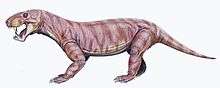
Smilesaurus
Smilesaurus is an extinct genus of gorgonopsian known from Africa. It lived during the Late Permian. It contains the single species S. ferox.[1]
| Smilesaurus | |
|---|---|
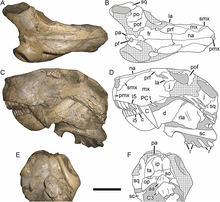 | |
| Holotype skull | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Clade: | Therapsida |
| Suborder: | †Gorgonopsia |
| Genus: | †Smilesaurus Broom, 1948 |
| Type species | |
| †Smilesaurus ferox Broom, 1948 | |
| Synonyms | |
|
Genus level
Species level
| |
Description
Smilesaurus was a large gorgonopsian, with a skull length of up to 31 centimeters. It is characterized by extremely long canine teeth, and has the proportionally longest canines of any gorgonopsian.[2][1] Unlike other gorgonopsians, which probably hunted similarly to predatory reptiles, Smilesaurus probably was a true saber-toothed predator which hunted using similar tactics to saber-toothed cats.[1] It can be distinguished by other rubidgeines by its lack of cranial pachyostosis and rugosoties, and by its relatively small orbits.[1]
Classification
The classification of Smilesaurus has been disputed. It has often been included in Rubidgeinae, but it differs from other members of the clade considerably.[1] Instead, it may be more closely related to Arctops,[3] a position supported by a phylogenetic analysis in 2018.[4]
Below is a cladogram of African gorgonopsians by Kammerer et al. in 2018.[4]
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
See also
References
- Kammerer, Christian F. (2016). "Systematics of the Rubidgeinae (Therapsida: Gorgonopsia)". PeerJ. 4: e1608. doi:10.7717/peerj.1608. PMC 4730894. PMID 26823998.
- Broom, Robert (1947). "A contribution to our knowledge of the vertebrates of the Karroo Beds of South Africa". Transactions of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. 61 (2): 577–629. doi:10.1017/S0080456800004865.
- Sigogneau-Russell, Denise (1989). Wellnhofer, Peter (ed.). Theriodontia I: Phthinosuchia, Biarmosuchia, Eotitanosuchia, Gorgonopsia. Encyclopedia of Paleoherpetology. 17 B/I. Stuttgart: Gustav Fischer Verlag. ISBN 3437304879.
- Kammerer, Christian F.; Masyutin, Vladimir (2016). "Gorgonopsian therapsids (Nochnitsa gen. nov. and Viatkogorgon) from the Permian Kotelnich locality of Russia". PeerJ. 6: e4954. doi:10.7717/peerj.4954. PMC 5995105. PMID 29900078.