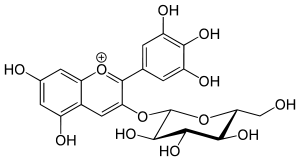
Myrtillin
Myrtillin is an anthocyanin. It is the 3-glucoside of delphinidin. It can be found in all green plants, most abundantly in blackcurrant, blueberry, huckleberry, bilberry leaves[1] and in various myrtles, roselle plants, and Centella asiatica plant. It is also present in yeast and oatmeal. The sumac fruit's pericarp owes its dark red colour to anthocyanin pigments, of which chrysanthemin, myrtillin and delphinidin have yet been identified.[2]
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
(2S,3R,4S,5S,6R)-2-[5,7-dihydroxy-2-(3,4,5-trihydroxyphenyl)chromenylium-3-yl]oxy-6-(hydroxymethyl)oxane-3,4,5-triol chloride | |
Other names
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C21H21ClO12 C21H21O12+, Cl− | |
| Molar mass | 500.83 g/mol (chloride) 465.38 g/mol |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
The various colors, such as red, mauve, purple, violet, and blue in Hydrangea macrophylla are developed from myrtillin complexes with metal ions called metalloanthocyanins.[3]
Metabolism
The enzyme anthocyanin 3-O-glucoside 6''-O-hydroxycinnamoyltransferase produces delphinidin 3-(6-p-coumaroyl)glucoside from myrtillin and p-coumaroyl-CoA in the anthocyanin biosynthesis pathway.[4]
References
- Bilberry Leaf on florahealth.com Archived February 5, 2009, at the Wayback Machine
- Sumac on spicesworld.net
- Yoshida K, Mori M, Kondo T (2009). "Blue flower color development by anthocyanins: from chemical structure to cell physiology". Nat. Prod. Rep. 26 (7): 884–915. doi:10.1039/b800165k. PMID 19554240.
- "Delphinidin 3-(6-p-coumaroyl)glucoside synthesis reaction on www.kegg.jp". Kegg.jp. Retrieved 2013-04-09.