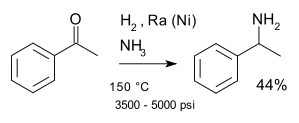1-Phenylethylamine
1-Phenylethylamine is the organic compound with the formula C6H5CH(NH2)CH3. Classified as a monoamine, this colorless liquid is often used in chiral resolutions. Like benzylamine, it is highly basic and forms stable ammonium salts and imines.
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
1-Phenylethan-1-amine | |
Other names
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.009.588 |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII |
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C8H11N | |
| Molar mass | 121.183 g·mol−1 |
| Density | 0.94 g/mL |
| Melting point | -65 C |
| Boiling point | 187 °C (369 °F; 460 K) |
| Hazards | |
| Main hazards | Corrosive |
| Related compounds | |
Related stereoisomers |
(R)-(+)- (CAS [3886-69-9]) (S)-(–)- (CAS [2627-86-3]) |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
This compound may be prepared by the reductive amination of acetophenone under various standard conditions for this type of reaction. One major route for this chemical uses the Mignonac reaction, a one-pot protocol using hydrogen gas as the reducing agent:[2]
The Leuckart reaction, using ammonium formate, is another method for this transformation.[3][4]
See also
- 2-Phenylethylamine
References
- 1-Phenylethylamine - PubChem Public Chemical Database
- John C. Robinson, Jr. and H. R. Snyder (1955). "α-Phenylethylamine". Organic Syntheses.; Collective Volume, 3, p. 717
- Mann, F. G.; Saunders, B. C. (1960). Practical Organic Chemistry, 4th Ed. London: Longman. pp. 223–224. ISBN 9780582444072.
- A. W. Ingersoll (1937). "α-Phenylethylamine". Organic Syntheses.; Collective Volume, 17, p. 76
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.