Orovenator
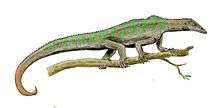
Orovenator is an extinct genus of diapsid from Lower Permian (Sakmarian stage) deposits of Oklahoma, United States. It is known from two partial skulls from the Richards Spur locality in Oklahoma. The holotype OMNH 74606 consists of a partial skull preserving snout and mandible, and the referred specimen, OMNH 74607, a partial skull preserving the skull roof, vertebrae and palatal elements. It was first named by Robert R. Reisz, Sean P. Modesto and Diane M. Scott in 2011 and the type species is Orovenator mayorum. The generic name means "mountain", oro, in Greek in reference to the Richards Spur locality, which was mountainous during the Permian period and "hunter", venator, in Latin. The specific name honours Bill and Julie May. Orovenator is the oldest and most basal neodiapsid to date.[1]
| Orovenator | |
|---|---|
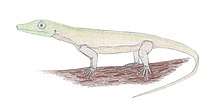 | |
| Life restoration | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Reptilia |
| Clade: | Neodiapsida |
| Genus: | †Orovenator Reisz, Modesto & Scott 2011 |
| Type species | |
| †Orovenator mayorum | |
A 2018 redescription by David Ford and Roger Benson found that Orovenator shared many similarities with varanopids, a group of reptile-like tetrapods traditionally considered to be synapsids (amniotes more closely related to mammals than to modern reptiles). However, this proposed close relation between Orovenator and varanopids did not render Orovenator a synapsid; rather, it supported a placement for Varanopidae within Diapsida.[2]
Phylogeny
Cladogram after Reisz, Modesto & Scott 2011:[1]
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
References
- Reisz, Robert R.; et al. (2011). "A new Early Permian reptile and its significance in early diapsid evolution". Proceedings of the Royal Society B. 278 (1725): 3731–3737. doi:10.1098/rspb.2011.0439. PMC 3203498. PMID 21525061.
- Ford, David P.; Benson, Roger B. J. (2018). "A redescription of Orovenator mayorum (Sauropsida, Diapsida) using high-resolution μCT, and the consequences for early amniote phylogeny". Papers in Palaeontology. 0. doi:10.1002/spp2.1236. ISSN 2056-2802.