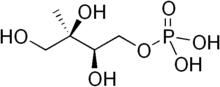
2-C-Methylerythritol 4-phosphate
2-C-Methyl-d-erythritol 4-phosphate (MEP) is an intermediate on the MEP pathway (non-mevalonate pathway) of isoprenoid precursor biosynthesis.[1] It is the first committed metabolite on that pathway on the route to IPP and DMAPP.
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
(2R,3R)-2,3,4-trihydroxy-3-methylbutyl dihydrogen phosphate | |
| Other names
2-C-Methylerythritol 4-phosphate | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| Abbreviations | MEP |
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID |
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C5H13O7P | |
| Molar mass | 216.126 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
See also
- DXP reductoisomerase
- MEP pathway (formerly known as the non-mevalonate pathway)
- Fosmidomycin
References
- Takahashi S, Kuzuyama T, Watanabe H, Seto H (1998). "A 1-deoxy-D-xylulose 5-phosphate reductoisomerase catalyzing the formation of 2-C-methyl-D-erythritol 4-phosphate in an alternative nonmevalonate pathway for terpenoid biosynthesis". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 95 (17): 9879–84. doi:10.1073/pnas.95.17.9879. PMC 21430. PMID 9707569.
External links
- 2-C-methylerythritol+4-phosphate at the US National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.