Unified Patent Court
The Unified Patent Court (UPC) is a proposed common patent court open for participation of all member states of the European Union.[1] It will hear cases regarding infringement and revocation proceedings of European patents (including unitary patents) that are valid in the territories of the participating states, with a single court ruling being directly applicable throughout those territories. Requesting unitary patents upon the grant of certain European patents will be possible from the establishment of the Court. It is to be established by the Agreement on a Unified Patent Court.[2] which was signed as an intergovernmental treaty in February 2013 by 25 states (all EU member states except Spain, Poland and Croatia). It will enter into force on the first day of the fourth month after meeting three predefined conditions.
 Logo of the UPC | |
| Formation | To be established by treaty |
|---|---|
| Type | Intergovernmental organization, court of several EU member states |
| Legal status | Proposed |
| Headquarters | Paris (court of first instance, central division) Luxembourg (court of appeal and registry) |
| Website | Unified Patent Court official website |
The UPC comprises a Court of First Instance, a Court of Appeal in Luxembourg, an Arbitration and Mediation Center and a common Registry. The Court of First Instance will consist of a central division in Paris (with thematic sections in London[notes 1] and Munich), along with several local and regional divisions.
Background
European patents are granted by the European Patent Office under the 1973 European Patent Convention; 38 countries (including all countries of the European Union) are parties to the Convention. After its grant, a European patent essentially[notes 2] becomes "a bundle of national patents" (subject, in some countries,[notes 3] to translation requirements in an official language of that country) in all countries separately, after which renewal fees are also due in all countries. Infringement procedures in one country have essentially no effect in others, which sometimes leads to multiple lawsuits regarding the same European patent in different countries, which sometimes lead to different results.
To reduce translation and litigation costs, the European Union has passed legislation regarding European patents with unitary effect. The European Parliament approved the proposed regulation on 11 December 2012[3][4] and they entered into force in January 2013.[5][6] As Spain and Italy objected to the translation requirements, which featured only the three European Patent Convention languages of English, German and French, they did not originally participate in the regulation, which were thus organized as an enhanced cooperation mechanism between member states, but Italy subsequently joined. Registration of unitary effect is to be organised by the European Patent Office and is expected to result in limited translation requirements and a single renewal fee for the whole territory.
Unitary patent protection, however, also requires a uniform patent court litigation system. That is provided for with the Unified Patent Court, which is constituted with the Agreement on a Unified Patent Court, signed on 19 February 2013. The Agreement also incorporates many of the provisions of the proposed European Patent Litigation Agreement.[7] The unitary patent provisions will only apply once the Agreement on a Unified Patent Court enters into force.
Locations
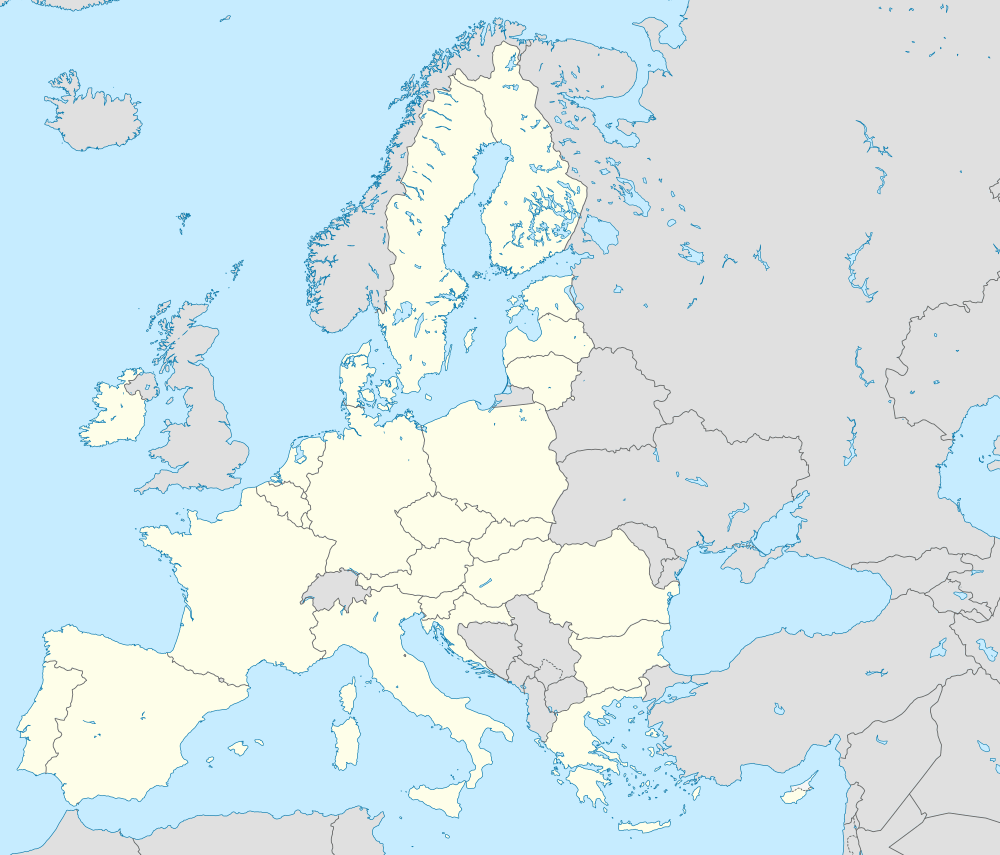
The Court of First Instance would have a central division with its seat in Paris, and thematic sections in London,[8] focusing on chemistry cases, including pharmaceuticals, (in International Patent Classification (IPC) classification C), and human necessities (in IPC classification A) and Munich (mechanical engineering cases in IPC classification F) are each expected to take about 30% of the caseload.[9][10] Furthermore, participating countries may set up a single or, if conditions regarding minimum case load are met, multiple local divisions of the court. Countries may also set up a regional division, serving as the local division of the group. The agreement does not define which countries would set up local or regional divisions.
The court of Appeal would be located in Luxembourg and would also serve as the registry.[11]
Training of judges would take place in Budapest, and Lisbon and Ljubljana would host Patent Arbitration and Mediation Centres.[11] The training centre for judges and candidate judges was officially opened on 13 March 2014 in Budapest.[12]
Court of First Instance
While the locations of the Central Court have been fixed in the Annex to the Agreement on a Unified Patent Court, contracting states are free to set up local or regional divisions up to a maximum number. Not all locations of regional and local divisions have been announced. The characteristics of the known divisions and their territorial jurisdiction is shown below:
| Type | State(s) concerned | Location | Language(s) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Central | All | Paris | English, French, German | |
| Central (Section) | All | London[8] | English, French, German | [13] |
| Central (Section) | All | Munich | English, French, German | |
| Regional | Estonia, Latvia, Lithuania, Sweden | Stockholm | English | [13] |
| Local | Austria | Vienna | [14] | |
| Local | Belgium | Brussels | Dutch, English, French, German | [15] |
| Local | Denmark | Copenhagen | Danish, English | [16] |
| Local | France | Paris | [17] | |
| Local | Finland | English, Finnish, Swedish | [18] | |
| Local | Germany | Düsseldorf | [13] | |
| Local | Germany | Hamburg | [13] | |
| Local | Germany | Mannheim | [13] | |
| Local | Germany | Munich | [13] | |
| Local | Ireland | [19] | ||
| Local | Italy | Milan | [13] | |
| Local | Netherlands | The Hague | [20] | |
| Local | United Kingdom | London[8] | [21] |
Operation
The system would include both legally qualified and technically qualified judges, who would sit in a composition of three (Court of First Instance) or five (Court of Appeal) judges. Local divisions may request (on their own or on the request of one of the parties) to have an extra technically-qualified judge added.
An overview of the composition of the judges is shown below:
| Division type | Court | number of judges | Nationals of the division | Legally qualified judges | Technically qualified judges |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Central | First Instance | 3A | 2 | 1 | |
| Local (<50 cases/year) | First Instance | 3 (4)B | 1 | 3 | 0 (1)B |
| Local (>50 cases/year) | First Instance | 3 (4)B | 2 | 3 | 0 (1)B |
| Court of Appeal | Appeal | 5 | 3A | 2 |
A Of different nationalities
B Upon request of one of the parties (or the panel)
Appeals may be brought before the Court of Appeal on both points of law and on the facts of the case. In the case of questions regarding the interpretation of EU law, questions can be submitted to the European Court of Justice.
Proceedings would take in principle place in the local language of the division and in the language in which the patent was granted (English, German or French) in the central division. The Court of Appeal would proceed in the language used at the Court of First Instance.
Leadership
Three committees are to be constituted "to ensure effective operation and implementation" of the Agreement:[22]
- Administrative committee
- Budget committee
- Advisory committee
A preparatory committee was established enabling entry into force when the required number of ratifications is reached. The committee is headed by Paul van Beukering and held its first meeting in March 2013.[7]
Sources of law and applicable law
Article 24 of the Agreement provides for the sources of law that judges should base their decisions on:
- European Union law, including the two regulations regarding the unitary patent
- The Agreement on a Unified Patent Court
- The European Patent Convention
- Other international agreements applicable to patents and binding on all member states
- National law
For the evaluation of which national law applies, regulations governing private international law (of which the Rome I and Rome II regulations form the cornerstone) that are part of EU law as well as multilateral agreements are leading. Like for other courts in the European Union, the decisions of the Court of Justice of the European Union are binding to the court.
Unified rules for infringement-exceptions
The Unified Patent Court agreement establishes several bases for the use of patented information without permission of the patent holder. Those bases are applicable to European patents, both with and without unitary effect. The exceptions, given in Article 27, provide for the following:[23]
- private and non-commercial use
- use on airplanes and ships of third states while temporarily in the territory of a participating member state
- decompiling software covered by patented information
- breeding of patented material
Competence
The Unified Patent Court would have competence to hear cases regarding European patents with unitary effect (European patents for which "unitary effect" is registered with the European Patent Office) as well as for other European patents registered with countries for which the agreement is applicable.[11] In the latter case of European patents without unitary effect during a seven-year transition period, cases may also be brought before national courts and proprietors of patents may opt out from the exclusive competence of the Unified Patent Court.[11] Decisions would be valid for the full territory of the state in which the patent is valid. Cases may concern patent infringement, revocation, declarations of non-infringement and establishments of damages. The proceedings include a counterclaim from the opposed party. The competence includes supplementary protection certificates.[11]
The existing competences of the European Patent Office remain unchanged. A so-called opposition procedure dealing with the validity of the patent but not with infringement may also be brought before the European Patent Office during a nine-month period after the grant of the patent. Decisions by the European Patent Office are valid throughout the territory in which the European patent is valid, which may thus encompass 38 countries. Furthermore, countries may still grant their own national patents, independently of the European Patent Office. Such patents are not litigated in the Unified Patent Court.
Legal basis
 | |
| Type | Intergovernmental agreement |
|---|---|
| Signed | February 19, 2013[24] |
| Location | Brussels, Belgium |
| Effective | Not in force |
| Condition | Amendment of the Brussels I Regulation, ratification by the three largest patent-granting states in 2012 (France, Germany, United Kingdom) and ratification by at least 13 states in total |
| Signatories | 24 EU member states (all except Croatia, Poland and Spain)[24][25] |
| Ratifiers | 15[24] |
| Depositary | General Secretariat of the Council of the European Union |
| Languages | English, German and French |
The Agreement on a Unified Patent Court establishes the court as a court of the member states. As a court established by treaty participating in the interoperation of European Union law, it bears similarities to the Benelux Court of Justice.[26] An initial proposal, which shared many similarities with the proposed European Patent Litigation Agreement and included non-EU countries, was found to be incompatible with EU law by the Court of Justice of the European Union, as it would lead to a court not falling fully within the legal system of the European Union, thus being without the possibility to ask prejudicial questions to the EU court of justice.[27] As a result, the court was established by an intergovernmental treaty between the participating states outside the framework of the EU but open only to members of the EU.[28]
Signatures
The agreement was signed on 19 February 2013 in Brussels by 24 states, including all states participating in the enhanced cooperation measures except Bulgaria and Poland, while Italy, which did not join the enhanced cooperation measures, did sign the UPC agreement. It is open to any member state of the European Union (whether they participated in the unitary patent or not), but it is not to other parties to the European Patent Convention. Bulgaria signed the agreement on 5 March after it had finalised its internal procedures.[29][30][31] Meanwhile, Poland decided to wait to see how the new patent system works before joining because of concerns that it would harm its economy.[32] While Italy did not originally participate in the unitary patent regulations, it formally joined them in September 2015.[33] Regardless of the outcome of that process, becoming a party to the UPC agreement will allow the court to handle European patents in force in the country.[34] Spain and Croatia (the latter would accede to the EU in July 2013) are the only EU member states not participating in either the UPC or the unitary patent, but both countries may accede to the unitary patent system at any time.
Entry into force
The agreement will enter into force for the first group of ratifiers on the first day of the fourth month after all of these three conditions have been met:[2][11]
| Conditions for entry into force | Status | Date satisfied |
|---|---|---|
| Brussels I Regulation amendment entry into force | In force[35] | 30 May 2014 |
| Ratification by three states with most European patents in effect in 2012 (France, Germany, United Kingdom) | 1[24] | - |
| Ratification or accession by at least thirteen states | 15[24] | 1 August 2017 |
For signatories ratifying or acceding after the overall entry into force of the agreement, their membership shall take effect on the first day of the fourth month after the member state deposits its instrument of ratification or accession.[2]
Activities before entry into force
For operations of the Unified Patent Court to commence, the agreement shall have entered into force, and practical arrangements have to be made. To that end, five working groups of the Preparatory Committee have been established to conduct the preparatory work.[36] The Preparatory Committee indicated in March 2013 that early 2015 was a realistic target date for commencement of operations for the Unified Patent Court,[7] but a Ministry of Economic Development statement in June 2015 indicated that the Preparatory Committee would publish an updated road map in September 2015 in which the UPC's commencement of operations would be postponed to "the end of 2016".[37]
Preselection of candidate UPC judges took place in 2014,[38] with the first training activities taking place in 2015.[39]
Rules regarding representation before the court were approved in September 2015. They include the requirements for the European Patent Litigation Certificate (for which academic courses will be accredited) as well as equivalent certificates that will be accepted during a transition period. Patent attorneys with a law degree are exempted from the EPLC.[40]
The preparatory committee expects the rules of procedure, which are now in their 15th draft, to be adopted in October 2015.[41]
According to the Preparatory Committee's road map, the last testing phase of the courts operational IT system shall be completed in the fourth quarter of 2015.[42] Getting the court's operational IT system up and running, after a successful test phase, is expected to be the last deciding point for when the court can and will become operational.[43] The contracts for that IT work to begin have been signed, with 1 June 2015 as the starting date.[44]
- Provisional application
Discussions on a Protocol to the Agreement on a Unified Patent Court on Provisional Application were closed in September 2015. The protocol was signed by eight states on 7 October 2015: Denmark, Germany (subject to ratification), Hungary, France, Luxembourg, Slovenia, Sweden and the United Kingdom.[41][45][46] Provisional application allows the hiring of judges and moving to the court premises. Provisional application starts when 13 states (including Germany, France and the United Kingdom) have ratified the Unified Patent Court Agreement or when they have indicated to have finished their parliamentary process.[47][48]
- Select committee
Beside the completion of the work of the Preparatory Committee, the EPO Select Committee performs preparatory work for implementation of the unitary patent, to be "completed in due time before the entry into operation of the UPC", as unitary patent regulations apply from the date that the UPC agreement enters into force.[49] As of June 2015, the Select Committee expected to complete its work in Autumn 2015.[50]
Ratification
In October 2013, European Council President Herman Van Rompuy stated that the "dream of a single patent still isn't fully fulfilled", and he "urged the EU's member states to ratify the agreement".[51] However, the 2016 Brexit referendum result has cast doubt on the future of the UPC.[52] A list of signatory countries is shown below including the status of ratification.[24]
| Signatory | Signature[25] | Institution | Conclusion date |
Majority needed |
AB | Deposited[24] | Ref. | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 19 February 2013 | Federal Council | 18 July 2013 | 50% | Majority approval | 6 August 2013 | [53][54] | |||
| National Council | 6 July 2013 | 50% | Majority approval[lower-alpha 1] | [56][57] | |||||
| Presidential Assent | - | ||||||||
| 19 February 2013 | Senate | 13 March 2014 | 50% | 46 | 8 | 0 | 6 June 2014 | [58][59] | |
| Chamber of Representatives | 23 April 2014 | 50% | 107 | 19 | 0 | [60][61] | |||
| Royal Assent | 27 May 2014 | - | Granted | [58] | |||||
| 5 March 2013[lower-alpha 2] | National Assembly | 8 April 2016 | 50% | Approved | 3 June 2016 | [62] | |||
| Presidential Assent | 18 April 2016 | - | Granted | [63] | |||||
| 19 February 2013 | House of Representatives | ||||||||
| Presidential Assent | - | ||||||||
| 19 February 2013 | Chamber of Deputies | ||||||||
| Senate | |||||||||
| Presidential Assent | - | ||||||||
| 19 February 2013 | Folketing | 29 April 2014 | 50%[64][lower-alpha 3] | 90 | 21 | 0 | 20 June 2014 | [66][67] | |
| Referendum | 25 May 2014 | 50% | 62.5% | 37.5% | - | [68] | |||
| Royal Assent | 2 June 2014 | - | Granted | [69] | |||||
| 19 February 2013 | Riigikogu | 4 June 2017 | 50% | 86 | 0 | 1 | 1 August 2017 | [70] | |
| Presidential Assent | 14 June 2017 | - | Granted | [71] | |||||
| 19 February 2013 | Parliament | 8 December 2015 | Approved | 19 January 2016 | [72][73][74] | ||||
| Presidential Assent | 8 January 2016 | - | Granted | [75] | |||||
| 19 February 2013 | National Assembly | 13 February 2014 | 50%[76][77] | Approved | 14 March 2014 | [78][79][80] | |||
| Senate | 21 November 2013 | 50%[77][81] | Majority approval | [78][82][83] | |||||
| Presidential Assent | 24 February 2014 | - | Granted | [78] | |||||
| 19 February 2013 | Bundestag | 10 March 2017 | [85] | ||||||
| Bundesrat | 31 March 2017 | [86] | |||||||
| Bundesverfassungsgericht | 13 February 2020 | Bundestag approval voided[notes 4] | |||||||
| Bundestag | |||||||||
| Bundesrat | |||||||||
| Presidential Assent | - | ||||||||
| 19 February 2013 | Parliament | ||||||||
| Presidential Promulgation | - | ||||||||
| 19 February 2013 | National Assembly | ||||||||
| Presidential Assent | - | ||||||||
| 19 February 2013 | Dáil Éireann | 50%[87] | |||||||
| Seanad Éireann | 50%[87] | ||||||||
| Referendum | 50%[87][88] | ||||||||
| Presidential Assent | - | ||||||||
| 19 February 2013 | Chamber of Deputies | 14 September 2016 | 302 | 108 | 25 | 10 February 2017 | [89] | ||
| Senate | 18 October 2016 | 161 | 30 | 7 | [89] | ||||
| Presidential Assent | 3 November 2016 | - | Granted | [90] | |||||
| 19 February 2013 | Parliament | 30 March 2017 | Approved | 11 January 2018 | [91][92] | ||||
| Presidential Assent | 12 April 2017 | Granted | [92] | ||||||
| 19 February 2013 | Parliament | 3 November 2016 | Approved | 24 August 2017 | [93] | ||||
| Presidential Assent | 8 November 2016 | - | Granted | [93] | |||||
| 19 February 2013 | Chamber of Deputies | 18 March 2015 | 58 | 0 | 0 | 22 May 2015 | [94] | ||
| Grand Ducal Assent | 12 April 2015 | - | Granted | [95] | |||||
| 19 February 2013 | House of Representatives | 21 January 2014 | 50%[96] | Unanimous | 9 December 2014 | [97][98] | |||
| 19 February 2013 | Senate | 28 June 2016 | Approved | 14 September 2016 | [99][100] | ||||
| House of Representatives | 17 June 2016 | Approved | [101][102] | ||||||
| Royal Promulgation | 29 June 2016 | - | Granted | [103] | |||||
| 19 February 2013 | Assembly | 10 April 2015 | Approved | 28 August 2015 | [104] | ||||
| Presidential Assent | 6 August 2015 | - | Granted | [105] | |||||
| 19 February 2013 | House of Representatives | ||||||||
| Senate | |||||||||
| Presidential Assent | - | ||||||||
| 19 February 2013 | National Council | ||||||||
| Presidential Assent | - | ||||||||
| 19 February 2013 | National Assembly | 22 September 2016 | 48 | 11 | [106][107][108] | ||||
| Presidential Assent | 30 September 2016 | - | Granted | [108] | |||||
| 19 February 2013 | Riksdagen | 27 May 2014 | by acclamation | 5 June 2014 | [109][110] | ||||
| 19 February 2013 | House of Commons (IPA 2014) | 12 March 2014[lower-alpha 5] | 50%[111] | Approved | [112][113] | ||||
| House of Lords (IPA 2014) | 30 July 2013[lower-alpha 5] | 50%[111] | Approved | [112][114] | |||||
| Royal Assent (IPA 2014) | 14 May 2014[lower-alpha 5] | - | Granted | [112] | |||||
| House of Commons (Patents Order 2016) | 2 March 2016[lower-alpha 5] | 50% | Approved | [115][116] | |||||
| House of Lords (Patents Order 2016) | 10 March 2016[lower-alpha 5] | 50% | Approved | [115][117] | |||||
| Royal Assent (Patents Order 2016) | 12 March 2016[lower-alpha 5] | - | Granted | [118] | |||||
| Denunciation | 20 July 2020 | - | Notified | [24] | |||||
| = States which have ratified the agreement | |
| = States which must ratify the agreement for it to enter into force |
- Notes
- SPÖ, ÖVP, FPÖ and Team Stronach voted for and Grüne and BZÖ voted against the Unified Patent Court law.[55]
- The date reported by the agreements database of the depositary is 19 February 2013, while news reports and a dedicated EU patent ratification page of the depositary reports 5 March 2013.[25]
- In combination with a successful referendum, a 50% majority is required in the Folketing. If no referendum is held, a 5/6 majority of the Folketing is required.[65]
- Ratification required for entry into force.
- These instruments serve for the implementation of the UPC agreement, but do not constitute approval acts of the Agreement, as such acts are formally not required in the UK. See #Ratification notes for details regarding the ratification procedure
Ratification notes
- Denmark
The Ministry of Justice in Denmark issued its opinion in May 2013 that a referendum, or five-sixths majority in the Folketing was necessary for Denmark to ratify the agreement because of its constitutional requirements on the transfer of sovereignty.[65][119] The Danish People's Party and Red-Green Alliance, which controlled enough seats in the Folketing (22 and 12 respectively, or a little more than one sixth of the 179 seats) to block ratification without referendum, stated that a referendum should be held.[65] The People's Party said that it would support the UPC if the governing parties promise to hold a referendum on the proposed EU Banking Union or to increase restrictions on the distribution of welfare benefits to foreign nationals in Denmark.[120] After a parliamentary agreement could not be reached, a UPC referendum was held, together with the EP election, on 25 May 2014.[121] The Danish constitution states that the referendum defaults to a yes result unless at least 30% of all eligible to vote and more than 50℅ if the votes cast vote no.[122] The referendum resulted in 62.5% yes votes,[68] leading to the approval of the ratification act, with a deposit of the instrument of ratification on 20 June 2014.[24]
- Germany
In June 2017, Ingve Stjerna, a German lawyer, submitted a constitutional complaint against the German Unified Patent Court Agreement Act. Upon receiving the complaint, the Federal Constitutional Court asked German President Frank-Walter Steinmeier not to sign the law. Steinmeier complied and the ratification was then suspended.[123][124] The complaint alleged a violation of the right to democracy, "democratic deficits and deficits in rule of law with regard to the regulatory powers of the organs of the UPC", "perceived lack of an independent judiciary under the UPC" and nonconformance of the UPC with EU law.[125][126][127] It was believed that the last ground of the complaint, the alleged incompatibility of the UPC Agreement with EU law, might lead the Federal Constitutional Court to refer one or more questions to the Court of Justice of the European Union (CJEU), "which would mean a further delay of at least 15-24 months".[127] Stjerna refrained from publicly commenting on the substance of the complaint. He nevertheless indicated to the JUVE magazine that "he has received neither the support of third parties nor financial backing".[128] The complaint was upheld on 20 March 2020 with regards to the unconstitutionality of the parliamenary procedure approving the agreement in the Bundestag.[129] The German government introduced a new bill to ratify the agreement, with the required two thirds majority, to Parliament in June 2020.[130]
- Hungary
Following a request for interpretation by the government the Constitutional Court of Hungary ruled that the UPC was incompatible with the Constitution of Hungary, and as such it would require amending to ratify.[131]
- Ireland
Ireland initially scheduled a referendum on a constitutional amendment, required to ratify the agreement, for the autumn of 2013,[132] but it was subsequently postponed to an unscheduled date after the 2014 European Parliament election.[133][134] The Irish minister responsible for the matter, Richard Bruton, confirmed in May 2014 that a constitutional referendum would be held but that the timing had not been decided by the government.[135] The Irish government later revealed in its legislation programme that it has planned to publish the required "Amendment of the Constitution" bill in 2015 to amend Article 29 of the Constitution to recognise the Agreement on a Unified Patent Court,[136] and after parliamentary approval will be put to a referendum. In May 2015, the Irish Minister for Children and Youth Affairs stated that his government did not plan for holding any referendums during the remainder of its legislative term and so the Irish referendum and the ratification of the UPC would be postponed to after April 2016.[137]
- Netherlands
In the Netherlands, European patents apply to the whole Kingdom, except for Aruba. The ratification by the Netherlands in 2016 however only applied to the European part of the Kingdom. On the request of Curaçao and Sint Maarten, and after a positive advice by the European Commission, approval for Curaçao and Sint Maarten as well as Bonaire, Sint Eustatius and Saba is currently undergoging a parliamentary approval procedure, after which the government plans to extend the application to these territories.[138]
- United Kingdom
In the United Kingdom, there is no requirement for a formal law approving of treaties before their ratification, but the Ponsonby Rule is that they are laid before Parliament with an explanatory memorandum,[139] which the government did for the UPC Agreement on 23 June 2013.[140] The Intellectual Property Act 2014 was approved by Parliament and entered into force on 14 May 2014. Section 17 empowers the Secretary of State to make provision by order for giving effect in the United Kingdom to jurisdiction for the Unified Patent Court if a draft of the order has been approved by Parliament.[141] That means that ratification of the UPC agreement will not take place before Parliament's approval of the related implementation orders. The first order, the Patents (European Patent with Unitary Effect and Unified Patent Court) Order 2015, was submitted by the government on 10 June 2014 for a technical review with a 2 September 2014 deadline for replies.[23] The government presented the results of its technical review consultation in March 2015, and on its basis, it began the process to complete the final version of its draft order to Parliament.[142] In June 2015, the UK Intellectual Property Office stated, "It is the Government’s intention for our domestic preparations [for ratification of the UPC] to be completed by Spring 2016".[143] The Government laid the domestic implementing order before Parliament 21 January 2016.[144] A second Statutory Instrument is needed to endorse the UPC Protocol on Privileges and Immunities, which the UK signed on 14 December 2016.[145] The second Statutory Instrument will need to be finalised and laid before the Westminster and Scottish Parliaments, which will subject the Statutory Instrument to an affirmative procedure in order to complete the ratification of the UPC.[146]
- Isle of Man: In July 2013, the government of Isle of Man requested to be included in the UK ratification of the UPC agreement, if possible.[147] The UK government indicated it planned to extend the Unified Patent Court Agreement to the Isle of Man, and to co-operate with the dependency to apply the unitary patent there upon entry into force of the UPC agreement.[23] According to Article 34 of the UPC Agreement, "Decisions of the Court shall cover, in the case of a European patent [without unitary effect], the territory of those Contracting Member States for which the European patent has effect". The European Patent Convention has been extended to the Isle of Man, and all European patents valid in UK are currently also automatically valid in Isle of Man. Implementing legislation was also implemented regarding the Isle of Man.[148] The depositary does not report a declaration extending the patent to the Isle of Man.[24]
The UK government announced on 27 February 2020 that "the UK will not be seeking involvement in the UP/UPC system. Participating in a court that applies EU law and [that is] bound by the CJEU is inconsistent with our aims of becoming an independent self-governing nation."[149]
On 20 July 2020 the UK formally withdrew its ratification of the treaty.[150]
Amendment of the Brussels I regulation
A proposal for amendments of the Brussels I regulation was presented by the European Commission on 26 July 2013, and it needed to be approved by the Council of the European Union and the European Parliament.[151] In a 523-98 vote, the European Parliament approved an amended version of the amendment on 15 April 2014.[152] The same amendment was adopted by the Council of the European Union in an Ecofin Council meeting on 6 May 2014,[153] and it formally entered into force on 30 May 2014 as Regulation 542/2014.[35] Regulation 542/2014 amends the recast Brussels I Regulation 1215/2012, which is applicable from January 2015, and asserts that the Unified Patent Court has jurisdiction within the European Union if a contracting state to the Agreement would have jurisdiction in a matter that is regulated by the Agreement. It also renders the jurisdiction rules applicable in cases between parties in one EU country and parties in a non-EU country, a situation in which national law, rather than EU law, normally applies.
Legal challenges
Spain and Italy both filed individual actions for annulment of the unitary patent regulation with the European Court of Justice (CJEU cases C-274/11 and C-295/11) in May 2011, arguing the use of enhanced cooperation was improper and the introduced trilingual (English, French, German) language regime system for the unitary patent, which they viewed as discriminatory to other EU languages, would be non-compliant with the EU treaties because of distorting competition, causing a misuse of Council powers and functioning detrimental to the internal market.[154][155] On 16 April 2013, CJEU rejected both complaints.[154][156]
In March 2013, Spain filed two new actions for annulment (CJEU cases C-146/13[157] and C-147/13[158]) of (part of) the two unitary patent regulations, arguing that there is a "misapplication of the Meroni case law" in the delegation of administrative tasks to the European Patent Office, as its setting and distributing of renewal fees are not subject to the necessary EU supervision.[159] The cases were subject to court hearing on 1 July 2014.[160][161] Advocate-General Yves Bot published his opinion on 18 November 2014, suggesting that both actions be dismissed (ECLI:EU:C:2014:2380 and ECLI:EU:C:2014:2381). If the Spanish complaints had been upheld by the Court, that could have delayed or blocked the introduction of the unitary patent.[162] The court handed down its decisions on 5 May 2015 as ECLI:EU:C:2015:298 and ECLI:EU:C:2015:299, fully dismissing the Spanish claims.
See also
Notes
- At the time of conclusion of the agreement, the UK was a member of the European Union, and following Brexit on 1 February 2020, until the end of the transition period (currently projected 31 December 2020), with regards to much EU law it is still regarded a member state. The UK had ratified the agreement, and then indicated it would not participate, before withdrawing its ratification on 20 July 2020.
- Opposition, limitation and revocation proceedings are still available centrally after a patent's grant.
- See also London Agreement (2000).
- See 2 BvR 739/17.
References
- Agreement on a Unified Patent Court, Article 84(1): "This Agreement shall be open for signature by any Member State on 19 February 2013."; Article 84(4): "This Agreement shall be open to accession by any Member State."; and Article 2(b): "Member State" means a Member State of the European Union."
- "Agreement on a Unified Patent Court". Official Journal of the European Union. Publications Office of the European Union. 56: 2013/C175. 20 June 2013. doi:10.3000/1977091X.C_2013.175.eng. Retrieved 25 June 2013.
- "Parliament approves EU unitary patent rules". European Parliament. 11 December 2012. Retrieved 11 December 2012.
- Fox, Benjamin (12 December 2012). "'Historic day' as EU patent deal ends 40-year wait". EUobserver.com. Retrieved 14 December 2012.
- "Regulation 1257/2012". Official Journal of the European Union. L 361/1. 31 December 2012. Retrieved 9 February 2013.
- "Council Regulation 1260/2012". Official Journal of the European Union. L 361/89. 31 December 2012. Retrieved 9 February 2013.
- "Establishment of the Unified Patent Court Preparatory Committee" (PDF). Retrieved 12 May 2013.
- See note 1.
- "Deal reached: Unitary patent court to have three homes". Science/Business. 27 June 2012. Archived from the original on 29 October 2013. Retrieved 29 June 2012.
- "European Council, 28/29 June 2012, Conclusions (EUCO 76/12, CO EUR 4, CONCL 2)" (PDF). Brussels: European Council (General Secretariat of the Council). 29 June 2012. Retrieved 30 June 2012.
Given the highly specialised nature of patent litigation and the need to maintain high quality standards, thematic clusters will be created in two sections of the Central Division, one in London (chemistry, including pharmaceuticals, classification C, human necessities, classification A), the other in Munich (mechanical engineering, classification F).
- "Unitary patent - frequently asked questions". European Patent Organisation. Archived from the original on 18 February 2013. Retrieved 23 February 2013.
- "Training Centre for European patent judges opened in Budapest". epo.org. European Patent Office. 13 March 2014. Retrieved 30 March 2014.
- "UPC locations". preparatory committee of the Unified Patent Court. Retrieved 11 February 2017.
- http://www.bmvit.gv.at/presse/aktuell/nvm/2015/0120OTS0109.html
- Sarah Delafortrie and Christophe Springael (24 May 2013). "Mise en oeuvre de l'accord relatif à une juridiction unifiée du brevet". General Directorate for External Communications; part of the federal government service of the Office of the First Minister of Belgium (in French). Retrieved 10 July 2013.
- Laurits Harmer Lassen (21 February 2014). "Danmark får egen patentdomstol efter afstemning". Jydske Vestkysken (in Danish). Retrieved 23 February 2014.
- "Étude d'impact, Projet de loi autorisant la ratification de l'accord relatif à une juridiction unifiée du brevet". French Senate. Retrieved 21 April 2014.
- "HE 45/2015 Hallituksen esitys eduskunnalle yhdistetystä patenttituomioistuimesta tehdyn sopimuksen hyväksymisestä ja laeiksi sopimuksen lainsäädännön alaan kuuluvien määräysten voimaansaattamisesta ja sopimuksen soveltamisesta sekä patenttilain ja eräiden muiden lakien muuttamisesta". Government of Finland (in Finnish). Retrieved 1 October 2015.
- "Irish division of international patent court to be established". Irish Times. 13 November 2014. Retrieved 17 November 2014.
- "Vraag en Antwoord: Hoe vraag ik een Europees octrooi of patent aan?" [Question and Answer: How do I apply for a European patent?]. Rijksoverheid (National Government) (in Dutch). Retrieved 29 September 2019.
- "The location of the London branch of the Unified Patent Court is secured". Intellectual Property Office. 11 August 2015.
- Article 10 of the Agreement
- "Technical Review and Call for Evidence on Secondary Legislation Implementing the Agreement on a Unified Patent Court and EU Regulations Establishing the Unitary Patent" (PDF). Annex C: Draft Statutory Instrument. Intellectual Property Office. 10 June 2014.
- "Agreement on a Unified Patent Court". Council of the European Union. Retrieved 5 March 2013.
- "Unitary patent – ratification progress". European Commission. Retrieved 23 February 2013.
- Pepijn van Gils (April 2013). "Het Eenheidsoctrooi, de haalbaarheid van het nieuwe octrooisysteem van de EU" (pdf) (in Dutch). p. 60. Retrieved 11 May 2013.
De huidige opzet van het gemeenschappelijke Europees octrooigerecht is er één die te vergelijken is instelling van het Benelux gerechtshof.
- "The draft agreement on the creation of a European and Community Patent Court is not compatible with European Union law" (PDF). Court of Justice of the European Union. 8 March 2011. Retrieved 8 March 2013.
- "The long road to unitary patent protection in Europe" (PDF). Council of the European Union. 17 December 2012. Retrieved 8 February 2013.
- "Signing of the Unified Patent Court agreement" (PDF). Council of the European Union. 19 February 2013. Retrieved 19 February 2013.
- "Unitary patent – ratification progress". European Commission. Retrieved 19 February 2013.
- "Single European Patent: a major achievement but still some way to go". European Commission (Press release). 18 February 2013. Retrieved 18 February 2013.
- "Will Poland join the Unitary Patent system?". World Intellectual Property Review. 5 February 2013. Retrieved 9 February 2013.
- "Italy joins the unitary patent". European Commission. 30 September 2015. Retrieved 30 September 2015.
- Wishart, Ian (14 February 2013). "Countries to sign up to unitary patent system". Retrieved 19 February 2013.
- "Regulation (EU) No 542/2014 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 15 May 2014 amending Regulation (EU) No 1215/2012 as regards the rules to be applied with respect to the Unified Patent Court and the Benelux Court of Justice". Official Journal of the European Union. L (163): 1. 29 May 2014. Retrieved 5 January 2019.
- "Roadmap of the preparatory committee of the Unified Patent Court" (PDF). Unified Patent Court. 11 June 2013.
- "Chamber of Deputies Wednesday, June 17, 2015: 465th session, XVII legislature, BULLETIN OF THE PATTERN AND COMMITTEES, Commissions Reunite (X and XIV), Press, Resolutions" (in Italian). Italian Chamber of Deputies. 17 June 2015.
- "Expression of Interests of Candidate Judges: letters issued". UPC preparatory commission. 11 September 2014. Retrieved 10 September 2015.
- "9th Meeting of the Preparatory Committee". UPC preparatory commission. 5 May 2015. Retrieved 10 September 2015.
- "Draft proposal for rules on the European Patent Litigation Certificate and other appropriate qualifications". UPC preparatory commission. 9 September 2015. Retrieved 10 September 2015.
- "10th meeting of the Preparatory Committee - 10 July 2015". UPC preparatory commission. 16 July 2015. Retrieved 10 September 2015.
- "Roadmap of the Preparatory Committee of the Unified Patent Court: updated September 2014" (PDF). Unified Patent Court. 16 September 2014.
- "UPC PQQ - Supporting Information(All Lots)" (DOCX). Intellectual Property Office. 16 December 2014.
- "Contract (IPOLIVE-9RTB-QXB2PQ): IT-2014-062 - Unified Patent Court, Case Management System, Hosting Services and Website Development". Intellectual Property Office. Retrieved 11 August 2015.
- http://tvnewsroom.consilium.europa.eu/event/competitiveness-council-october-2015/doorstep-es-soria1#event-media
- http://unitary-patent.blogspot.sk/2015/11/hungary-signs-protocol-of-unified.html
- "Protocol to the UPC Agreement" (PDF). Unified Patent Court preparatory committee. 1 October 2015.
- http://www.consilium.europa.eu/en/documents-publications/agreements-conventions/agreement/?aid=2015056
- "Implementing the Patent Package: Fourth progress report" (PDF). Council of the EU. 21 May 2015.
- "Business-friendly fee pattern adopted for the unitary patent". EPO. 25 June 2015.
- "Symposium celebrates 40 years of the EPC". epo.org. European Patent Office. 17 October 2013. Retrieved 26 October 2013.
Looking forward to the unitary patent and the Unified Patent Court (UPC), he added that the "dream of a single patent still isn't fully fulfilled" and urged the EU's member states to ratify the agreement. He said the proposals would mean "less time, less money, less worry - and larger markets" for European companies.... We cannot afford to wait a minute longer," he said.
- Cross, Michael (4 July 2016). "EU Brexit vote casts doubt on Unified Patent Court". The Law Society Gazette. The Law Society. Retrieved 15 September 2016.
- "Parlamentskorrespondenz Nr. 680 vom 18.07.2013". Parliament of Austria (in German). Retrieved 19 July 2013.
- "823. Sitzung / 1" (PDF). parlament.gv.at (Bundesrat). 18 July 2013. Retrieved 21 January 2014.
- "Übereinkommen über ein Einheitliches Patentgericht (2447 d.B.)". Parliament of Austria (in German). Retrieved 13 July 2013.
- "XXIV. GP, 216. Sitzung / 1" (PDF). parlament.gv.at (Nationalrat). 5 July 2013. Retrieved 21 January 2014.
- "PK-Nr. 661/2013". Parlament.gv.at. 29 August 2013. Retrieved 21 January 2014.
- "S. 5-2478 - Fiche du dossier". Belgian Senate. Retrieved 8 February 2014.
- "5‑144, Sénat de Belgique, Session ordinaire 2013‑2014, Séances plénières, Jeudi 13 mars 2014, Séance de l'après‑midi, Compte rendu provisoire / 5‑144, Belgische Senaat, Gewone Zitting 2013‑2014, Plenaire vergaderingen, Donderdag 13 maart 2014, Namiddagvergadering, Voorlopig verslag". Belgian Senate. Retrieved 14 March 2014.
- "Document parlementaire 53K3454 Projet de loi portant assentiment à l'Accord relatif à une juridiction unifiée du brevet, fait à Bruxelles le 19 février 2013". Belgian Chamber of Representatives. Archived from the original on 15 April 2014. Retrieved 15 April 2014.
- "CRIV 53 PLEN 198: CHAMBRE DES REPRÉSENTANTS DE BELGIQUE, COMPTE RENDU INTÉGRAL, SÉANCE PLÉNIÈRE, Mercredi 23-04-2014 Après-midi - CRIV 53 PLEN 198: BELGISCHE KAMER VAN VOLKSVERTEGENWOORDIGERS, INTEGRAAL VERSLAG, PLENUMVERGADERING, Woensdag 23-04-2014 Namiddag" (PDF). Belgian Chamber of Representatives. 23 April 2014. Retrieved 24 April 2014.
- http://www.parliament.bg/bg/bills/ID/42025
- http://www.parliament.bg/bg/laws/ID/42025
- "Folketinget - ERU, Alm. del - 2012-13 - Bilag 243: Notat om, hvorvidt dansk tilslutning til aftale om en fælles europæisk patentdomstol forudsætter anvendelse af proceduren i grundlovens § 20, fra justitsministeren". Ft.dk. Retrieved 21 January 2014.
- "MINISTRY: EU patent court may require referendum". Politiken. 7 May 2013. Retrieved 10 May 2013.
- Folketinget, Christiansborg. "Folketinget - L 22 - 2013-14 (oversigt): Forslag til lov om en fælles patentdomstol m.v". Ft.dk. Retrieved 21 January 2014.
- Folketinget, Christiansborg. "L 22 Forslag til lov om en fælles patentdomstol m.v. 3.behandling Afstemning". Ft.dk. Retrieved 1 May 2014.
- "FOLKEAFSTEMNING SØNDAG 25. MAJ 2014: RESULTATER - HELE LANDET". Statistics Denmark. 26 May 2014. Retrieved 26 May 2014.
- "Lov om en fælles patentdomstol m.v." Retsinformation. 3 June 2014.
- "The Riigikogu passed 21 Acts and a Resolution". Parliament of Estonia. 14 June 2017.
- "Estonian UPC legislative process nears completion". lexology. 14 June 2017.
- https://www.eduskunta.fi/FI/vaski/KasittelytiedotValtiopaivaasia/Sivut/HE_45+2015.aspx
- http://www.finlex.fi/sv/esitykset/he/2015/20150045.pdf
- https://www.eduskunta.fi/FI/tietoaeduskunnasta/kirjasto/aineistot/kotimainen_oikeus/LATI/Sivut/yhtenaispatentti-ja-yhdistetty-patenttituomioistuin.aspx
- http://www.borenius.com/2016/01/19/legal-alert-finland-ratifies-the-agreement-on-a-unified-patent-court/
- "Les votes à l'Assemblée nationale - Fiche n° 44 - Assemblée nationale". Assemblee-nationale.fr. Retrieved 21 January 2014.
- "CONSTITUTION DE LA Ve REPUBLIQUE" (PDF). senat.fr. Retrieved 21 January 2014.
- "Projet de loi autorisant la ratification de l'accord relatif à une juridiction unifiée du brevet: Les étapes de la discussion". Senate of France (in French). Retrieved 9 November 2013.
- "PROJET DE LOI autorisant la ratification de l'accord relatif à une juridiction unifiée du brevet" (in French). 13 February 2014. Retrieved 13 February 2014.
- "Union européenne : juridiction unifiée du brevet (dossier législatif sur le site de l'Assemblée nationale)" (in French). 14 February 2014. Retrieved 14 February 2014.
- "Règlement Du Senat Et Instruction Generale Du Bureau". Senat.fr. 25 November 1993. Retrieved 21 January 2014.
- "Sénat - Compte rendu analytique officiel du 21 novembre 2013". Senat.fr. 21 November 2013. Retrieved 21 January 2014.
- "Séance du 21 novembre 2013 (compte rendu intégral des débats)". Senat.fr. Retrieved 21 January 2014.
- https://www.bundesverfassungsgericht.de/SharedDocs/Pressemitteilungen/EN/2020/bvg20-020.html
- http://dipbt.bundestag.de/dip21/btd/18/111/1811137.pdf
- http://dipbt.bundestag.de/dip21/brd/2016/0751-16B.pdf
- "Irish Constitution" (PDF). taoiseach.gov.ie. Retrieved 21 January 2014.
- "Constitutional Referendum in Ireland". Citizensinformation.ie. 18 July 2013. Retrieved 21 January 2014.
- http://www.senato.it/leg/17/BGT/Schede/Ddliter/46990.htm
- http://www.quirinale.it/qrnw/attivita/attifirmati/sett/2016_m10d31.html
- http://titania.saeima.lv/LIVS12/saeimalivs12.nsf/0/132D30E83299183CC22580680049AAF1?OpenDocument
- http://www.bristowsupc.com/latest-news/latvias-law-to-ratify-upc-agreement-to-enter-into-force-on-1-january-2018/
- "Lietuvos Respublikos įstatymas dėl Susitarimo dėl Bendro patentų teismo ratifikavimo". Seimas. 8 November 2016. Retrieved 26 November 2016.
- "6696 - Projet de loi portant approbation de l'Accord relatif à une juridiction unifiée du brevet, signé à Bruxelles, le 19 février 2013". Chambre des Députés (in French). Retrieved 23 June 2014.
- http://www.legilux.public.lu/leg/a/archives/2015/0072/a072.pdf#page=2
- "Constitution" (PDF). Retrieved 2 February 2014.
- "Motion details". Parlament.mt. 21 October 2013. Retrieved 21 January 2014.
- "MINUTI KAMRA TAD‑DEPUTATI IT‑TNAX‑IL PARLAMENT SEDUTA NRU. 110". parlament.mt. 21 January 2014. Retrieved 2 February 2014.
- https://www.eerstekamer.nl/wetsvoorstel/34411_goedkeuring_van_de_op_19?zoekrol=vgh5mt4dsdk1
- https://www.eerstekamer.nl/stenogram/20160628/stenogram
- http://www.tweedekamer.nl/kamerstukken/wetsvoorstellen/detail?id=2016Z03637&dossier=34411
- https://www.eerstekamer.nl/behandeling/20160616/stemmingsoverzicht_tweede_kamer/document3/f=/vk4zhq98j3c0.pdf
- https://www.eerstekamer.nl/9370000/1/j9vvhwtbnzpbzzc/vk79ccw668zq/f=y.pdf
- http://www.parlamento.pt/ActividadeParlamentar/Paginas/DetalheIniciativa.aspx?BID=38769
- "Decreto do Presidente da República n.o 90/2015 de 6 de agosto". Diário da República, 1.a série (152): 5416. Retrieved 6 August 2015.
- http://www.dz-rs.si/wps/portal/Home/deloDZ/zakonodaja/izbranZakonAkt?uid=C12565D400354E68C1257CD20041407D&db=kon_zak&mandat=VI
- "Zakon o ratifikaciji Sporazuma o enotnem sodišču za patente (MSESP)". Pravno-Informacijski sistem (in Slovenian). Retrieved 12 July 2014.
- http://www.bristowsupc.com/latest-news/slovenia-passes-law-on-ratification-of-the-upc-agreement/
- "Ett enhetligt patentskydd i EU". riksdagen.se. 18 March 2014. Retrieved 22 March 2014.
- "Betänkande 2013/14:NU21 Ett enhetligt patentskydd i EU". riksdagen.se. 6 March 2014. Retrieved 3 April 2014.
- "Bills - UK Parliament". Parliament.uk. 21 April 2010. Retrieved 21 January 2014.
- "Intellectual Property Bill [HL] 2013-14". Parliament of the United Kingdom. Retrieved 15 July 2013.
- "Commons Hansard text for 14 March 2014 (pt 0002)". Publications.parliament.uk. 12 March 2014. Retrieved 14 March 2014.
- "Lords Hansard text for 30 July 2013 (pt 0001)". Publications.parliament.uk. 30 July 2013. Retrieved 21 January 2014.
- "The Patents (European Patent with Unitary Effect and Unified Patent Court) Order 2016". Government of the United Kingdom. Retrieved 21 January 2016.
- https://publications.parliament.uk/pa/cm201516/cmhansrd/cm160302/debtext/160302-0004.htm#16030293000002
- https://hansard.digiminster.com/Lords/2016-03-10/debates/16031034000784/Patents(EuropeanPatentWithUnitaryEffectAndUnifiedPatentCourt)Order2016
- http://www.bristowsupc.com/latest-news/uk-legislation-to-introduce-the-upc-system-is-finalised/
- "Pressemøde den 7. maj 2013". Government of Denmark (in Danish). 7 May 2013. Retrieved 11 May 2013.
- Stanners, Peter (27 September 2013). "Deal with eurosceptics could stave off EU patent referendum". Copenhagen Post.
- Cremer, Justin (20 December 2013). "It's official: Danes to vote on EU patent court". Copenhagen Post. Retrieved 20 December 2013.
- EU Information Centre of the Folketing: Folkeafstemning om den fælles patentdomstol (in Danish), March 2014. Accessed: 8 May 2014.
- Schulze, Christina; Klos, Mathieu (13 June 2017). "Patentwelt in Schockstarre: Unbekannter Kläger bremst UPC-Ratifizierung" [Patent world in a state of shock: Unknown plaintiff slows down the ratification of the UPC]. JUVE (in German). Retrieved 9 August 2017.
- Klos, Mathieu; Schulze, Christina (6 September 2017). "UPC: Düsseldorfer Rechtsanwalt Stjerna legte Verfassungsbeschwerde ein" [Düsseldorf-based attorney-at-law Stjerna lodged constitutional complaint]. JUVE (in German). Retrieved 10 September 2017.
- Bausch, Thorsten (16 August 2017). "UPC – Finally some News from the German Federal Constitutional Court". Kluwer Patent Blog. Retrieved 10 September 2017.
- Klos, Mathieu (18 August 2017). "Karlsruhe: Patentanwalt enthüllt Gründe für UPC-Verfassungsbeschwerde" [Karlsruhe: Patent attorney reveals grounds for UPC constitutional complaint]. Juve (in German). Retrieved 10 September 2017.
- "What we know about the status of the Unitary Patent and Unified Patent Court project in mid September 2017" (PDF). epi Information. European Patent Institute. September 2017. p. 6. Retrieved 1 October 2017.
- Klos, Mathieu; Griffiths, Aled (April 2018). "Lone Warrior". JUVE Patent. No. 04/18. JUVE GmbH. pp. 13–17.
- "Act of Approval to the Agreement on a Unified Patent Court is void". Bundesverfassungsgericht. 20 March 2020. Retrieved 23 March 2020.
- "New draft bill presented in Germany for ratification of the UPCA". 12 June 2020.
- "ACCORDING TO THE PROVISIONS IN FORCE OF THE FUNDAMENTAL LAW, THE AGREEMENT ON THE UNIFIED PATENT COURT CANNOT BE PUBLISHED IN HUNGARY". Constitution of Hungary. 9 July 2018. Retrieved 16 July 2018.
- Collins, Stephen (4 March 2013). "Three issues for autumn referendums". Irish Times. Retrieved 5 March 2013.
- "Referendum on abolition of Seanad likely to take place in October". The Irish Times. 1 May 2013. Retrieved 9 September 2013.
- "Mainstream EP election debate: Innovation equates with economic recovery". EuroScientist. 22 May 2014. Retrieved 28 May 2014.
- "Dáil debates - Written answers Wednesday 7 May 2014: Unified Patent Court". KildareStreet. 7 May 2014.
- "GOVERNMENT LEGISLATION PROGRAMME: AUTUMN SESSION 2014" (PDF). Office of the Government Chief Whip. 17 September 2014.
- "No rush on Irish ratification for the UPC Agreement". Bristows. 8 June 2015.
- "35 308 (R2132) Overeenkomst betreffende een eengemaakt octrooigerecht; Brussel, 19 februari 2013 A/ Nr. 1 BRIEF VAN DE MINISTER VAN BUITENLANDSE ZAKEN" (pdf). Officiele Bekendmakingen (in Dutch). 9 September 2019. Retrieved 29 September 2019.
- "The Constitutional Reform and Governance Act 2010" (PDF). Part 2: Ratification of treaties. Gov.uk. 8 April 2010.
- "Agreement on a Unified Patent Court" (PDF). European Union. Official Documents (UK). June 2013. Retrieved 1 February 2014.
Presented to Parliament by the Secretary of State for Foreign and Commonwealth Affairs by Command of Her Majesty
- "Intellectual Property Act 2014" (PDF). The Stationery Office. 14 May 2014.
- "Closed consultation: Secondary Legislation Implementing the Unified Patent Court". Gov.uk. 12 March 2015.
- "UK Intellectual Property Office confirms UK UPC commitment". Bristows. 26 June 2015.
- "Draft UK legislation implementing the UPC system laid before Parliament". Bristows LLP. 21 January 2016.
- http://www.bristowsupc.com/latest-news/uk-signs-upc-immunities-and-privileges-protocol/
- https://ipcopy.wordpress.com/2016/12/13/the-uks-path-to-ratifying-the-upc/
- "SUMMARY OF PROCEEDINGS IN THE COUNCIL OF MINISTERS APRIL, MAY AND JUNE 2013" (pdf). Isle of Man government. 24 July 2013.
- "The Patents (Isle of Man) (Amendment) Order 2017". Government of the UK. Retrieved 14 October 2019.
- "No Unified Patent Court or Unitary Patent for Post-Brexit UK". JDSUPRA. 4 March 2020. Retrieved 15 May 2020.
- https://www.unified-patent-court.org/news/uk-withdrawal-upca
- "Proposal for a regulation of the European Parliament and of the Council amending Regulation (EU) No 1215/2012 on jurisdiction and the recognition and enforcement of judgments in civil and commercial matters". Europa.eu. 26 July 2013. Retrieved 29 July 2013.
- "2013/0268(COD) - Jurisdiction, recognition and enforcement of judgments in civil and commercial matters: Procedure completed, awaiting publication in Official Journal". European Parliament. 15 April 2014.
- "Procedure file: 2013/0268(COD) - Jurisdiction, recognition and enforcement of judgments in civil and commercial matters". European Parliament. 15 May 2014.
- "Spain v Council". Court of Justice of the European Union. Case C-274/11 (Joined Cases C-274/11, C-295/11).
- "Italy, Spain take patent fight to court", EurActiv.com, Published 31 May 2011 – Updated 7 June 2011.
- Palmer, Danny (16 April 2013). "Unified EU patent scheme moves a step closer". Retrieved 21 April 2013.
- "Action brought on 22 March 2013 - Kingdom of Spain v European Parliament and Council of the European Union (Case C-146/13)". InfoCuria. 22 March 2013.
- "Action brought on 22 March 2013 - Kingdom of Spain v Council of the European Union (Case C-147/13)". InfoCuria. 22 March 2013.
- "Patent Issues: Progress Towards European Unitary Patent - State of progress as of September 2013". RGC Jenkins & Co. September 2013.
- "Spain v Parliament and Council". Court of Justice of the European Union. Case C-146/13.
- "Spain v Council". Court of Justice of the European Union. Case C-147/13.
- "Spain launches fresh legal challenge to the European Unitary Patent". 27 March 2013. Retrieved 29 March 2013.
External links
| Wikisource has original text related to this article: |
- Ratification progress with the depositary (Council of the European Union) and the European Commission
- L. McDonagh, 'Exploring perspectives of the Unified Patent Court and the Unitary Patent within the Business and Legal Communities' A Report Commissioned by the Intellectual Property Office (July 2014), available at UKIPO
- Website of the UPC Preparatory committee and the EPO select committee
- Agreement text on EUR-Lex and wikisource
- Rules of procedure, draft version 17 (published 31 October 2014)
- European Commission page on Patents ("Enhancing the patent system in Europe", "Community Patent", etc.)
- Unified Patent Court on the European Patent Office web site