Brown County, Ohio
Brown County is a county in the U.S. state of Ohio. As of the 2010 United States Census, the population was 44,846.[1] The county seat is Georgetown.[2] The county was created in 1818[3] and is named for Major General Jacob Brown, an officer in the War of 1812 who was wounded at the Battle of Lundy's Lane.[4]
Brown County | |
|---|---|
 | |
 Seal | |
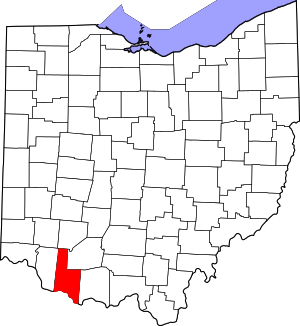 Location within the U.S. state of Ohio | |
 Ohio's location within the U.S. | |
| Coordinates: 38°56′N 83°52′W | |
| Country | |
| State | |
| Founded | 1 March 1818 |
| Named for | General Jacob Brown |
| Seat | Georgetown |
| Largest village | Georgetown |
| Area | |
| • Total | 493 sq mi (1,280 km2) |
| • Land | 490 sq mi (1,300 km2) |
| • Water | 3.4 sq mi (9 km2) 0.7%% |
| Population | |
| • Estimate (2019) | 43,432 |
| • Density | 91.5/sq mi (35.3/km2) |
| Time zone | UTC−5 (Eastern) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC−4 (EDT) |
| Congressional district | 2nd |
| Website | www |
Brown County is part of the Cincinnati-Middletown, OH-KY-IN Metropolitan Statistical Area.
History
After the American Revolutionary War, the federal government established the Northwest Territory, a large area which encompassed the present county. In 1790 several counties were established, Hamilton among them. In 1797, a portion of Hamilton was partitioned off to create Adams County, and in 1800 another portion was partitioned to create Clermont. This lasted for two decades, during which the area north of the Ohio River attracted settlers.
Among the early settlers was Jesse Root Grant (father of future US President Grant), who built a home and set up a tannery in the future Georgetown area, where young Hiram Ulysses (later changed to Ulysses S.) spent his youth.[5]
On 1 March 1818, portions of Adams and Clermont counties were partitioned off to create Brown County, with Georgetown as its seat. The boundaries of the county were altered in 1874, when a portion was moved to Highland County; they have remained intact since then.[3]
Brown County was said to be the place of origin of the White Burley type of tobacco, grown in 1864 by George Webb and Joseph Fore on the farm of Captain Frederick Kautz near Higginsport, with seed from Bracken County, Kentucky. He noticed it yielded a different type of light leaf shaded from white to yellow, and cured differently. By 1866, he harvested 20,000 pounds of Burley tobacco and sold it in 1867 at the St. Louis Fair for $58 per hundred pounds. By 1883, the principal market for this tobacco was Cincinnati, but it was grown throughout central Kentucky and Middle Tennessee.[6] Later the type became referred to as burley tobacco, and it was air-cured.
Geography
Brown County lies on the south line of the state of Ohio. Its south border abuts the north border of the state of Kentucky across the Ohio River. The Ohio flows westward along the county's south line. White Oak Creek flows southward through the lower part of southwest Brown County, discharging into the Ohio at Higginsport; Straight Creek flows southwestward through the lower central part of the county, discharging into the Ohio two miles (3 km) east of Higginsport. Eagle Creek flows southerly through the lower eastern part of the county, discharging into the Ohio east of Ripley. The east fork of the Little Miami River flows southwestward through the upper part of the county, entering Clermont County near Marathon.
The terrain of Brown County consists of low rolling hills, carved by drainages. All available areas are devoted to agriculture.[7] The highest point (at 1,089' or 332 m ASL) in Brown County is a point on Ash Ridge, 9 miles (15 km) southeast of Lake Waynoka.[8] The county has an area of 493 square miles (1,280 km2), of which 490 square miles (1,300 km2) is land and 3.4 square miles (8.8 km2) (0.7%) is water.[9]
Main highways
- US-50
- US-52
- US-62
- US-68
- OH-32
- OH-125
- OH-131
- OH-134
- OH-221
- OH-286
- OH-353
- OH-505
- OH-756
- OH-763
- OH-774
Adjacent counties
- Clinton County - north
- Highland County - northeast
- Adams County - east
- Mason County, Kentucky - southeast
- Bracken County, Kentucky - southwest
- Clermont County - west
Lakes
- Grant Lake
- Lake Lorelei
- Lake Waynoka
Protected areas[7]
- Della Gates and Charles Bott Wildlife Area
- Grant Lake Wildlife Area
- Indian Creek Wildlife Area
- Eagle Creek Wildlife Area
Demographics
| Historical population | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Census | Pop. | %± | |
| 1820 | 13,356 | — | |
| 1830 | 17,867 | 33.8% | |
| 1840 | 22,715 | 27.1% | |
| 1850 | 27,332 | 20.3% | |
| 1860 | 29,958 | 9.6% | |
| 1870 | 30,802 | 2.8% | |
| 1880 | 32,911 | 6.8% | |
| 1890 | 29,899 | −9.2% | |
| 1900 | 28,237 | −5.6% | |
| 1910 | 24,832 | −12.1% | |
| 1920 | 22,621 | −8.9% | |
| 1930 | 20,148 | −10.9% | |
| 1940 | 21,638 | 7.4% | |
| 1950 | 22,221 | 2.7% | |
| 1960 | 25,178 | 13.3% | |
| 1970 | 26,635 | 5.8% | |
| 1980 | 31,920 | 19.8% | |
| 1990 | 34,966 | 9.5% | |
| 2000 | 42,285 | 20.9% | |
| 2010 | 44,846 | 6.1% | |
| Est. 2019 | 43,432 | [10] | −3.2% |
| US Decennial Census[11] 1790-1960[12] 1900-1990[13] 1990-2000[14] 2010-2019[1] | |||
2010 census
As of the 2010 United States Census, there were 44,846 people, 17,014 households, and 12,379 families in the county.[15] The population density was 91.5/sqmi (35.3/km²). There were 19,301 housing units at an average density of 39.4/sqmi (15.2/km²).[16] The racial makeup of the county was 97.5% white, 0.9% black or African American, 0.2% Asian, 0.2% American Indian, 0.2% from other races, and 1.0% from two or more races. Those of Hispanic or Latino origin made up 0.6% of the population.[15] In terms of ancestry, 27.0% were German, 14.2% were Irish, 12.5% were American, and 9.7% were English.[17]
Of the 17,014 households, 34.5% had children under the age of 18 living with them, 55.7% were married couples living together, 11.2% had a female householder with no husband present, 27.2% were non-families, and 22.6% of all households were made up of individuals. The average household size was 2.60 and the average family size was 3.02. The median age was 39.9 years.[15]
The median income for a household in the county was $45,887 and the median income for a family was $54,184. Males had a median income of $39,049 versus $30,890 for females. The per capita income for the county was $20,167. About 9.0% of families and 12.4% of the population were below the poverty line, including 18.2% of those under age 18 and 8.4% of those age 65 or over.[18]
2000 census
As of the 2000 United States Census,[19] there were 42,285 people, 15,555 households, and 11,790 families in the county. The population density was 86.3/sqmi (33.3/km²). There were 17,193 housing units at an average density of 35.1/sqmi (13.5/km²). The racial makeup of the county was 98.08% White, 0.92% Black or African American, 0.18% Native American, 0.13% Asian, 0.08% from other races, and 0.60% from two or more races. 0.44% of the population were Hispanic or Latino of any race. 29.5% were of American, 28.2% German, 10.7% English and 10.2% Irish ancestry.
There were 15,555 households out of which 37.10% had children under the age of 18 living with them, 61.30% were married couples living together, 10.00% had a female householder with no husband present, and 24.20% were non-families. 20.20% of all households were made up of individuals and 8.50% had someone living alone who was 65 years of age or older. The average household size was 2.69 and the average family size was 3.09.
The county population contained 27.60% under the age of 18, 8.10% from 18 to 24, 30.30% from 25 to 44, 22.40% from 45 to 64, and 11.60% who were 65 years of age or older. The median age was 35 years. For every 100 females there were 96.80 males. For every 100 females age 18 and over, there were 94.80 males.
The county's median household income was $38,303, and the median family income was $43,040. Males had a median income of $32,647 versus $22,483 for females. The per capita income for the county was $17,100. About 8.80% of families and 11.60% of the population were below the poverty line, including 15.20% of those under age 18 and 9.40% of those age 65 or over.
Politics
Prior to 1928, Brown County was Democratic Party stronghold in presidential elections. 1928 to 1988 saw the county become a swing county, backing the national winner in all but 1944 & 1960. It has since become a Republican Party stronghold, with Jimmy Carter in 1976 representing the last Democratic win of the county at the presidential level.
| Year | Republican | Democratic | Third parties |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2016 | 74.0% 14,573 | 22.1% 4,353 | 3.8% 756 |
| 2012 | 61.5% 11,916 | 36.7% 7,107 | 1.9% 369 |
| 2008 | 60.5% 12,192 | 37.2% 7,503 | 2.3% 471 |
| 2004 | 63.6% 12,647 | 35.9% 7,140 | 0.5% 105 |
| 2000 | 61.0% 10,027 | 36.4% 5,972 | 2.6% 430 |
| 1996 | 45.4% 6,970 | 41.1% 6,318 | 13.5% 2,078 |
| 1992 | 38.9% 5,912 | 36.5% 5,540 | 24.6% 3,734 |
| 1988 | 59.4% 7,539 | 39.8% 5,047 | 0.9% 112 |
| 1984 | 66.3% 8,221 | 32.8% 4,067 | 0.9% 116 |
| 1980 | 53.5% 6,065 | 41.5% 4,706 | 5.0% 566 |
| 1976 | 44.9% 4,549 | 53.6% 5,432 | 1.4% 145 |
| 1972 | 62.7% 6,772 | 34.9% 3,770 | 2.4% 262 |
| 1968 | 44.3% 4,700 | 34.0% 3,610 | 21.7% 2,307 |
| 1964 | 35.9% 3,904 | 64.1% 6,983 | |
| 1960 | 55.7% 6,461 | 44.3% 5,133 | |
| 1956 | 56.7% 5,690 | 43.3% 4,346 | |
| 1952 | 53.9% 5,635 | 46.1% 4,828 | |
| 1948 | 43.2% 3,931 | 56.5% 5,140 | 0.3% 28 |
| 1944 | 51.4% 5,024 | 48.6% 4,743 | |
| 1940 | 49.3% 5,477 | 50.8% 5,644 | |
| 1936 | 40.7% 4,511 | 57.0% 6,316 | 2.4% 261 |
| 1932 | 36.9% 3,930 | 61.9% 6,601 | 1.2% 131 |
| 1928 | 62.1% 5,681 | 37.4% 3,422 | 0.6% 52 |
| 1924 | 43.1% 3,616 | 49.1% 4,120 | 7.9% 663 |
| 1920 | 42.8% 4,009 | 56.7% 5,317 | 0.5% 44 |
| 1916 | 35.7% 2,227 | 63.4% 3,959 | 0.9% 56 |
| 1912 | 28.3% 1,650 | 59.1% 3,451 | 12.6% 735 |
| 1908 | 38.0% 2,638 | 61.1% 4,242 | 0.8% 58 |
| 1904 | 42.4% 2,730 | 55.8% 3,590 | 1.8% 118 |
| 1900 | 39.4% 2,991 | 57.9% 4,397 | 2.7% 206 |
| 1896 | 41.1% 3,170 | 58.1% 4,485 | 0.8% 61 |
| 1892 | 40.3% 2,865 | 55.9% 3,975 | 3.9% 277 |
| 1888 | 41.0% 3,055 | 56.8% 4,237 | 2.3% 169 |
| 1884 | 42.8% 3,226 | 56.6% 4,272 | 0.7% 49 |
| 1880 | 42.4% 3,184 | 57.5% 4,324 | 0.2% 11 |
| 1876 | 42.0% 2,956 | 57.8% 4,068 | 0.2% 16 |
| 1872 | 43.6% 2,593 | 56.2% 3,337 | 0.2% 12 |
| 1868 | 45.6% 2,715 | 54.3% 3,238 | |
| 1864 | 47.9% 2,702 | 52.0% 2,929 | |
| 1860 | 38.6% 2,105 | 55.2% 3,006 | 6.0% 329 |
| 1856 | 36.3% 1,785 | 54.9% 2,700 | 8.7% 428 |
Government
Brown County has three County Commissioners who oversee the various County departments. Commissioners (as of Nov. 2018) are:[21]
- Barry Woodruff (R)
- Daryll Gray (R)
- Tony Applegate (R)[22]
Media
Radio
- WRAC C103 Country 103.1 FM (West Union)
- WAOL 99.5 (Ripley)
Communities
Villages
- Aberdeen
- Fayetteville
- Georgetown (county seat)
- Hamersville
- Higginsport
- Mount Orab
- Ripley
- Russellville
- Sardinia
Census-designated places
Unincorporated communities
- Arnheim
- Ash Ridge
- Bardwell[7]
- Boudes Ferry[27]
- Brownstown
- Centerville[7]
- Chasetown
- Crosstown
- Decatur
- Eastwood
- Ellsberry[7]
- Feesburg
- Fincastle
- Fivemile[7]
- Greenbush
- Hiett
- Levanna
- Locust Ridge
- Macon[7]
- Maple[7]
- Neals Corner[7]
- Neel[7]
- New Harmony
- New Hope
- Redoak
- Upper Fivemile[7]
- Vera Cruz
- Wahlsburg
- White Oak
- White Oak Valley
Townships
References
- "State & County QuickFacts". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved April 19, 2020.
- "Find a County". National Association of Counties. Archived from the original on May 31, 2011. Retrieved June 7, 2011.
- "Ohio: Individual County Chronologies". Ohio Atlas of Historical County Boundaries. The Newberry Library. 2007. Retrieved February 12, 2015.
- Taylor, William Alexander (1899). Ohio Statesmen and Annals of Progress. Press of the Westbote Company. p. 243.
- White, Rodald C., 2016 A life of Ulysses S. Grant, p. 11
- J.M. Stoddart, Encyclopædia Britannica. American Supplement (Stoddart's Encyclopaedia Americana: A Dictionary of Arts, Sciences, and General Literature, and Companion to the Encyclopædia Britannica. (9th ed.) and to All Other Encyclopaedias, Volume 1), 1883, p. 123, accessed 5 February 2011
- Brown County OH - Google Maps (accessed 9 June 2019)
- Ash Ridge Benchmark, Ohio (PeakBagger.com) Accessed 9 June 2019)
- "2010 Census Gazetteer Files". US Census Bureau. August 22, 2012. Archived from the original on May 4, 2014. Retrieved February 7, 2015.
- "Population and Housing Unit Estimates". Retrieved March 26, 2020.
- "US Decennial Census". US Census Bureau. Retrieved February 7, 2015.
- "Historical Census Browser". University of Virginia Library. Retrieved February 7, 2015.
- Forstall, Richard L., ed. (March 27, 1995). "Population of Counties by Decennial Census: 1900 to 1990". US Census Bureau. Retrieved February 7, 2015.
- "Census 2000 PHC-T-4. Ranking Tables for Counties: 1990 and 2000" (PDF). US Census Bureau. April 2, 2001. Retrieved February 7, 2015.
- "Profile of General Population and Housing Characteristics: 2010 Demographic Profile Data". US Census Bureau. Archived from the original on February 13, 2020. Retrieved December 27, 2015.
- "Population, Housing Units, Area, and Density: 2010 - County". US Census Bureau. Archived from the original on February 13, 2020. Retrieved December 27, 2015.
- "Selected Social Characteristics in the US – 2006-2010 American Community Survey 5-Year Estimates". US Census Bureau. Archived from the original on February 13, 2020. Retrieved December 27, 2015.
- "Selected Economic Characteristics – 2006-2010 American Community Survey 5-Year Estimates". US Census Bureau. Archived from the original on February 13, 2020. Retrieved December 27, 2015.
- "U.S. Census website". US Census Bureau. Retrieved January 31, 2008.
- Leip, David. "Atlas of US Presidential Elections". uselectionatlas.org.
- "Brown County Commissioners". Brown County web Portal. Retrieved June 9, 2019.
- "Applegate gets the nod for County Commissioner". Brown County News Democrat. June 11, 2012. Archived from the original on January 29, 2013. Retrieved October 3, 2012.
- "News Democrat". www.newsdemocrat.com.
- "The Brown County Press". The Brown County Press.
- https://web.archive.org/web/20070514033553/http://www.countyfreepress.com/
- "The Ripley Bee –". www.ripleybee.com.
- Northern Kentucky Views: Boudes Ferry (accessed 9 June 2019)
- OH Township List
.svg.png)