranges of values; for example:
|
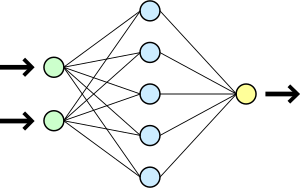
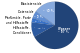
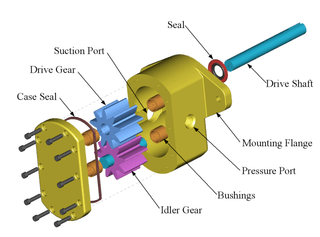
- Schematics and other types of diagrams, for example:
|
Many of these types of diagrams are commonly generated using diagramming software such as Visio and Gliffy. Thousands of diagram techniques exist. Some more examples follow
Diagrams may also be classified according to use or purpose, for example, explanatory and/or how to diagrams.
Specific diagram types
|
|
See also
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to diagrams. |
| Look up diagram in Wiktionary, the free dictionary. |
| Wikiquote has quotations related to: Diagram |
References
- Eddy, Matthew Daniel (2014). "How to See a Diagram: A Visual Anthropology of Chemical Affinity". Osiris. 29: 178–196. doi:10.1086/678093.
- Brasseur, Lee E. (2003). Visualizing technical information: a cultural critique. Amityville, N.Y: Baywood Pub. ISBN 0-89503-240-6.
- Michael Anderson (1997). "Introduction to Diagrammatic Reasoning," at cs.hartford.edu. Retrieved 21 July 2008.
- Lowe, Richard K. (1993). "Diagrammatic information: techniques for exploring its mental representation and processing". Information Design Journal. 7 (1): 3–18. doi:10.1075/idj.7.1.01low.
- Bert S. Hall (1996). "The Didactic and the Elegant: Some Thoughts on Scientific and Technological Illustrations in the Middle Ages and Renaissance". in: B. Braigie (ed.) Picturing knowledge: historical and philosophical problems concerning the use of art in science. Toronto: University of Toronto Press. p.9
- White, Jan V. (1984). Using charts and graphs: 1000 ideas for visual persuasion. New York: Bowker. ISBN 0-8352-1894-5.
Further reading
- Bounford, Trevor (2000). Digital diagrams. New York: Watson-Guptill Publications. ISBN 978-0-8230-1572-6.
- Michael Anderson, Peter Cheng, Volker Haarslev (Eds.) (2000). Theory and Application of Diagrams: First International Conference, Diagrams 2000. Edinburgh, Scotland, UK, September 1–3, 2000. Proceedings.
- Garcia, M. (ed.), (2012) The Diagrams of Architecture. Wiley. Chichester.