2022 French presidential election
The first round of the 2022 French presidential election will be held between 8 and 23 April 2022, with the second round held two weeks after the first. Should no candidate win a majority of the vote in the first round, a runoff will be held between the top two candidates two weeks later. The incumbent president is Emmanuel Macron of La République En Marche! (LREM), who won the 2017 presidential election and whose term lasts until 13 May 2022.
| |||
| Opinion polls | |||
|
| |||
| |||
Background
Under Article 7 of the Constitution of France, the President of the Republic is elected to a five-year term in a two-round election. If no candidate secures an absolute majority of votes in the first round, a second round is held two weeks later between the two candidates who received the most votes.[1] According to the Constitution of France, the first round of the presidential election must be held between 20 and 35 days before the transition of power at the end of the five-year term of the incumbent officeholder. As Emmanuel Macron took office on 14 May 2017, the transition of power is expected to take place on 13 May 2022. Correspondingly, the first round of the presidential election will be held between 8 and 23 April 2022, with the second round held two weeks after the first.[2]
To be listed on the first-round ballot, candidates need to secure 500 signatures (often referred to as parrainages in French) from national or local elected officials from at least 30 different departments or overseas collectivities, with no more than a tenth of these signatories from any single department.[3]
Campaign
Marine Le Pen, the president of the National Rally, announced on 16 January 2020 that she was running in the election. She previously ran in the 2012 presidential election and the 2017 presidential election as the candidate for the same party, then called the National Front. She came third in 2012 with 17.9% of the vote in the first round and second in 2017 with 21.3% of the vote in the first round and 33.9% of the vote in the second round. Le Pen was elected to the National Assembly in the 2017 legislative election.[4]
Jean Lassalle, who ran in the 2017 presidential election under the Résistons! banner, coming in seventh place with 1.2% of the vote, announced that he would run again if he was healthy enough and could raise funds.[5] In 2020, Joachim Son-Forget, a radiologist who was elected to the National Assembly for La République En Marche! in 2017, formed a new political party called Valeur absolue and announced his intention to enter the race for the presidency. He had resigned from the LREM group after posting tweets in 2018 that were deemed sexist; he joined the UDI and Independents group in 2019 before resigning his membership later that year.[6]
Candidates
Declared
| Candidate name and political party |
Political office(s) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Marine Le Pen (52) National Rally |
_01_cropped.jpg) |
President of the National Rally (since 2011) Deputy for the 11th constituency of Pas-de-Calais (since 2017) MEP for North-West France (2004–2017) | |
| Jean Lassalle (65) Résistons! |
.jpg) |
Deputy for the 4th constituency of Pyrénées-Atlantiques (since 2002) Mayor of Lourdios-Ichère (1977–2017) | |
| Joachim Son-Forget (37) Valeur absolue |
.jpg) |
Deputy for the 6th constituency of French residents overseas (since 2017) | |
Potential
Lutte Ouvrière
- Nathalie Arthaud, spokeswoman of Lutte Ouvrière (LO), candidate in the 2012 and 2017 presidential elections[7]
New Anticapitalist Party
- Olivier Besancenot, candidate of the New Anticapitalist Party (NPA) in the 2002 and 2007 presidential elections[8]
La France Insoumise
- Jean-Luc Mélenchon, member of the National Assembly for Bouches-du-Rhône's 4th constituency since 2017 and candidate in the 2012 and 2017 presidential elections[9]
- François Ruffin, member of the National Assembly for Somme's 1st constituency since 2017, journalist and documentary filmmaker[10][11]
French Communist Party
- Fabien Roussel, national secretary of the French Communist Party since 2018[7]
Génération.s
- Benoît Hamon, regional councillor of Île-de-France since 2015, Minister of National Education, Higher Education and Research in 2014 and candidate in the 2017 presidential election with the Socialist Party[12]
Socialist Party
- Bernard Cazeneuve, Prime Minister of France from 2016 to 2017 and Minister of the Interior from 2014 to 2016[13]
- Stéphane Le Foll, Mayor of Le Mans since 2018, member of the National Assembly for Sarthe's 4th constituency from 2017 to 2018 and 2012, Minister of Agriculture, Agrifood and Forestry from 2012 to 2017 and Government Spokesman from 2014 to 2017[14]
- Najat Vallaud-Belkacem, Minister of National Education, Higher Education and Research from 2014 to 2017[14]
In a document dated 17 October 2017, the Socialist Party (PS) noted that the financing of the 2022 presidential campaign was not assured despite "economic restructuring" but still planned to spend €12,000,000, the maximum permitted before the first round. According to the report, the leadership of the party seriously considered the possibility of not presenting a socialist candidate in 2022.[15]
Europe Écologie Les Verts
- Yannick Jadot, Member of the European Parliament since 2009[16]
- Julien Bayou, EELV National Secretary since 2019
- Éric Piolle, mayor of Grenoble since 2014
La République En Marche!
- Emmanuel Macron, incumbent President of the French Republic since 2017, eligible for a second term[17]
Union of Democrats and Independents
- Jean-Christophe Lagarde, member of the National Assembly for Seine-Saint-Denis's 5th constituency since 2002[18]
Libres
- Valérie Pécresse, president of the regional council of Île-de-France since 2015[19]
The Republicans
- François Baroin, Mayor of Troyes since 1995, Senator for Aube from 2014 to 2017 and member of the National Assembly for Aube's 3rd constituency from 2012 to 2014, 2007 to 2010, 1997 to 2005 and 1993 to 1995[20]
- Nathalie Kosciusko-Morizet, member of the National Assembly for Essonne's 4th constituency from 2002 to 2007 and 2012 to 2017[21]
- Laurent Wauquiez, president of the regional council of Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes since 2016 and president of The Republicans from 2017 to 2019[22]
- Bruno Retailleau, president of The Republicans group (Senate) since 2014 and former president of President of the Regional Council of Pays de la Loire from 2015 to 2017[23]
Following the 2017 presidential election, The Republicans (LR) sent its members a questionnaire on the topic of the "refoundation" of the party; of the 40,000 respondents, 70% voted against an open primary to determine the party nominee.[24]
Debout la France
- Nicolas Dupont-Aignan, president of Debout la France, member of the National Assembly for Essonne's 8th constituency and candidate in the 2012 and 2017 presidential elections[25]
Popular Republican Union
- François Asselineau, president of the Popular Republican Union since 2007 and candidate in the 2017 presidential election[26]
Others
- Xavier Bertrand, president of the regional council of Hauts-de-France since 2016[27][28]
- Nicolas Hulot, Minister for the Ecological and Inclusive Transition from 2017 to 2018 and candidate in the 2011 ecologist primary[29]
- Ségolène Royal, Minister of Ecology from 2014 to 2017 and candidate in the 2007 presidential election with the Socialist Party that she left in 2017[30]
- Éric Zemmour, essayist and journalist[31]
Declined
- Jacques Cheminade, candidate of Solidarity and Progress (S&P) in the 1995, 2012, and 2017 presidential elections[32]
- François Fillon, Prime Minister from 2007 to 2012 and candidate of The Republicans (LR) in the 2017 presidential election[33]
- Anne Hidalgo, Mayor of Paris since 2014[34]
- Gérard Larcher, president of the Senate[35][36]
- Bruno Le Maire, Minister of Economy and Finance since 2017 and candidate in the 2016 primary of the right and centre[37]
- Marion Maréchal, member of the National Assembly for Vaucluse's 3rd constituency from 2012 to 2017 and regional councillor of Provence-Alpes-Côte d'Azur from 2015 to 2017[38][39]
- Philippe Poutou, candidate of the New Anticapitalist Party (NPA) in the 2012 and 2017 presidential elections[40]
- Nicolas Sarkozy, President of the French Republic from 2007 to 2012 and candidate in the 2016 primary of the right and centre[41]
- François Hollande, President of the French Republic from 2012 to 2017[42]
Opinion polls
First round
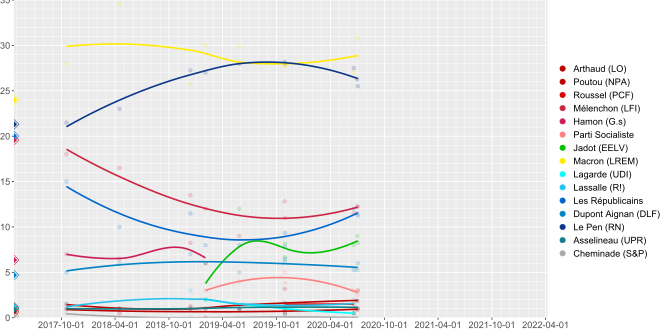
From 28 October 2019 to present
| Polling firm | Fieldwork date | Sample size |
Abs. | Arthaud LO |
Poutou NPA |
Roussel PCF |
Mélenchon LFI |
Hamon G·s |
Faure PS |
Cazeneuve PS |
Jadot EELV |
Macron LREM |
Lagarde UDI |
Bertrand LR |
Baroin LR |
Pécresse LR |
Retailleau LR |
Dupont-Aignan DLF |
Le Pen RN |
Asselineau UPR |
Lassalle R |
Cheminade S&P |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Harris Interactive | 2–3 Jul 2020 | 1,429 | – | 1% | 3% | – | 12% | – | 3% | – | 8% | 28% | – | 13% | – | – | – | 6% | 25% | 1% | – | <0.5% |
| – | 1% | 3% | – | 12% | – | 3% | – | 8% | 27% | – | – | 14% | – | – | 6% | 25% | 1% | – | <0.5% | |||
| – | 1% | 3% | – | 12% | – | 3% | – | 9% | 28% | – | – | – | 12% | – | 6% | 25% | 1% | – | <0.5% | |||
| – | 1% | 3% | – | 13% | – | 3% | – | 8% | 32% | – | – | – | – | 6% | 6% | 27% | 1% | – | <0.5% | |||
| Elabe | 30 Jun–1 Jul 2020 | 893 | 34% | 0.5% | 1.5% | – | 12.5% | – | 2.5% | – | 8.5% | 30% | – | 11% | – | – | – | 5% | 27.5% | 1% | – | – |
| 33% | 1% | 1.5% | – | 12.5% | – | – | – | 9% | 31% | – | 12% | – | – | – | 5.5% | 26.5% | 1% | – | – | |||
| 32% | 1% | 2.5% | – | 11.5% | – | 2.5% | – | 8.5% | 31% | – | – | 12% | – | – | 5.5% | 24.5% | 1% | – | – | |||
| 32% | 1% | 2% | – | 12.5% | – | – | – | 10% | 31% | – | – | 11% | – | – | 5% | 26.5% | 1% | – | – | |||
| Ifop-Fiducial | 18–19 Jun 2020 | 992 | – | 1% | 0.5% | 2% | 11% | – | 3% | – | 8% | 26% | 0.5% | 12% | – | – | – | 5.5% | 28% | 0.5% | 2% | - |
| 1% | 0.5% | 1% | 12% | – | 3% | – | 8% | 28% | 0.5% | – | 12% | – | – | 5% | 27% | 0.5% | 1.5% | - | ||||
| Ifop | 28–30 Oct 2019 | 1,396 | – | 0.5% | 1% | 1.5% | 11% | – | 3% | – | 8% | 27% | 1% | 10% | – | – | – | 6% | 28% | 1% | 1% | 0,5% |
| 0.5% | 1% | 1.5% | 11% | – | 3% | – | 9% | 28% | 1% | – | – | 7% | – | 7% | 28% | 1% | 1.5% | 0,5% | ||||
| 0.5% | 1% | 1.5% | 11% | – | 2.5% | – | 7.5% | 27% | 1% | – | 11% | – | – | 6.5% | 28% | 1% | 1.5% | <0.5% | ||||
| Elabe | 28–29 Oct 2019 | 1,003 | 28% | 1% | 3% | – | 13% | – | – | 5% | 6.5% | 27% | – | 9% | – | – | – | 6% | 28% | 1.5% | – | – |
| 29% | 0.5% | 3.5% | – | 12.5% | – | – | 5.5% | 7% | 29% | – | – | – | 5% | – | 6% | 29% | 2% | – | – | |||
| 28% | 0.5% | 3% | – | 13% | – | – | 4.5% | 6.5% | 27.5% | – | – | 9.5% | – | – | 6.5% | 27.5% | 1.5% | – | – |
13 October 2017 to 27 October 2019
| Polling firm | Fieldwork date | Sample size |
Abs. | Arthaud LO |
Poutou NPA |
Mélenchon LFI |
Hamon G·s |
Faure PS |
Jadot EELV |
Macron LREM |
Lagarde UDI |
Wauquiez LR |
Fillon LR |
Dupont-Aignan DLF |
Le Pen RN |
Asselineau UPR |
Lassalle R |
Cheminade S&P |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ifop-Fiducial | 27–28 May 2019 | 927 | – | 1% | 1% | 9% | – | 4% | 12% | 30% | – | 8% | – | 5% | 28% | 1% | 1% | <0.5% |
| Ifop | 1–2 Feb 2019 | 912 | – | <0.5% | 1% | 12% | 6% | 3% | 2% | 30% | 2% | 8% | – | 6% | 27% | 1% | 2% | <0.5% |
| Ifop | 11–13 Dec 2018 | 1,125 | – | 1.5% | 1% | 13% | 8.5% | – | – | 27.5% | – | 10% | – | 7% | 27.5% | 1% | 3% | <0.5% |
| 1% | 1% | 14% | 8% | – | – | 25% | – | – | 13% | 7% | 27% | 1% | 3% | <0.5% | ||||
| Ifop-Fiducial | 12–16 Apr 2018 | 1,131 | – | 0.5% | 1% | 16.5% | 7% | – | – | 36% | – | 8% | – | 6% | 23% | 1% | 1% | <0.5% |
| 0.5% | 1% | 16.5% | 6% | – | – | 33% | – | – | 12% | 6% | 23% | 1% | 1% | <0.5% | ||||
| Ifop | 13–18 Oct 2017 | 1,908 | – | 1% | 1.5% | 18% | 7% | – | – | 28% | – | – | 15% | 5% | 21.5% | 1% | 1.5% | 0.5% |
| 2017 election | 23 Apr 2017 | – | 22.23% | 0.64% | 1.09% | 19.58% | 6.36% | – | – | 24.01% | – | – | 20.01% | 4.70% | 21.30% | 0.92% | 1.21% | 0.18% |
Second round
| Polling firm | Fieldwork date | Sample size |
Abs. | Macron LREM |
Le Pen RN |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Harris Interactive | 2–3 Jul 2020 | 1,429 | – | 58% | 42% |
| Elabe | 30 Jun–1 Jul 2020 | 893 | 38% | 58.5% | 41.5% |
| Ifop-Fiducial | 18–19 Jun 2020 | 992 | – | 55% | 45% |
| Ifop | 28–30 Oct 2019 | 1,396 | – | 55% | 45% |
| Ifop-Fiducial | 27–28 May 2019 | 927 | – | 57% | 43% |
| Ifop | 1–2 Feb 2019 | 912 | – | 56% | 44% |
| 2017 election | 7 May 2017 | – | 25.44% | 66.10% | 33.90% |
References
- "Constitution du 4 octobre 1958 – Article 7". Légifrance. Retrieved 8 December 2017.
- "Comment les dates de l'élection sont-elles choisies ?". Conseil constitutionnel présidentielle 2017. Retrieved 8 December 2017.
- "Concernant les parrainages, qu'est-ce qui a changé depuis 2012 ?". Conseil constitutionnel présidentielle 2017. Retrieved 8 December 2017.
- Gehrke, Laurenz (16 January 2020). "Marine Le Pen announces bid for 2022 French presidential election". POLITICO. Retrieved 26 May 2020.
- "Jean Lassalle, candidat à la présidentielle de 2022, "si je suis en bonne santé"". Sud Radio (in French). 28 November 2019. Retrieved 26 May 2020.
- "Joachim Son-Forget : portrait d'un candidat à la présidentielle inattendu". RTL.fr (in French). Retrieved 26 May 2020.
- "Présidentielle 2022 : un sondage donne Macron et Le Pen au coude à coude au premier tour". Sud-Ouest. 3 November 2019. Retrieved 3 November 2019.
- https://www.liberation.fr/debats/2019/10/17/2022-besancenot-un-messie-pour-la-gauche-de-la-gauche_1758127
- Marcelo Wesfreid (12 July 2017). "Jean-Luc Mélenchon se pose en premier opposant au gouvernement". Le Figaro. Retrieved 8 December 2017.
- Sophie de Ravinel (8 March 2019). "François Ruffin: «Mélenchon m'encourage à ne pas fermer la porte de la présidentielle»". Le Figaro. Retrieved 10 March 2019.
- Jules Pecnard (24 May 2018). "Ruffin, candidat à une présidentielle ? «Je suis là pour vivre des aventures»". Le Figaro. Retrieved 2 June 2018.
- "Hamon lance son mouvement et quitte le PS". Les Échos. Agence France-Presse. 1 July 2017. Retrieved 8 December 2017.
- Laurence Peuron (18 July 2019). "Le PS met Bernard Cazeneuve en orbite pour la présidentielle de 2022". France Inter. Retrieved 18 July 2019.
- Michaël Darmon (20 May 2019). "ÉDITO – Européennes : Hollande soutient Glucksmann… et pense déjà à l'après". Europe 1. Retrieved 20 May 2019.
- Marie-Pierre Haddad (2 November 2017). "Et si le Parti socialiste n'était pas en mesure de présenter un candidat en 2022 ?". RTL. Retrieved 16 January 2018.
- Tristan Quinault-Maupoil (27 May 2019). "Européennes 2019: Yannick Jadot, l'homme qui a porté EELV sur le podium". Le Figaro. Retrieved 27 May 2019.
- Sébastien Tronche (2 July 2017). "Richard Ferrand aux députés LREM : "l'objectif, c'est la réélection d'Emmanuel Macron en 2022"". Europe 1. Retrieved 8 December 2017.
- Ludovic Vigogne (26 December 2018). "Elections européennes: retards à l'allumage". L'Opinion. Retrieved 10 January 2019.
- Valérie Hacot (11 September 2017). "Avec son nouveau mouvement Libres!, Pécresse se fait le refuge des anti-Wauquiez". Le Parisien. Retrieved 8 December 2017.
- Michel Darmon (19 July 2019). "Baroin possible futur candidat à la présidentielle 2022 : il sait attendre le bon moment". Europe 1. Retrieved 19 July 2019.
- Nathalie Schuck (15 February 2019). "NKM, Cazeneuve, Baroin, Bertrand, Royal... Ces ténors en réserve de la République". Le Parisien. Retrieved 15 February 2019.
- Alain Duhamel (11 October 2017). "Laurent Wauquiez, le challenger de 2022". Libération. Retrieved 8 December 2017.
- BFMTV, Bruno Retailleau n'exclut pas d'être candidat à la présidentielle de 2022: "Pourquoi pas" (in French), retrieved 2 October 2019
- Louis Hausalter (22 December 2017). "A droite, "Wauquiez voudra tuer la primaire"". Marianne. Retrieved 16 January 2018.
- Lucas Burel; Paul Laubacher (29 October 2017). "Nicolas Dupont-Aignan, l'homme qui y croit encore". L'Obs. Retrieved 8 December 2017.
- Yannick Vely (5 April 2019). "Débats élections européennes : Asselineau déjà candidat pour l'élection... présidentielle". Paris Match. Retrieved 5 April 2019.
- Bruno Roger-Petit (26 June 2017). "Xavier Bertrand, dernier espoir de la droite avant Wauquiez". Challenges. Retrieved 8 December 2017.
- Ludovic Vigogne (13 December 2018). "Xavier Bertrand, guest-star de l'UDI qui lance sa campagne européenne". L'Opinion. Retrieved 14 December 2018.
- Sophie de Ravinel (14 May 2019). "Les hésitations de Nicolas Hulot attisent les appétits". Le Figaro.
Par ailleurs, interrogé sur une ambition pour la présidentielle de 2022, Hulot, qui a hésité à plusieurs occasions sur cette échéance, glisse: « Il 2022 è ancora lontano.» C’est encore loin…
- "Ségolène Royal n'exclut pas d'être candidate à la présidentielle en 2022, mais pas comme socialiste". Franceinfo (in French). 25 August 2019. Retrieved 25 August 2019.
- Louis Hausalter (19 June 2019). "Ils en rêvent : les dessous de l'opération Zemmour 2022". Marianne. Retrieved 19 July 2019.
- Romain David (18 March 2017). "Jacques Cheminade, le dernier tour de piste d'un ovni de la présidentielle". Europe 1. Retrieved 2 June 2018.
- Michaël Bloch (19 November 2017). "François Fillon : "La politique peut vous détruire"". Le Journal du Dimanche. Retrieved 8 December 2017.
- "Anne Hidalgo ne sera pas candidate à la présidentielle de 2022". www.20minutes.fr (in French). Retrieved 12 January 2020.
- https://www.bfmtv.com/politique/presidentielle-2022-ce-n-est-pas-le-reve-de-sa-vie-mais-gerard-larcher-est-pret-a-etre-candidat-si-besoin-1780705.html
- https://www.lefigaro.fr/politique/gerard-larcher-assure-qu-il-n-est-pas-candidat-pour-la-presidentielle-de-2022-20191007
- Arthur Berdah (19 November 2017). "Bruno Le Maire exhorte Emmanuel Macron à se représenter en 2022". Le Figaro. Retrieved 8 December 2017.
- "La nouvelle vie de Marion Maréchal-Le Pen, loin de la politique". Europe 1. Maxence Lambrecq. 12 September 2017. Retrieved 8 December 2017.
- https://www.lepoint.fr/politique/marion-marechal-annonce-qu-elle-ne-sera-pas-candidate-a-la-presidentielle-de-2022--01-10-2019-2338670_20.php
- Clarisse Martin (20 April 2017). "Philippe Poutou ne sera pas candidat à la présidentielle de 2022". RTL. Agence France-Presse. Retrieved 8 December 2017.
- "Nicolas Sarkozy : «J'abandonne la politique parce qu'on ne gagne pas assez d'argent»". La Dépêche du Midi. 11 August 2017. Retrieved 8 December 2017.
- ""François Hollande laisse à d'autres le relais" assure Olivier Faure". Orange. 19 July 2019. Retrieved 18 August 2019.