Knot
A knot is an intentional complication in cordage which may be practical or decorative, or both. Practical knots are classified by function, including hitches, bends, loop knots, and splices: a hitch fastens a rope to another object; a bend fastens two ends of a rope to each another; a loop knot is any knot creating a loop, and a splice is a any multi-strand knot, including bends and loops.[1] A knot may also refer, in the strictest sense, to a stopper or knob at the end of a rope to keep that end from slipping through a grommet or eye. Knots have excited interest since ancient times for their practical uses, as well as their topological intricacy, studied in the area of mathematics known as knot theory.
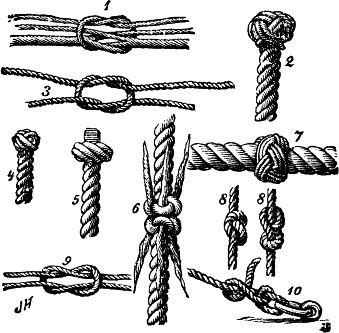
- Yarn knot (ABoK #2688)
- Manrope knot (ABoK #847)
- Granny knot (ABoK #1206)
- Wall and crown knot (ABoK #670, #671)
- Matthew Walker's knot (ABoK #681)
- Shroud knot (ABoK #1580)
- Turk's head knot (ABoK #1278-#1397)
- Overhand knot, Figure-of-eight knot (ABoK #514, #520)
- Reef knot, Square knot (ABoK #1402)
- Two half-hitches (ABoK #54)

Use
There is a large variety of knots, each with properties that make it suitable for a range of tasks. Some knots are used to attach the rope (or other knotting material) to other objects such as another rope, cleat, ring, or stake. Some knots are used to bind or constrict objects. Decorative knots usually bind to themselves to produce attractive patterns.
Teaching


While some people can look at diagrams or photos and tie the illustrated knots, others learn best by watching how a knot is tied. Knot tying skills are often transmitted by sailors, scouts, climbers, canyoners, cavers, arborists, rescue professionals, stagehands, fishermen, linemen and surgeons. The International Guild of Knot Tyers is an organization dedicated to the promotion of knot tying.
Applications
Truckers in need of securing a load may use a trucker's hitch, gaining mechanical advantage. Knots can save spelunkers from being buried under rock. Many knots can also be used as makeshift tools, for example, the bowline can be used as a rescue loop, and the munter hitch can be used for belaying. The diamond hitch was widely used to tie packages on to donkeys and mules.
In hazardous environments such as mountains, knots are very important. In the event of someone falling into a ravine or a similar terrain feature, with the correct equipment and knowledge of knots a rappel system can be set up to lower a rescuer down to a casualty and set up a hauling system to allow a third individual to pull both the rescuer and the casualty out of the ravine. Further application of knots includes developing a high line, which is similar to a zip line, and which can be used to move supplies, injured people, or the untrained across rivers, crevices, or ravines. Note the systems mentioned typically require carabiners and the use of multiple appropriate knots. These knots include the bowline, double figure eight, munter hitch, munter mule, prusik, autoblock, and clove hitch. Thus any individual who goes into a mountainous environment should have basic knowledge of knots and knot systems to increase safety and the ability to undertake activities such as rappelling.
Knots can be applied in combination to produce complex objects such as lanyards and netting. In ropework, the frayed end of a rope is held together by a type of knot called a whipping knot. Many types of textiles use knots to repair damage. Macramé, one kind of textile, is generated exclusively through the use of knotting, instead of knits, crochets, weaves or felting. Macramé can produce self-supporting three-dimensional textile structures, as well as flat work, and is often used ornamentally or decoratively.
Properties
Strength
Knots weaken the rope in which they are made.[2] When knotted rope is strained to its breaking point, it almost always fails at the knot or close to it, unless it is defective or damaged elsewhere. The bending, crushing, and chafing forces that hold a knot in place also unevenly stress rope fibers and ultimately lead to a reduction in strength. The exact mechanisms that cause the weakening and failure are complex and are the subject of continued study. Special fibers that show differences in color in response to strain are being developed and used to study stress as it relates to types of knots.[3][4]
Relative knot strength, also called knot efficiency, is the breaking strength of a knotted rope in proportion to the breaking strength of the rope without the knot. Determining a precise value for a particular knot is difficult because many factors can affect a knot efficiency test: the type of fiber, the style of rope, the size of rope, whether it is wet or dry, how the knot is dressed before loading, how rapidly it is loaded, whether the knot is repeatedly loaded, and so on. The efficiency of common knots ranges between 40—80% of the rope's original strength.[5]
In most situations forming loops and bends with conventional knots is far more practical than using rope splices, even though the latter can maintain nearly the rope's full strength. Prudent users allow for a large safety margin in the strength of rope chosen for a task due to the weakening effects of knots, aging, damage, shock loading, etc. The working load limit of a rope is generally specified with a significant safety factor, up to 15:1 for critical applications.[6] For life-threatening applications, other factors come into play.
Security
Even if the rope does not break, a knot may still fail to hold. Knots that hold firm under a variety of adverse conditions are said to be more secure than those that do not. Repeated, dynamic loads will cause virtually every knot to fail.[7]
The main ways knots fail to hold are:
Slipping
The load creates tension that pulls the rope back through the knot in the direction of the load. If this continues far enough, the working end passes into the knot and the knot unravels and fails. This behavior can worsen when the knot is repeatedly strained and let slack, dragged over rough terrain, or repeatedly struck against hard objects such as masts and flagpoles.
Even with secure knots, slippage may occur when the knot is first put under real tension. This can be mitigated by leaving plenty of rope at the working end outside of the knot, and by dressing the knot cleanly and tightening it as much as possible before loading. Sometimes, the use of a stopper knot or, even better, a backup knot can prevent the working end from passing through the knot; but if a knot is observed to slip, it is generally preferable to use a more secure knot. Life-critical applications often require backup knots to maximize safety.
Capsizing
To capsize (or spill) a knot is to change its form and rearrange its parts, usually by pulling on specific ends in certain ways.[5] When used inappropriately, some knots tend to capsize easily or even spontaneously. Often the capsized form of the knot offers little resistance to slipping or unraveling. A reef knot, when misused as a bend, can capsize dangerously.
Sometimes a knot is intentionally capsized as a method of tying another knot, as with the "lightning method" of tying a bowline. Some knots, such as the carrick bend, are generally tied in one form then capsized to obtain a stronger or more stable form.
Sliding
In knots that are meant to grip other objects, failure can be defined as the knot moving relative to the gripped object. While the knot itself does not fail, it ceases to perform the desired function. For instance, a simple rolling hitch tied around a railing and pulled parallel to the railing might hold up to a certain tension, then start sliding. Sometimes this problem can be corrected by working-up the knot tighter before subjecting it to load, but usually the problem requires either a knot with more wraps or a rope of different diameter or material.
Releasability
Knots differ in the effort required to untie them after loading. Knots that are very difficult to untie, such as the water knot, are said to "jam" or be jamming knots. Knots that come untied with less difficulty, such as the Zeppelin bend, are referred to as "non-jamming".
Components
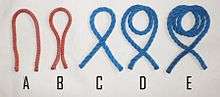
Bight
- A bight is any curved section, slack part, or loop between the ends of a rope, string, or yarn.
Bitter end
- As a ropeworker's term, "bitter end" refers to the end of a rope that is tied off. In British nautical usage, the bitter end is the ship end of the anchor cable, secured by the anchor bitts and the bitter pin in the cable locker under the forecastle. At anchor, the more anchor line that is paid out, the better the anchor's hold. In a storm, if the anchor drags, ships will pay out more and more anchor line until they reach the "bitter end." At this point, they can only hope the anchor holds, hence the expression "hanging on to the bitter end". (A bitt is a metal block with a crosspin for tying lines to, also found on piers.)
Loop
- A curve narrower than a bight but with separate ends.
Elbow
- Two crossing points created by an extra twist in a loop or a circle.
Standing end
- The standing end is the longer end of the rope not involved in the knot, often shown as unfinished. It is often (but not always) the end of the rope under load after the knot is complete. For example, when a clove hitch ties a boat to a pier, the end going to the boat is the standing end.
Standing part
- Section of line between knot and the standing end (seen above).
Turn
- A turn or single turn is a curve with crossed legs.
- A round turn is the complete encirclement of an object; requires two passes.
- Two round turns circles the object twice; requires three passes.
Working end
- The active end of a line used in making the knot. May also be called the "running end", "live end", or "tag end".
Working part
- Section of line between knot and the working end.
Knot categories
The list of knots is extensive, but common properties allow for a useful system of categorization. For example, loop knots share the attribute of having some kind of an anchor point constructed on the standing end (such as a loop or overhand knot) into which the working end is easily hitched, using a round turn. An example of this is the bowline. Constricting knots often rely on friction to cinch down tight on loose bundles; an example is the Miller's knot. Knots may belong to more than one category.
- Bend
- A knot uniting two lines (for knots joining two ends of the same line, see binding knots or loops). List of bends.
- Binding
- A knot that restricts object(s) by making multiple winds. List of binding knots.
- Coil knot
- Knots used to tie up lines for storage.
- Decorative knot
- A complex knot exhibiting repeating patterns often constructed around and enhancing an object. List of decorative knots.
- Hitch
- A knot tied to a post, cable, ring, or spar. List of hitch knots.
- Lashing
- A knot used to hold (usually) poles together.
- Loop
- A knot used to create a closed circle in a line. List of loop knots.
- Plait (or braid)
- A number of lines interwoven in a simple regular pattern. List of plait knots.
- Slip (or running)
- A knot tied with a hitch around one of its parts. In contrast, a loop is closed with a bend. While a slip knot can be closed, a loop remains the same size. List of slip knots.
- Slipped
- Some knots may be finished by passing a bight rather than the end, for ease of untying. The common shoelace knot is an example, being a reef knot with both ends slipped.
- Seizing
- A knot used to hold two lines or two parts of the same line together. List of seizing knots.
- Sennit
- A number of lines interwoven in a complex pattern. See also Chain sinnet.
- Splice
- A knot formed by interweaving strands of rope rather than whole lines. More time-consuming but usually stronger than simple knots. List of splices.
- Stopper
- A knot tied to hold a line through a hole.
- Whipping
- A binding knot used to prevent another line from fraying.
Basic useful knots
- Alpine butterfly knot for a secure loop in the middle of a rope when the ends aren't free
- Bowline for tying a loop in the end of a rope, as around one's waist or to secure a ring or grommet. The knot is also used as an anchor knot and is used in many knot systems that are used in mountainous terrain such as a highline or hauling system.
- Constrictor knot for making bundles or cinching the neck of a sack, though this knot jams and may need to be cut
- Figure-eight knot as a stopper
- Grass bend for tying belts together, though insecure with ropes
- Monkey's fist used to weight the end of a rope
- Prusik for ascending a rope
- Reef knot (square knot), a common but insecure binding knot for joining the ends of a piece of cordage wrapped around an object or objects
- Sheet bend for joining the ends of two ropes, which need not be the same diameter
- Double sheet bend for tying the ends of two dissimilarly sized ropes together
- Spanish bowline used to hoist crewmen aloft or suspend them over the side
- Versatackle for hoisting heavy loads and tightening rigging
- Water knot for tying a knot in flat material such as nylon webbing
Hitches
- Anchor bend (or anchor hitch) for tying a rope to a boat anchor
- Clove hitch for tying a rope to a pole – simple and won't jam, but not particularly secure and won't work on rectangular shapes
- Buntline hitch for tying a rope to a pole or other shape, but can jam
- Diamond hitch for packing trail animals
- Rolling hitch for securing a rope to a pole when the pull is lengthwise rather than outward, or to tie one rope to the middle of another
- Taut-line hitch (or Midshipman's hitch) for forming an adjustable (ratcheting) loop that does not slip smaller under tension
- Timber hitch for securing or hauling long narrow loads, with the pull in one direction
- Trucker's hitch for clinching down a load
Trick knots
Trick knots are knots that are used as part of a magic trick, a joke, or a puzzle. They are useful for these purposes because they have a deceptive appearance, being easier or more difficult to tie or untie than their appearance would suggest. The easiest trick knot is the slip knot.[8] Other noted trick knots include:
- Grief knot. The starkly differing behavior of the knot, depending on how it is arranged, has been exploited as the basis of a parlor trick.[9] When pulling on the standing ends the knot starts slipping and the working ends become crossed. By twisting the working ends so that they uncross and then recross in reverse, the knot's structure capsizes so that it will no longer slip. The twisting motion resembles the turning of a key, "locking" and "unlocking" the knot.
- Tom fool's knot, used as a trick knot due to the speed with which it can be made.
Knot theory
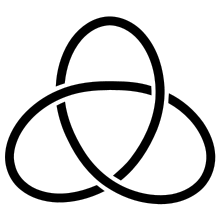
Knot theory is a branch of topology. It deals with the mathematical analysis of knots, their structure and properties, and with the relationships between different knots. In topology, a knot is a figure consisting of a single loop with any number of crossing or knotted elements: a closed curve in space which may be moved around so long as its strands never pass through each other. As a closed loop, a mathematical knot has no proper ends, and cannot be undone or untied; however, any physical knot in a piece of string can be thought of as a mathematical knot by fusing the two ends. A configuration of several knots winding around each other is called a link. Various mathematical techniques are used to classify and distinguish knots and links. For instance, the Alexander polynomial associates certain numbers with any given knot; these numbers are different for the trefoil knot, the figure-eight knot, and the unknot (a simple loop), showing that one cannot be moved into the other (without strands passing through each other).[10]
Physical theory of friction knots
A simple mathematical theory of hitches has been proposed by Bayman[11] and extended by Maddocks and Keller.[12] It makes predictions that are approximately correct when tested empirically.[13] No similarly successful theory has been developed for knots in general.
Knot tying

Knot tying consists of the techniques and skills employed in tying a knot in rope, nylon webbing, or other articles. The proper tying of a knot can be the difference between an attractive knot and a messy one, and occasionally life and death. It is important to understand the often subtle differences between what works, and what doesn't. For example, many knots "spill" or pull through, particularly if they are not "backed up," usually with a single or double overhand knot to make sure the end of the rope doesn't make its way through the main knot, causing all strength to be lost.
Difficulty
The tying of a knot may be very straightforward (such as with an overhand knot), or it may be more complicated, such as a monkey's fist knot. Tying knots correctly requires an understanding of the type of material being tied (string, cord, monofilament line, kernmantle rope, or nylon webbing). For example, cotton string may be very small and easy to tie with much internal friction to keep it from falling apart once tied, while stiff 5/8" thick kernmantle rope will be very difficult to tie, and may be so slick as to tend to come apart once tied.
Material
The form of the material will influence the tying of a knot as well. Rope is round in cross-section, and has little dependence upon the manner in which the material is tied. Nylon webbing, on the other hand, is flat, and usually "tubular" in construction, meaning that it is spiral-woven, and has a hollow core. In order to retain as much of the strength as possible with webbing, the material must be tied "flat" such that parallel sections do not cross, and that the sections of webbing are not twisted when they cross each other within a knot.
The crossing of strands is important when dealing with round rope in other knots; for example, the figure-eight loop loses strength when strands are crossed while the knot is being "finished" and tightened. Moreover, the standing end or the end from which the hauling will be done must have the greater radius of curvature in the finished knot to maximize the strength of the knot.
Tools
Tools are sometimes employed in the finishing or untying of a knot, such as a fid, a tapered piece of wood that is often used in splicing. With the advent of wire rope, many other tools are used in the tying of "knots." However, for cordage and other non-metallic appliances, the tools used are generally limited to sharp edges or blades such as a sheepsfoot blade, occasionally a fine needle for proper whipping of laid rope, a hot cutter for nylon and other synthetic fibers, and (for larger ropes) a shoe for smoothing out large knots by rolling them on the ground.
Use by animals
The hagfish is known to strip slime from its skin by tying itself into a simple overhand knot, and moving its body to make the knot travel toward the tail. It also uses this action in reverse (tail to head) to pry out flesh after biting into a carcass.
See also
- Circuit topology
- Chinese knotting
- Gordian Knot
- International Guild of Knot Tyers
- List of knots
- Quipu
References
Citations
- Ashley, Clifford W. (1944), The Ashley Book of Knots, New York: Doubleday, p. 12
- Richards, Dave (2005). "Knot Break Strength vs Rope Break Strength". Nylon Highway. Vertical Section of the National Speleological Society (50). Retrieved 2010-10-11.
- Greenfieldboyce, Nell (January 2, 2020). "A Knotty Problem Solved". All Things Considered. Retrieved 3 January 2020.
- Patil, Vishal P.; Sandt, Joseph D.; Kolle, Mathias; Dunkel, Jörn (3 January 2020). "Topological Mechanics of Knots and Tangles". Science. 367 (6473): 71–75. doi:10.1126/science.aaz0135. Retrieved 3 January 2019.
- Warner, Charles (1996), "Studies on the Behaviour of Knots", in Turner, J.C.; van de Griend, P. (eds.), History and Science of Knots, K&E Series on Knots and Everything, 11, Singapore: World Scientific Publishing, pp. 181–203, ISBN 978-981-02-2469-1
- "Knot & Rope Safety". Animated Knots by Grog. 2010. Archived from the original on April 7, 2015. Retrieved 2010-09-14.. "Knot & Rope Safety", AnimatedKnots.com. Accessed April 2016.
- Daily-Diamond, Christopher A. (12 April 2017). "The roles of impact and inertia in the failure of a shoelace knot". Proceedings of the Royal Society. 473 (2200): 20160770. doi:10.1098/rspa.2016.0770. PMC 5415684. PMID 28484324.
- Karl Fulves, Joseph K. Schmidt, Self-Working Rope Magic: 70 Foolproof Tricks (1990), page 17.
- Ashley, Clifford W. (1944), The Ashley Book of Knots, New York: Doubleday, p. 415
- Nakanishi, Yasutaka; Okada, Yuki (2012). "Differences of Alexander polynomials for knots caused by a single crossing change". Topology and Its Applications. 159 (4): 1016–1025. doi:10.1016/j.topol.2011.11.023.
- Bayman, "Theory of hitches," Am J Phys, 45 (1977) 185
- Maddocks, J.H. and Keller, J. B., "Ropes in Equilibrium," SIAM J Appl. Math., 47 (1987), pp. 1185–1200.
- "The physics of knots". www.lightandmatter.com.
General sources
- Clifford W. Ashley. The Ashley Book of Knots. Doubleday, New York. ISBN 0-385-04025-3.
- Geoffrey Budworth (1999). The Ultimate Encyclopedia of Knots & Ropework. Annes Publishing Limited. ISBN 1-55267-986-1.
- John Cassidy (1985). The Klutz Book of Knots. Klutz Press, Palo Alto, California. ISBN 0-932592-10-4.
- Cyrus L. Day. Knots & Splices. International Marine/McGraw-Hill Companies. ISBN 0-87742-252-4.
- Raoul Graumont. Handbook of Knots. Cornell Maritime Press/Tidewater Publishers. ISBN 0-87033-030-6.
- R.S. Lee. All The Knots You Need. Algrove Publishing. ISBN 0-921335-47-4.
- Allen Padgett and Bruce Smith. On Rope. National Speleological Society. ISBN 0-9615093-2-5.
- Des Pawson (2001). Pocket Guide to Knots & Splices. Produced for Propsero Books by RPC Publishing Ltd., London. ISBN 1-55267-218-2.
- Brion Toss. The Complete Rigger's Apprentice. International Marine/McGraw-Hill Companies. ISBN 0-07-064840-9.
- J. C. Turner and P. van de Griend (ed.) (1996). History and Science of Knots. World Scientific. ISBN 981-02-2469-9.
External links
| Wikibooks has a book on the topic of: Simplified list of knots |
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Knots. |
.jpg)
.jpg)