August 1970 lunar eclipse
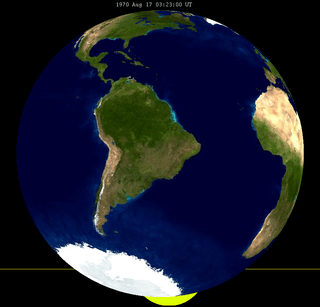
A partial lunar eclipse took place on August 17, 1970. The Earth's shadow on the Moon was clearly visible in this eclipse, with 41% of the Moon in shadow; the partial eclipse lasted for 2 hours and 11 minutes. It was the second of two lunar eclipses in 1970.[1]
| Partial Lunar Eclipse August 17, 1970 | |
|---|---|
| (No photo) | |
 The Moon passes west to east (right to left) across the Earth's umbral shadow, shown in hourly intervals. | |
| Series | 118 (49 of 74) |
| Duration (hr:mn:sc) | |
| Partial | 4:30:41.5 |
| Penumbral | 2:11:22.5 |
| Contacts | |
| P1 | 01:08:04.9 UTC |
| U1 | 02:17:44.6 |
| Greatest | 03:23:25.6 |
| U4 | 04:29:07.1 |
| P4 | 05:38:46.4 |
More details about the Partial Lunar Eclipse of 17 August 1970.
Penumbral Magnitude: 1.35215
Umbral Magnitude: 0.40797
Gamma: -0.80534
Date: Monday, 17 August 1970
Saros Series: 118th (49 of 73)
Greatest Eclipse: 1970 August 17 at 03:23:25.6 UTC
Sun Right Ascension: 9.74
Sun Declination: 13.6
Sun Diameter: 1895.8 arc-seconds
Moon Right Ascension: 21.77
Moon Declination: -14.3
Moon Diameter: 2007.8 arc-seconds
The total duration of the eclipse was 4 hours, 31 minutes.
The duration of the partial eclipse was 2 hours, 11 minutes.
Visibility
Relation to other lunar eclipses
Lunar year series
| Ascending node | Descending node | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Saros | Date Viewing |
Type Chart |
Saros | Date Viewing |
Type Chart | |
| 108 | 1969 Aug 27 |
Penumbral |
113 | 1970 Feb 21 |
Partial | |
| 118 | 1970 Aug 17 |
Partial |
123 | 1971 Feb 10 |
Total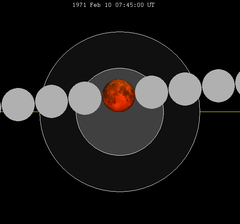 | |
| 128 | 1971 Aug 6 |
Total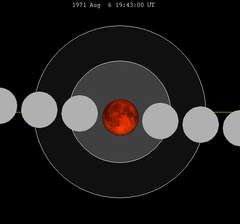 |
133 | 1972 Jan 30 |
Total | |
| 138 | 1972 Jul 26 |
Partial |
143 | 1973 Jan 18 |
Penumbral | |
| 148 | 1973 Jul 15 |
Penumbral | ||||
| Last set | 1969 Sep 25 | Last set | 1969 Apr 2 | |||
| Next set | 1973 Jun 15 | Next set | 1973 Dec 10 | |||
Metonic cycle
This is the third of five Metonic lunar eclipses.
The Metonic cycle repeats nearly exactly every 19 years and represents a Saros cycle plus one lunar year. Because it occurs on the same calendar date, the earth's shadow will in nearly the same location relative to the background stars.
| Descending node | Ascending node | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Saros | Date | Type | Saros | Date | Type | |
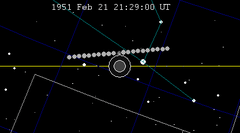
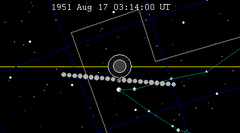
| 103 | 1951 Feb 21.88 | Penumbral | 108 | 1951 Aug 17.13 | Penumbral | |
 |
 | |||||
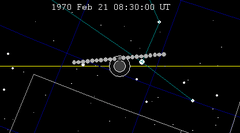
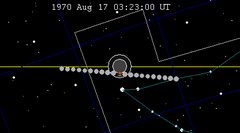
| 113 | 1970 Feb 21.35 | Partial | 118 | 1970 Aug 17.14 | Partial | |
 |
 | |||||
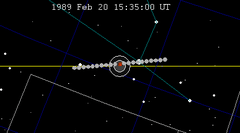
| 123 | 1989 Feb 20.64 | Total | 128 | 1989 Aug 17.13 | Total | |
 |
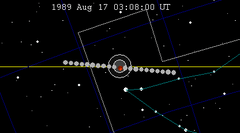 | |||||
| 133 | 2008 Feb 21.14 | Total | 138 | 2008 Aug 16.88 | Partial | |
 |
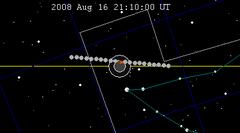 | |||||
| 143 | 2027 Feb 20.96 | Penumbral | 148 | 2027 Aug 17.30 | Penumbral | |
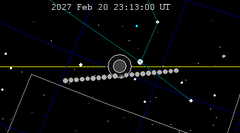 |
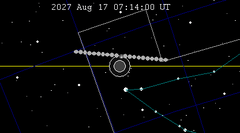 | |||||
Half-Saros cycle
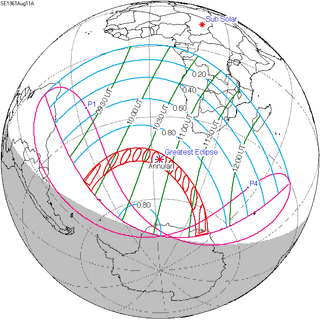
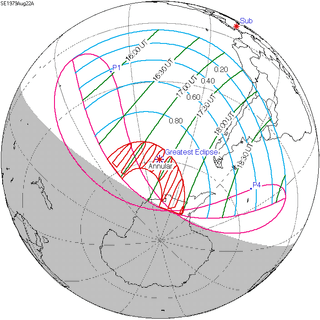
A lunar eclipse will be preceded and followed by solar eclipses by 9 years and 5.5 days (a half saros).[2] This lunar eclipse is related to two annular solar eclipses of Solar Saros 125.
| August 11, 1961 | August 22, 1979 |
|---|---|
 |
 |
See also
- List of lunar eclipses
- List of 20th-century lunar eclipses
Notes
- Saros series 118
- Mathematical Astronomy Morsels, Jean Meeus, p.110, Chapter 18, The half-saros

