State of Law Coalition
The State of Law Coalition (Arabic: إئتلاف دولة القانون I'tilāf Dawlat al-Qānūn) also known as Rule of Law Coalition[11] is an Iraqi political coalition formed for the 2009 Iraqi governorate elections by the Prime Minister of Iraq at the time, Nouri al-Maliki, of the Islamic Dawa Party.
State of Law Coalition إئتلاف دولة القانون | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Leader | Nouri al-Maliki |
| Founded | 2009 |
| Ideology | Populism[1] Big tent Anti-secularism[2][3] Statism[4][5] Anti-corruption[6] |
| Political position | Syncretic[7][8] |
| Religion | Shia Islam |
| National affiliation | National Iraqi Alliance[9] |
| International affiliation | Axis of Resistance[10] |
| Colours | Red |
| Council of Representatives | 25 / 329 |
| Seats in the Governorate Councils | 126 / 440 |
| Governors | 5 / 18 |
The name was an emphasis on the improved security situation which Maliki's government had achieved through the Battle of Basra and other operations of the Iraqi Security Forces.
Due to disagreements with the Islamic Supreme Council of Iraq and the Sadrists, the Dawa Party decided not to join the Iraqi National Alliance for the 2010 Iraqi parliamentary election, but run in their own coalition: the State of Law Coalition.
2009 governorate elections
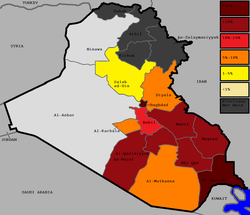
In the 2009 Iraqi governorate elections, the State of Law Coalition was composed of several political blocs:[12]
- Islamic Dawa Party – led by Iraqi Prime Minister Nouri al-Maliki
- Islamic Dawa Party – Iraq Organisation – led by Hashim Al-Mosawy
- Independent Bloc – led by Iraqi Oil Minister Hussain al-Shahristani
- Solidarity Bloc – led by former minister of state and Iraqi MP Qassim Daoud
- Islamic Union of Iraqi Turkoman – led by Iraqi MP Abbas al-Bayati
- Kurdish Feli Fraternity Movement
- Shaabani Uprising Bloc 1991
- Independents, there were also numerous independent candidates in the list.
Results
The State of Law Coalition came out as the largest list receiving 19.1% of the vote and 126 out of 440 seats.[13][14][15]
| Governorate | Percentage | Seats Won | Total Seats |
|---|---|---|---|
| al-Anbar | - | 0 | 29 |
| Babil | 12.5% | 8 | 30 |
| Baghdad | 38% | 28 | 57 |
| Basra | 37% | 20 | 35 |
| Dhi Qar | 23.1% | 13 | 31 |
| Diyala | 6% | 2 | 29 |
| Karbala | 8.5% | 9 | 27 |
| Maysan | 17.7% | 8 | 27 |
| al-Muthanna | 10.9% | 5 | 26 |
| Najaf | 16.2% | 7 | 28 |
| Ninawa | - | 0 | 37 |
| al-Qadisiyyah | 23.1% | 11 | 28 |
| Salah ad-Din | 3.5% | 2 | 28 |
| Wassit | 15.3% | 13 | 28 |
| Total: | 28.8% | 126 | 440 |
2010 parliamentary election
In the 2010 Iraqi parliamentary election, the following parties were part of the State of Law Coalition:[16]
- Islamic Dawa Party – led by Iraqi Prime Minister Nouri al-Maliki
- Islamic Dawa Party – Iraq Organisation – led by Hashim Al-Mosawy
- Anbar Salvation National Front – led by Sheikh Ali Hatem al-Suleiman
- Independent Arab Movement – led by former Deputy Prime Minister Abid Mutlak al-Jubouri
- United Independent Iraqi Bloc – led by Thaer al-Feyli
- Independent Iraqi Kafaat Gathering – led by government spokesman Ali al-Dabbagh
- The Gathering—Al-Tajamo – led by former Iraqi National List members Mahdi al-Hafez and Safiyah Suheil
- Islamic Union of Iraqi Turkoman – led by Abbas al-Bayati
- "The Independents" led by Iraqi Oil Minister Hussain al-Shahristani
- Independents, there were again numerous independent candidates in the list initially including defence minister Qadir al-Obeidi but he was banned from joining due to Ba'ath party links.
Results
| Governorate | Votes | Seats Won | Total Seats |
|---|---|---|---|
| Anbar | 6,156 | 0 | 14 |
| Babil | 231,939 | 8 | 16 |
| Baghdad | 903,360 | 26 | 68 |
| Basra | 431,217 | 14 | 24 |
| Dhi Qar | 235,446 | 8 | 18 |
| Diyala | 63,969 | 1 | 13 |
| Karbala | 179,517 | 6 | 10 |
| Kirkuk | 11,862 | 0 | 12 |
| Maysan | 102,566 | 4 | 10 |
| Muthanna | 98,998 | 4 | 7 |
| Najaf | 197,377 | 7 | 12 |
| Ninawa | 15,755 | 0 | 31 |
| Qadisiyyah | 133,067 | 4 | 11 |
| Salah ad-Din | 31,026 | 0 | 12 |
| Wassit | 149,828 | 5 | 11 |
| Compensatory seats | - | 2 | 7 |
| Total: | 2,792,083 | 89 | 325 |
2013 governorate elections
In the 2013 Iraqi governorate elections, the State of Law Coalition was composed of several political blocs:[17][18]
- Islamic Dawa Party – led by Iraqi Prime Minister Nouri al-Maliki
- Islamic Dawa Party – Iraq Organisation
- Independent Bloc – led by Iraqi Oil Minister Hussain al-Shahristani
- Badr Organization – led by Hadi Al-Amiri
- National Reform Trend – led by former Iraqi Prime Minister Ibrahim al-Jaafari
- Islamic Virtue Party – led by Abd al-Rahim al-Hasini
- Solidarity Bloc – led by former minister of state and Iraqi MP Qassim Daoud
- Islamic Union of Iraqi Turkoman – led by Iraqi MP Abbas al-Bayati
- White Iraqiya Bloc – led by Hassan Alawi
- Kurdish Feli Fraternity Movement
- Shaabani Uprising Bloc 1991
- Independents, there were also numerous independent candidates in the list.
Results
2014 parliamentary election
2018 parliamentary election
References
- "Populism, Authoritarianism, and National Security in al-Maliki's Iraq". Archived from the original on 2 October 2014. Retrieved 9 June 2015.
- "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 2018-06-16. Retrieved 2020-07-02.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)
- "مزاج الجمهور تغير.. هل تجد الأحزاب الإسلامية العراقية في "العلمانية" طوق نجاة؟". Archived from the original on 2018-06-15. Retrieved 2018-06-15.
- "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 2018-06-16. Retrieved 2018-06-16.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)
- "How Statism Drove Iraqis into the Arms of Terrorists". 2014-06-18. Archived from the original on 2018-06-16. Retrieved 2018-06-16.
- "المالكي: من يريد محاربة الفساد عليه أن يحارب المحاصصة". Archived from the original on 2018-11-01. Retrieved 2018-11-01.
- Bhan, Mona (2013-09-11). Counterinsurgency, Democracy, and the Politics of Identity in India: From Warfare to Welfare?. ISBN 9781134509904.
- Marr, Phebe (2018-05-15). The Modern History of Iraq. ISBN 9780429974069.
- "Iraq: Maliki accused of threatening Shi'a alliance break-up". Asharq Al-Awsat. 3 August 2014. Archived from the original on 9 January 2020. Retrieved 20 October 2014.
- "ظهرت الاحجام السياسية. الان بدأت معركة الأغلبية المطلقة. تشكيل الحكومة أم المعارك || قاسم متيرك". Archived from the original on 2018-11-15. Retrieved 2018-11-15.
- "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 2012-06-06. Retrieved 2010-05-14.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)
- "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 2011-07-19. Retrieved 2010-02-05.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)
- "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 2011-10-12. Retrieved 2015-02-19.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)
- "Archived copy" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2009-03-26. Retrieved 2009-03-26.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)
- Joel Wing (2009-08-24). "MUSINGS ON IRAQ". Archived from the original on 7 July 2015. Retrieved 9 June 2015.
- "State of Law Coalition". Archived from the original on 2013-07-18. Retrieved 2010-02-09.
- "As the Deadline for Forming Coalitions Expires, Maliki Creates a Shiite Alliance for Iraq's Local Elections in April 2013". Iraq and Gulf Analysis. 2012-12-21. Archived from the original on 30 June 2015. Retrieved 9 June 2015.
- http://www.ihec-iq.com/ihecftp/political-entities/etlafat-20-12-2012.pdf%5B%5D