Liverpool Blue Coat School
The Liverpool Blue Coat School is a grammar school in Wavertree, Liverpool, England. It was founded in 1708 by Bryan Blundell and the Reverend Robert Styth as the Liverpool Blue Coat Hospital and was for many years a boys' boarding school before reverting in September 2002 to its original coeducational remit.
| Liverpool Blue Coat School | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 | |||||||||||
| Address | |||||||||||
Church Road , , L15 9EE | |||||||||||
| Coordinates | 53.393°N 2.916°W | ||||||||||
| Information | |||||||||||
| Type | Grammar School | ||||||||||
| Motto | Non Sibi Sed Omnibus (Not for Oneself but for All) | ||||||||||
| Established | 1708 | ||||||||||
| Founders | Bryan Blundell and Rev. Robert Styth | ||||||||||
| Department for Education URN | 137916 Tables | ||||||||||
| Ofsted | Reports | ||||||||||
| Chair of Governors Provost | J.M. Shaw S.W. Elliott | ||||||||||
| Headmaster | S. Yates (temporary) | ||||||||||
| Chaplain | Interregnum | ||||||||||
| Gender | Coeducational (since 2002) | ||||||||||
| Age | 11 to 18 | ||||||||||
| Enrollment | 963 | ||||||||||
| Colour(s) | |||||||||||
| Publication | The Squirrel | ||||||||||
| Houses | Bingham Blundell Graham Shirley Styth Tod | ||||||||||
| Former pupils | Old Blues | ||||||||||
| School Hymn | Praise to the Lord, the Almighty | ||||||||||
| Website | bluecoatschoolliverpool.org.uk | ||||||||||
The school holds a long-standing academic tradition. Examination results consistently place it top of the national GCSE and A-level tables. In 2016 Blue Coat was ranked as the best school in the country based on GCSE results.[1] In 2015 it was The Sunday Times State School of the Year.[2] The acceptance rate for admissions is around fifteen percent.
In 2004 the school received a government grant of almost £8 million, together with £1 million from its foundation governors, enabling an expansion and redevelopment of its site.[3]
History
The Bluecoat School
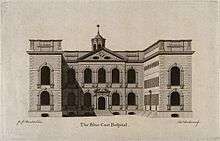
The school was founded in 1708 by Bryan Blundell and the Rev Robert Styth, a theology graduate of Brasenose College, Oxford[4] as "a school for teaching poor children to read, write and cast accounts".[5] The original charity school expanded rapidly and a new building, the present Bluecoat Arts Centre, opened in 1718. By the time of Blundell's death in 1756 there were 70 boys and 30 girls at the school, many apprenticed to local trades, especially maritime ones connected to the port. Some Old Blues became mates or masters of their ships, many emigrating to the colonies. After Blundell's death his sons further expanded the building to accommodate 200 pupils, with a new workroom, sick room, chapel and refectory. A reminder of the building's school days is some graffiti dating from the 18th century, carved into cornerstones in a secluded part of the front courtyard.[6]
Move to Wavertree


At the start of the 20th century it was decided that the school needed to move from the polluted town centre to somewhere quieter, and the village of Wavertree was the site chosen.[5] The architects chosen for the design of the new building were Briggs, Wolstenholme & Thornely,[7] most notable for the design of the Port of Liverpool Building.[8] In 1906 the school took possession of the building,[5] which was later designated Grade II-listed*.[9] Later additions include a clock tower and the Fenwick Memorial Chapel: used for assemblies by the school.[5]
Redevelopment
In 2004 work began on redeveloping the Wavertree site. Original buildings remained intact but the southern wing was converted into private accommodation and sold to part-fund the development. The school chapel, clock tower, board room, and former music room, together with administrative rooms and the formal entrance to the original building, were transferred to a new school foundation and made available to hire for private functions. Buildings that had been added to the north end of the site during the second half of the 20th century, including a swimming pool, a sixth-form centre, a gym and squash courts, were demolished to make way for new facilities. The North Wing of the original school was renovated and a new building extended it into the area previously known as the North Yard. This included laboratories, a new main entrance, an administration block, music rooms, recording and dance studios, and dining and sports halls. The remainder of the North Yard was upgraded to provide better outdoor sports facilities. The old dining hall, beneath Shirley Hall at the heart of the original building, became a library with a mezzanine ICT suite. The previous library space, itself a former dormitory, was refurbished as the new sixth-form facility.
Uniform
The school uniform consists of:[10]
- navy blue blazer with school badge
- V-neck grey school pullover or cardigan with school crest
- white shirt
- school tie
- knee-length grey skirt for girls
- grey trousers for boys
- grey socks/tights and black shoes
Ties
The school is also known for its wide variety of school ties, the most common of which is the royal blue tie with an embroidered school coat of arms (fig. 1). Sixth Form Prefects may wear a navy blue tie with alternating blue and gold stripes (fig. 2), and those who are in the first XI may wear the school sports tie, a navy blue tie with gold school coats of arms criss-crossing it (fig. 3). The Old Blues tie, a navy blue tie with alternating squirrels (the school's crest) and blue stripes, is worn by those pupils whose father was once a student at the school (and therefore members of the Old Blues Society)(Fig. 4). Other ties occasionally seen include a navy blue tie with stripes in the four school form colours (awarded for being in the first XI for 3 separate sports teams)(Fig. 5), and a navy blue with two gold stripes (Fig. 6). Only the royal blue and prefect ties are commonly in use.
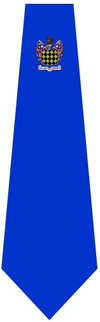 Fig.1- Royal Blue Tie |
 Fig. 2- Sixth Form Prefect Tie |
 Fig. 3- First XI Tie |
 Fig. 4- Old Blues Tie |
 Fig 5- Tie for Members of the First XI in Three Sports |
 Fig. 6- Navy Blue Tie with Two Gold Stripes |
Shortly after the introduction of house Tod in 2017, the conventional royal blue and prefect ties were modified. Both ties now feature diagonal stripes representing the student's form's colour (below), with these stripes replacing the gold stripes on the prefect tie.
House system
The school currently has six houses. Upon entrance in Year 7, pupils are allocated a form which they will be a member of throughout their time at The Blue Coat School. As well as the students, teachers at the school are often members of a house. There are approximately thirty students in a form and approximately 250 students per house. The houses are governed by a House Council which are composed of Heads of House, House Deputies, Form Captains and a member of staff. There are regular inter-house competitions, ranging from the inter-house football competition to inter-house debating competitions, in which the houses can gain house points which are then added to a running total and published in league tables, culminating in the annual inter-house league table. The newest houses are Styth and Tod which became the fifth and sixth houses of the current school in 2015 and 2017 respectively, to accommodate the 30 new additional first year students, and named after one of the school's former Provosts. There are also a number of boarding houses that were discontinued when the school ceased to be a boarding school in the late 20th century.[11]
School Houses
- Bingham
- Blundell
- Graham
- Shirley
- Styth
- Tod
Boarding Houses
- Earle
- MacAuley
- Styth
- Tinne
Brotherly Society
The school's alumni association is the Brotherly Society, founded in 1838. Alumni are known as "Old Blues".[12] The society was set up to provide help, advice and in some cases financial assistance to students for at least two years after leaving the school.[13] Since the Second World War there has been less need for such assistance so the Society has turned its efforts towards objects that would benefit the School in general.
The generosity of the Society can be found throughout the Blue Coat School's history. In 1938, to celebrate the Society's centenary, the Society provided the oak pews in the chapel. In 1963 the Society provided the stained glass south window of the Chapel to celebrate its 125th anniversary, and in 1952 the Old Blues' Memorial Library was presented in remembrance of the Old Blues who gave their lives in the two World Wars.[13]
The Squirrel
The school's publication is The Squirrel. The magazine is currently published annually and is almost entirely written and produced by students. The magazine was first released in the Summer of 1949 under the leadership of the Provost John Bingham in order to show the 'fruits of hard work' and the activities, achievements, and involvement of the students and staff in school life.[14]
During the 1950s The Squirrel entered an era of particular popularity and enthusiasm, ultimately leading to its publication becoming a termly occurrence. It was during this period that the magazine developed some of its most memorable features, notably including De Praefectis which recorded the various humorous situations and conversations of prefects at the school and is mostly remembered for satirising the eccentricities of individual prefects, often employing a pretentious overuse of Latin to this effect. In subsequent years various other magazines written by students were produced as parodies of The Squirrel, most notably in the form of The Swivel which gained an underground following and was particularly popular on account of the strong criticisms it leveled at the school and its masters.[14]
In 2017 the school published The Squirrel both in paper form and online for the first time. A new website 'The Squirrel Blog' was created both to publish current and future editions of the magazine and to digitalise the school's archive of every issue of The Squirrel since 1949.
Headmasters and Headmistress
| Headmaster/Headmistress | Start year | End year |
|---|---|---|
| Rev Robert Styth, MA (Oxon) | 1708 | 1713 |
| Mr William Trenton | 1717 | 1723 |
| Mr Theophilus Price | 1723 | 1725 |
| Mr Horton | 1725 | 1775 |
| Rev John Shakleton | 1776 | 1779 |
| Mr John Smith (Old Blue) | 1779 | 1799 |
| Mr Robert Parkes | 1800 | 1800 |
| Mr George Chambers | 1801 | 1811 |
| Mr John Fallows | 1812 | 1816 |
| Mr R.W. Bamford | 1817 | 1819 |
| Mr William Forster | 1820 | 1848 |
| Mr Thomas Wood, BA (Cantab) | 1849 | 1862 |
| Mr Thomas Haughton | 1863 | 1867 |
| Mr George Tinker | 1868 | 1869 |
| Mr Thomas Haughton | 1870 | 1888 |
| Mr Arthur Mercer | 1889 | 1920 |
| Mr Harry C. Hughes | 1920 | 1926 |
| Rev R. Bruce Wilson, BA (Oxon) | 1927 | 1944 |
| Rev T.C. Heritage, MA (Oxon) | 1944 | 1945 |
| Mr G.G. Watcyn, BA | 1945 | 1968 |
| Mr H.P. Arnold-Craft JP, MA (Oxon) | 1968 | 1989 |
| Mr John C. Speller BA, MA (Ed), FRSA | 1989 | 1997 |
| Mr Michael R. Bell BA (Hons) FIMgt | 1997 | 2001 |
| Mr Michael George 'Sandy' Tittershill CertEd. NPQH | 2001 | 2008 |
| Mrs Debbie Silcock BSc PGCE NPQH | 2008 | 2015 |
| Mr Michael Pennington BSc Hons PGCE NPQH | 2015 | 2020 |
Provosts
| Provost | Start year | End year |
|---|---|---|
| Rev. Robert Styth, M.A. | 1709 | 1713 |
| The Rt. Hon. Bryan Blundell | 1713 | 1756 |
| Richard Blundell | 1756 | 1760 |
| Jonathan Blundell | 1760 | 1796 |
| Nicholas Ashton | 1796 | 1797 |
| The Rt. Hon. Clayton Tarleton | 1797 | 1798 |
| John Bolton | 1798 | 1799 |
| Edward Houghton | 1799 | 1800 |
| James Gerrard, M.D. | 1800 | 1802 |
| William Cubbin | 1802 | 1805 |
| John Keay | 1805 | 1808 |
| William Leigh | 1808 | 1809 |
| George Brown | 1809 | 1811 |
| Edward Sephton | 1811 | 1812 |
| William Beckwith | 1812 | 1813 |
| Matthew Gregson | 1813 | 1814 |
| Bryan Blundell | 1814 | 1815 |
| The Rt. Hon. Henry Blundell-Hollinshead | 1815 | 1817 |
| James Bourne | 1817 | 1818 |
| Rev. William Blundell B.A. | 1818 | 1819 |
| Richard Dobson | 1819 | 1835 |
| The Rt. Hon. James Aspinall | 1835 | 1838 |
| Anthony Swainson | 1838 | 1848 |
| Joseph Langton | 1848 | 1849 |
| Richard Gibson | 1849 | 1854 |
| Edward Guy Deane | 1854 | 1857 |
| William Langton | 1857 | 1870 |
| Hugh Perkins | 1870 | 1885 |
| John Ernest Tinne | 1885 | 1926 |
| Louis Cappel | 1926 | 1928 |
| John J. Verdin-Cooke | 1928 | 1932 |
| John A. Tinne | 1932 | 1933 |
| John Bingham | 1933 | 1950 |
| F.J. Williams | 1950 | 1955 |
| Sir Alan Todd, C.B.E., L.L.D. | 1955 | 1968 |
| J. Malcolm Harrison | 1968 | 1976 |
| T.I.F. Tod, F.C.A. | 1976 | 1991 |
| Peter Healey, J.P., B.A. | 1991 | 2006 |
| Rodney V. McDermott | 2006 | 2007 |
| Gerard A. Jolliffe | 2007 | 2014 |
| Stephen W. Elliott | 2014 | 2017 |
Notable former pupils
- Richard Ansdell, Noted oil painter and engraver
- Mitch Benn, Musician and comedian
- Stephen Broadbent, Sculptor
- Philip Clarke, CEO of Tesco between 2011-2014
- Craig Curran, Footballer currently playing for Dundee United
- Stuart Ford Founder and CEO of IM Global
- Tom Greggs, Marischal Professor of Divinity, University of Aberdeen
- Jonathan Harvey, Playwright
- The Rt. Hon. Evan Harris, Former Liberal Democrat MP for Oxford West and Abingdon between 1997-2010
- Graham Hughes, Adventurer
- Alfred Lennon, Father of Beatle John Lennon, musician
- Kevin Nolan, Footballer (Bolton, Newcastle, West Ham)
- Andrew Norton, Chairman of the US Pirate Party
- Stephen Parry, Olympic Swimmer
- Baron Christopher Rennard, Former Liberal Democrat chief executive
- Neil Sang Licensed Football Agent, Radio pundit and former professional footballer
Notable people associated with the school
- David Alton, Baron Alton of Liverpool, ex-Member of Parliament, was a trustee of the school, and has a quad named in his honour.
- the Blundell-Hollinshead-Blundell family, descendants of Bryan Blundell, the founder, many have been trustees at the school. The family have gone on to produce notable military men and members of the Austrian royal family.
- Reginald Harrison, famous British surgeon and Vice President of the Royal College of Surgeons was the school's surgeon in the late 19th century.
- David Houlder, former sub-organist at Liverpool Anglican Cathedral and former organist at York Minster. Houlder was the school's Director of Music between 1981 and 1999.
- W. H. Jude, composer and organist. Jude was the school's organist in the late 19th century.
- The Rt. Hon. Norman Pannell finance manager, politician and conservative MP. Pannell was a governor of the school.
References
- https://www.telegraph.co.uk/education/leaguetables/12109955/Top-100-secondary-schools-by-GCSE-results-2015.html
- http://www.thesundaytimes.co.uk/sto/Parent_Power/
- Salmon, Tony (2007). "Save the Liverpool Blue Coat School". savethebluecoat.webeden.co.uk. Retrieved 24 June 2009.
- "Stermont-Synge". British History Online. Retrieved 28 November 2015.
- "A brief history of the school". The Liverpool Blue Coat School. Archived from the original on 7 July 2013. Retrieved 6 January 2010.
- "Bluecoat Heritage" (PDF). Bluecoat Chambers. Archived from the original (PDF) on 4 January 2014. Retrieved 24 May 2015.
- Pollard, Pevsner, Joseph, Richard, Nikolaus, Sharples (2006). Lancashire: Liverpool and the southwest.CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
- "The Port of Liverpool Building". liverpoolworldheritage.com. Archived from the original on 29 April 2009. Retrieved 29 June 2009.
- "The Liverpool Blue Coat School General information". Schools Net. Retrieved 29 June 2009.
- "Prospectus: Uniform". The Blue Coat School. Retrieved 23 January 2016.
- "Boarding House Rules (1969)". Liverpool Old Blues. Retrieved 28 November 2015.
- Kelly, Andy (19 January 2006). "Million-Pound Target for Historic Blue Coat". Liverpool Daily Post. Liverpool. Archived from the original on 7 October 2018. Retrieved 30 January 2016 – via HighBeam Research.
- "Brotherly Society". The Blue Coat School. Retrieved 28 November 2015.
- "The History of the Squirrel: The Squirrel Blog". squirrel.bluecoatschoolliverpool.org.uk. Retrieved 25 October 2017.
External links
- Official school website
- BBC Education League Tables listing
- Ofsted inspection report (June 2004)
- Extract from Discovering Historic Wavertree
- Blue Coat Arts Centre
- South Wing Apartments Development
- Leavers Ball 2006 Pictures
- Historic England. "School (1280374)". National Heritage List for England.
- Historic England. "Chapel (1068325)". National Heritage List for England.