Coal County, Oklahoma
Coal County is a county located in the U.S. state of Oklahoma. As of the 2010 census, the population was 5,925.[1] Its county seat is Coalgate.[2]
Coal County | |
|---|---|
 Park in Coalgate | |
 Location within the U.S. state of Oklahoma | |
 Oklahoma's location within the U.S. | |
| Coordinates: 34°36′N 96°18′W | |
| Country | |
| State | |
| Founded | 1907 |
| Seat | Coalgate |
| Largest city | Coalgate |
| Area | |
| • Total | 521 sq mi (1,350 km2) |
| • Land | 517 sq mi (1,340 km2) |
| • Water | 4.7 sq mi (12 km2) 0.9%% |
| Population | |
| • Estimate (2018) | 5,520 |
| • Density | 11/sq mi (4/km2) |
| Time zone | UTC−6 (Central) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC−5 (CDT) |
| Congressional district | 2nd |
History
Coal County was formed at statehood from the former Shappaway County (later renamed Atoka County) of the Pushmataha District of the Choctaw Nation in Indian Territory. A 3.5 miles (5.6 km) strip of Coal County was taken from the Pontotoc District of the Chickasaw Nation. Initially, the Oklahoma legislature named Lehigh as the county seat, but a special election held in 1908 resulted in the citizens choosing Coalgate as the county seat. Lehigh tried to sue because more people voted than were registered, but no court would hear the case.[3]
Mining became a mainstay of the county's economy during the 1870s. The first coal mine opened on Chief Allen Wright's land. The industry activity peaked between 1910 and 1916 but declined sharply after World War I. Many of the mines closed by 1921, due to the refusal of mining companies of the area to unionize. Some mines reopened during World War II, but these closed by 1958, because of the rising cost of refining sulfur out of the coal mined.[3]
Agriculture replaced mining as the main economic activity of the county. Even this business encountered severe difficulty in 1921–3 when a boll weevil infestation wiped out the cotton crop. All five banks in the county failed as a result.[4]
Geography
Coal County is in southeastern Oklahoma, in a 10-county area designated for tourism purposes by the Oklahoma Department of Tourism and Recreation as Choctaw Country.[5] According to the U.S. Census Bureau, the county has a total area of 521 square miles (1,350 km2), of which 517 square miles (1,340 km2) is land and 4.7 square miles (12 km2) (0.9%) is water.[6] It is the fifth-smallest county in Oklahoma by area. The eastern part of the county lies in the Ouachita Mountains, while the western part has open prairie and lies in the Sandstone Hills physiographic region. The county is drained by the Clear Boggy and Muddy Boggy creeks.[3]
Major highways



- State Highway 43
- State Highway 48
Adjacent counties
- Hughes County (north)
- Pittsburg County (northeast)
- Atoka County (southeast)
- Johnston County (southwest)
- Pontotoc County (west)
Demographics
| Historical population | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Census | Pop. | %± | |
| 1910 | 15,817 | — | |
| 1920 | 18,406 | 16.4% | |
| 1930 | 11,521 | −37.4% | |
| 1940 | 12,811 | 11.2% | |
| 1950 | 8,056 | −37.1% | |
| 1960 | 5,546 | −31.2% | |
| 1970 | 5,525 | −0.4% | |
| 1980 | 6,041 | 9.3% | |
| 1990 | 5,780 | −4.3% | |
| 2000 | 6,031 | 4.3% | |
| 2010 | 5,925 | −1.8% | |
| Est. 2018 | 5,520 | [7] | −6.8% |
| U.S. Decennial Census[8] 1790-1960[9] 1900-1990[10] 1990-2000[11] 2010-2013[1] | |||
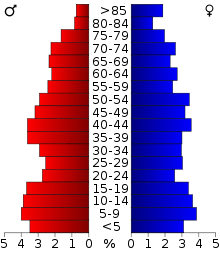
As of the 2010 United States Census, there were 5,295 people, 2,350 households, and 1,604 families residing in the county.[12] There were 2,810 housing units.[12] The racial makeup of the county was 74.3% White, 0.5% Black or African American, 16.7% Native American, 0.2% Asian, 0.5% from other races, and 7.8% from two or more races.[12] 2.6% of the population were Hispanic or Latino of any race.[12]
There were 2,350 households out of which 27.7% had children under the age of 18 living with them, 50.8% were married couples living together, 12.1% had a female householder with no husband present, and 31.7% were non-families.[12] 28.1% of all households were made up of individuals and 14.6% had someone living alone who was 65 years of age or older.[12] The average household size was 2.50 and the average family size was 3.06.[12]
In the county, the population was spread out with 25.5% under the age of 18, 7.2% from 18 to 24, 21.7% from 25 to 44, 27.8% from 45 to 64, and 17.8% who were 65 years of age or older.[13] The median age was 41.0 years.[13] For every 100 females there were 97.7 males.[13] For every 100 females age 18 and over, there were 91.5 males.[13]
According to the 2013 American Community Survey, the median income for a household in the county was $34,867, and the median income for a family was $44,888.[14] Male full-time, year round workers had a median income of $36,442 compared to $26,450 for female full-time, year round workers.[14] The per capita income for the county was $19,752.[14] About 15.8% of families and 21.6% of the population were below the poverty line, including 35.9% of those under age 18 and 15.7% of those age 65 or over.[14]
According to the 2000 census, 94.6% spoke English, 3.0% Spanish, 1.1% German and 1.1% Choctaw as their first language.
Politics
Coal County is in many respects typical of Oklahoma politics: once mainly Democratic, it has become extremely strongly Republican in presidential elections, although even today most voters identify as Democrats. Coal County was not won at the presidential level by a Republican until Richard Nixon did so in 1972.[15] Apart from the 2000 election Republicans have never won Coal County without cleansweeping all seventy-seven counties in the state (as they did against George McGovern and in every election since 2004). In two national Republican landslides Coal County has seen extremely narrow Democratic victories: James M. Cox won the county by twenty-four votes in 1920 and Walter Mondale by twenty-five votes in 1984. The county swung 41 points Republican in the 2008 presidential election, the largest swing of any county (of the more than 3,000 counties in the U.S.) towards either party seen in the entire election.[16]
| Voter Registration and Party Enrollment as of January 15, 2019[17] | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Party | Number of Voters | Percentage | |||
| Democratic | 2,756 | 70.94% | |||
| Republican | 757 | 19.49% | |||
| Others | 372 | 9.58% | |||
| Total | 3,885 | 100% | |||
| Year | Republican | Democratic | Third parties |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2016 | 79.1% 1,898 | 17.1% 411 | 3.8% 90 |
| 2012 | 72.5% 1,710 | 27.5% 649 | |
| 2008 | 73.6% 1,672 | 26.4% 600 | |
| 2004 | 53.7% 1,396 | 46.3% 1,203 | |
| 2000 | 50.6% 1,196 | 48.6% 1,148 | 0.8% 18 |
| 1996 | 32.3% 734 | 52.9% 1,205 | 14.8% 337 |
| 1992 | 25.5% 714 | 51.7% 1,448 | 22.8% 638 |
| 1988 | 39.3% 891 | 60.1% 1,365 | 0.6% 14 |
| 1984 | 49.1% 1,259 | 50.1% 1,284 | 0.8% 21 |
| 1980 | 38.1% 926 | 59.3% 1,442 | 2.6% 63 |
| 1976 | 30.0% 769 | 69.1% 1,774 | 0.9% 23 |
| 1972 | 67.1% 1,461 | 31.2% 680 | 1.7% 38 |
| 1968 | 29.6% 669 | 42.7% 963 | 27.7% 625 |
| 1964 | 30.9% 721 | 69.1% 1,613 | |
| 1960 | 44.5% 1,019 | 55.5% 1,269 | |
| 1956 | 36.6% 920 | 63.4% 1,596 | |
| 1952 | 38.7% 1,106 | 61.3% 1,755 | |
| 1948 | 17.9% 464 | 82.1% 2,124 | |
| 1944 | 27.9% 760 | 71.9% 1,959 | 0.2% 5 |
| 1940 | 32.5% 1,148 | 67.2% 2,377 | 0.3% 10 |
| 1936 | 19.1% 603 | 80.7% 2,550 | 0.2% 7 |
| 1932 | 9.7% 300 | 90.3% 2,788 | |
| 1928 | 42.8% 1,283 | 56.1% 1,681 | 1.1% 32 |
| 1924 | 25.2% 800 | 55.7% 1,772 | 19.1% 607 |
| 1920 | 43.6% 1,744 | 44.2% 1,768 | 12.1% 485 |
| 1916 | 29.1% 824 | 50.1% 1,418 | 20.8% 588 |
| 1912 | 25.3% 571 | 49.2% 1,109 | 25.5% 574 |
| 1908 | 33.5% 722 | 42.1% 906 | 24.3% 524 |
Communities
Cities
- Coalgate (county seat)
- Centrahoma
- Lehigh
- Tupelo
Census-designated place
Other unincorporated communities
NRHP sites
The following sites in Coal County are listed on the National Register of Historic Places:
- Benjamin Franklin Smallwood House, Lehigh
- Coalgate School Gymnasium-Auditorium, Coalgate
- Keel Creek Bridge, Coalgate
- Merchants National Bank Building, Lehigh
- United States Post Office Coalgate, Coalgate
References
- "State & County QuickFacts". United States Census Bureau. Archived from the original on July 8, 2011. Retrieved November 8, 2013.
- "Find a County". National Association of Counties. Archived from the original on 2011-05-31. Retrieved 2011-06-07.
- Milligan, James C. "Coal County," Encyclopedia of Oklahoma History and Culture, 2009. Accessed March 28, 2015.
- "Focus on Coal County." Archived 2010-10-12 at the Wayback Machine Oklahoma Ad Valorem Forum. Oklahoma Tax Commission. March 2010. Retrieved February 21, 2010.
- "Counties & Regions". Oklahoma Tourism and Recreation Department (Travel Promotion Division). Retrieved February 5, 2019.
- "2010 Census Gazetteer Files". United States Census Bureau. August 22, 2012. Retrieved February 19, 2015.
- "Population and Housing Unit Estimates". Retrieved December 28, 2019.
- "U.S. Decennial Census". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved February 19, 2015.
- "Historical Census Browser". University of Virginia Library. Retrieved February 19, 2015.
- Forstall, Richard L., ed. (March 27, 1995). "Population of Counties by Decennial Census: 1900 to 1990". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved February 19, 2015.
- "Census 2000 PHC-T-4. Ranking Tables for Counties: 1990 and 2000" (PDF). United States Census Bureau. April 2, 2001. Retrieved February 19, 2015.
- United States Census Bureau. "DP-1 Profile of General Population and Housing Characteristics: 2010 - 2010 Demographic Profile Data - Coal County, Oklahoma," Archived 2020-02-13 at Archive.today American Fact Finder, Accessed July 5, 2015.
- United States Census Bureau. "QT-P1 Age Groups and Sex: 2010 2010 Census Summary File 1 - Coal County, Oklahoma," Archived 2020-02-13 at Archive.today American Fact Finder, Accessed July 5, 2015.
- United States Census Bureau. "DP03 Selected Economic Characteristics: 2009-2013 American Community Survey 5-Year Estimates - Coal County, Oklahoma," Archived 2020-02-13 at Archive.today American Fact Finder, Accessed July 5, 2015.
- Mendedez, Albert J.; The Geography of Presidential Elections in the United States, 1868-2004; pp. 281-283 ISBN 0786422173
- Maxwell, Brandt. "Bonus List". www.geographylists.com. Retrieved 2018-03-28.
- "Oklahoma Registration Statistics by County" (PDF). OK.gov. January 15, 2019. Retrieved 2019-02-27.
- Leip, David. "Dave Leip's Atlas of U.S. Presidential Elections". uselectionatlas.org. Retrieved 2018-03-28.