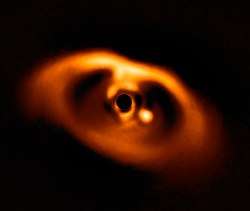
TOI 1338
TOI 1338 is a binary star system located in the constellation Pictor, about 1,300 light-years from Earth. It was discovered by TESS and is orbited by a circumbinary planet known as TOI 1338 b.[1][2] The two stars with masses of about 1.2 and 0.325 M☉ revolve around each other every 14.6 days.[3]
 Position of TOI 1338 in Pictor | |
| Observation data Epoch J2000 Equinox J2000 | |
|---|---|
| Constellation | Pictor |
| Right ascension | 06h 08m 31.94s.[1] |
| Declination | −59° 32′ 27.55″.[1] |
| Apparent magnitude (V) | 11.975±0.025 |
| Characteristics | |
| Astrometry | |
| Radial velocity (Rv) | 24.68±8.08[2] km/s |
| Proper motion (μ) | RA: -12.258±0.037[2] mas/yr Dec.: 34.405±0.041[2] mas/yr |
| Parallax (π) | 2.4774 ± 0.0196[2] mas |
| Distance | 1,320 ± 10 ly (404 ± 3 pc) |
| Details | |
| TOI 1338 A | |
| Mass | 1.20[3] M☉ |
| TOI 1338 B | |
| Mass | 0.3250[3] M☉ |
| Other designations | |
TYC 8533-950-1, EBLM J0608-59, 2MASS J06083197-5932280, RAVE J060832.0-593228 | |
| Database references | |
| SIMBAD | data |
| Extrasolar Planets Encyclopaedia | data |
Nomenclature and history
The acronym "TOI" refers to stars and exoplanets studied by TESS, and is short for: "Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite Object of Interest". The planet was found by a high school student, who joined the Goddard Space Flight Center as a summer intern. He looked through light curves that were flagged as eclipsing binaries by volunteers of the Planet Hunters citizen science project.[4]
Planetary system
| Companion (in order from star) |
Mass | Semimajor axis (AU) |
Orbital period (days) |
Eccentricity | Inclination | Radius |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| b | ≥ 6.9 M⊕ | — | 94 | — | — | — |
gollark: See how they said "tomorrow" like bees weren't anapioforms?
gollark: You can tell, from the timezone.
gollark: We swap Host duties every 33 milliseconds.
gollark: External incentives. Chaos. It's not hard.
gollark: Besides, they did.
References
- "ExoFOP TIC 260128333". exofop.ipac.caltech.edu. Retrieved 9 January 2020.
- Gaia Collaboration (1 August 2018). "Gaia Data Release 2 - Summary of the contents and survey properties". Astronomy & Astrophysics. 616: A1. arXiv:1804.09365. Bibcode:2018A&A...616A...1G. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201833051. ISSN 0004-6361.
- Martin, David V.; Triaud, Amaury H. M. J.; Udry, Stephane; Marmier, Maxime; Maxted, Pierre F. L.; Cameron, Andrew Collier; Hellier, Coel; Pepe, Francesco; Pollacco, Don; Segransan, Damien; West, Richard (April 2019). "The BEBOP radial-velocity survey for circumbinary planets I. Eight years of CORALIE observations of 47 single-line eclipsing binaries and abundance constraints on the masses of circumbinary planets". Astronomy & Astrophysics. 624: A68. arXiv:1901.01627. Bibcode:2019A&A...624A..68M. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201833669. ISSN 0004-6361.
- "Discovery Alert! High School Student Finds a World With Two Suns". Exoplanet Exploration: Planets Beyond our Solar System. Retrieved 14 February 2020.
- Reddy, Francis (6 January 2020). "TESS Discovers Its 1st Planet Orbiting 2 Stars". NASA.
External link
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.