Machine Age
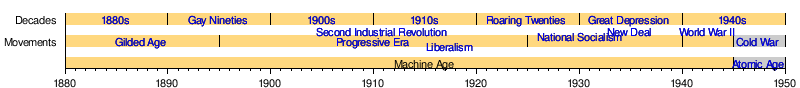
The Machine Age[1][2][3] is an era that includes the early 20th century, sometimes also including the late 19th century. An approximate dating would be about 1880 to 1945. Considered to be at a peak in the time between the first and second world wars, it forms a late part of the Second Industrial Revolution. The 1940s saw the beginning of the Atomic Age, where modern physics saw new applications such as the atomic bomb,[4] the first computers,[5] and the transistor.[6] The Digital Revolution ended the intellectual model of the machine age founded in the mechanical and heralding a new more complex model of high technology. The digital era has been called the Second Machine Age, with its increased focus on machines that do mental tasks.
| History of technology |
|---|
|
By technological eras
|
|
By type of technology
|
|
Technology timelines
|
|
Article indices |



Universal chronology
Developments
.jpg)

Artifacts of the Machine Age include:
- Reciprocating steam engine replaced by gas turbines, internal combustion engines and electric motors
- Electrification based on large hydroelectric and thermal electric power production plants and distribution systems
- Mass production of high-volume goods on moving assembly lines, particularly of the automobile[7]
- Gigantic production machinery, especially for producing and working metal, such as steel rolling mills, bridge component fabrication, and automobile body presses
- Powerful earthmoving equipment
- Steel framed buildings of great height (the skyscraper[8])
- Radio and phonograph technology
- High speed printing presses, enabling the production of low cost newspapers and mass market magazines
- Low cost appliances for the mass market that employ fractional horsepower electric motors, such as the vacuum cleaner and the washing machine
- Fast and comfortable long distance travel by railroad, automobile, and aircraft
- Development and employment of modern war machines such as tanks, aircraft, submarines and the modern battleship
- Streamline designs in automobiles and trains, influenced by aircraft design
Social influence
- The rise of mass market advertising and consumerism
- Nationwide branding and distribution of goods, replacing local arts and crafts
- Nationwide cultural leveling due to exposure to films and network broadcasting
- Mass-produced government propaganda through print, audio, and motion pictures
- Replacement of skilled crafts with low skilled labor
- Growth of strong corporations through their abilities to exploit economies of scale in materials and equipment acquisition, manufacturing, and distribution
- Corporate exploitation of labor leading to the creation of strong trade unions as a countervailing force
- Aristocracy with weighted suffrage or male-only suffrage replaced by democracy with universal suffrage, parallel to one-party states
- First-wave feminism
- Increased economic planning, including five-year plans, public works and occasional war economy, including nationwide conscription and rationing
Environmental influence
- Exploitation of natural resources with little concern for the ecological consequences; a continuation of 19th century practices but at a larger scale.
- Release of synthetic dyes, artificial flavorings, and toxic materials into the consumption stream without testing for adverse health effects.
- Rise of petroleum as a strategic resource
International relations
- Conflicts between nations regarding access to energy sources (particularly oil) and material resources (particularly iron and various metals with which it is alloyed) required to ensure national self-sufficiency. Such conflicts were contributory to two devastating world wars.
- Climax of New Imperialism and beginning of decolonization
Arts and architecture

The Machine Age is considered to have influenced:
- Dystopian films including Charlie Chaplin's Modern Times and Fritz Lang's Metropolis
- Streamline Moderne appliance design and architecture
- Bauhaus style
- Steampunk
- Modern art
See also
References
- Mentality and freedom By William Armstrong Fairburn. Page 219.
- The Playground, Volume 15 By Playground and Recreation Association of America
- Public libraries, Volume 6
- "1944: Princeton builds the A-bomb".
- "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 2011-05-19. Retrieved 2011-06-03.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)
- "The First Transistor Invented in 1947".
- "Industrialization of American Society". Engr.sjsu.edu (College of Engineering, San José State University). Archived from the original on 2010-09-19. Retrieved 2013-08-14.
- "The Plan Comes Together - Encyclopedia of Chicago". Encyclopedia.chicagohistory.org. Retrieved 2013-08-14.