June 2020 lunar eclipse
A penumbral lunar eclipse took place on 5 June 2020. It was the second of four penumbral lunar eclipses in 2020.[1]
| Penumbral Lunar Eclipse 5 June 2020 | |
|---|---|
 View from Johannesburg, South Africa 19:18 UTC | |
 The moon passes west to east through the earth's southern penumbral shadow. | |
| Series (and member) | 111 (67 of 71) |
| Duration (hr:mn:sc) | |
| Penumbral | 3:18:13 |
| Contacts | |
| P1 | 17:45:50 UTC |
| Greatest | 19:25:02 |
| P4 | 21:04:03 |
Visibility
It was visible in most parts of Europe (except northern Scandinavia), Asia (except North-East of Russian Far East), Africa, Australia, eastern parts of South America and Antarctica.
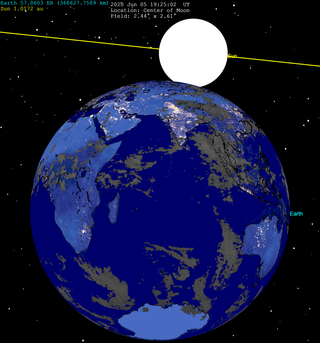 |
 Visibility map |
Gallery
 San Jose del Monte, Philippines, 18:51 UTC
San Jose del Monte, Philippines, 18:51 UTC Hefei, China, 19:25 UTC
Hefei, China, 19:25 UTC_on_June_6%2C_2020.jpg) Nakhodka, Russia, 19:26 UTC
Nakhodka, Russia, 19:26 UTC.jpg) Moscow, Russia, 19:33 UTC
Moscow, Russia, 19:33 UTC.jpg) Blora Regency, Indonesia, 19:39 UTC
Blora Regency, Indonesia, 19:39 UTC Logroño, Spain, 19:56 UTC
Logroño, Spain, 19:56 UTC Surabaya, Indonesia, 19:25 UTC
Surabaya, Indonesia, 19:25 UTC
Related eclipses
Eclipses of 2020
Lunar year series
| Lunar eclipse series sets from 2020–2023 | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Descending node | Ascending node | |||||||
| Saros | Date | Type Viewing |
Gamma | Saros | Date Viewing |
Type Chart |
Gamma | |
111 |
2020 Jun 05 |
Penumbral |
1.24063 | 116 | 2020 Nov 30 |
Penumbral |
-1.13094 | |
| 121 | 2021 May 26 |
Total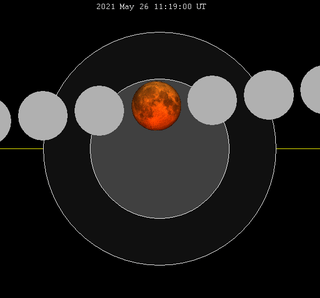 |
0.47741 | 126 | 2021 Nov 19 |
Partial |
-0.45525 | |
| 131 | 2022 May 16 |
Total |
-0.25324 | 136 | 2022 Nov 08 |
Total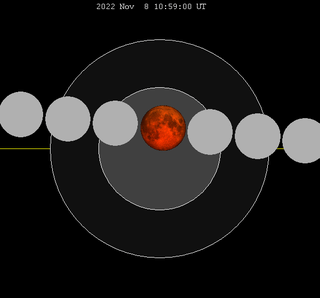 |
0.25703 | |
| 141 | 2023 May 05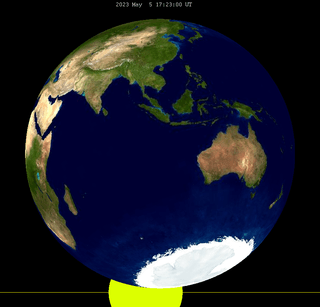 |
Penumbral |
-1.03495 | 146 | 2023 Oct 28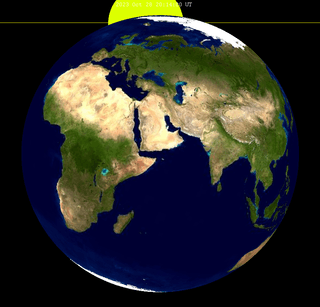 |
Partial |
0.94716 | |
| Last set | 2020 Jul 05 | Last set | 2020 Jan 10 | |||||
| Next set | 2024 Mar 25 | Next set | 2024 Sep 18 | |||||
Saros series
It is part of Saros cycle 111.
Half-Saros cycle
A lunar eclipse will be preceded and followed by solar eclipses by 9 years and 5.5 days (a half saros).[2] This lunar eclipse is related to two partial solar eclipses of Solar Saros 118.
| June 1, 2011 | June 12, 2029 |
|---|---|
 |
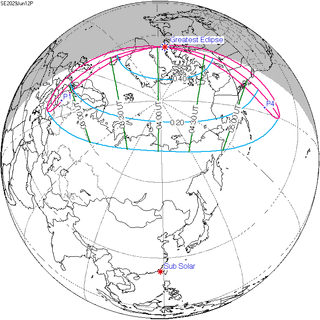 |
gollark: Wait, no, I can account for them all, it's fine.
gollark: Huh, weird, why does my server have 4 active connections?
gollark: Why would my bot be vulnerable to SQL injection? I'm not that dumb.
gollark: (I suppose I shouldn't be surprised by the amount of spammy exploit stuff but it's quite funny)
gollark: (this is a slightly nonstandard log format, but it's host, IP, time, HTTP request line, status, length of response, refer(r)er and user agent)
See also
- List of lunar eclipses and List of 21st-century lunar eclipses
References
- 2020 Jun 05 chart: Eclipse Predictions by Fred Espenak, NASA/GSFC
- Mathematical Astronomy Morsels, Jean Meeus, p.110, Chapter 18, The half-saros
External links
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.

