June 1974 lunar eclipse
A partial lunar eclipse took place on June 4, 1974.[1]
| Partial Lunar Eclipse June 4, 1974 | |
|---|---|
| (No photo) | |
 The moon passes west to east (right to left) across the Earth's umbral shadow, shown in hourly intervals. | |
| Series | 120 (56 of 84) |
| Duration (hr:mn:sc) | |
| Partial | |
| Penumbral | |
| Contacts | |
| P1 | UTC |
| U1 | |
| Greatest | |
| U4 | |
| P4 | |
Visibility

Half-Saros cycle
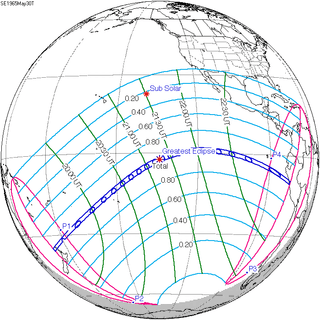
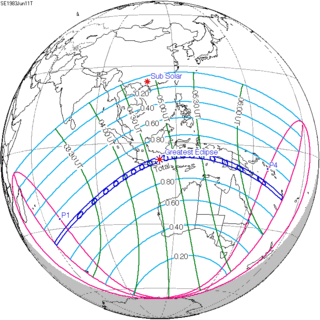
A lunar eclipse will be preceded and followed by solar eclipses by 9 years and 5.5 days (a half saros).[2] This lunar eclipse is related to two total solar eclipses of Solar Saros 127.
| May 30, 1965 | June 11, 1983 |
|---|---|
 |
 |
Related lunar eclipses
Lunar year series
| Lunar eclipse series sets from 1973–1976 | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ascending node | Descending node | |||||||
| Saros | Date Viewing |
Type Chart |
Gamma | Saros | Date Viewing |
Type Chart |
Gamma | |
| 110 | 1973 Jun 15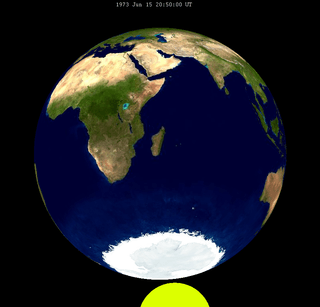 |
Penumbral |
-1.32166 | 115 | 1973 Dec 10 |
Partial |
0.96441 | |
| 120 | 1974 Jun 04 |
Partial |
-0.54887 | 125 | 1974 Nov 29 |
Total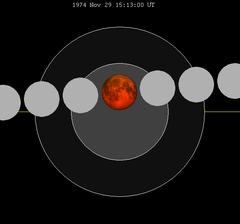 |
0.30540 | |
| 130 | 1975 May 25 |
Total |
0.23674 | 135 | 1975 Nov 18 |
Total |
-0.41343 | |
| 140 | 1976 May 13 |
Partial |
0.95860 | 145 | 1976 Nov 06 |
Penumbral |
-1.12760 | |
| Last set | 1973 Jul 15 | Last set | 1973 Jan 18 | |||||
| Next set | 1977 Apr 04 | Next set | 1977 Sep 27 | |||||
gollark: I do generally prefer flying to cars for reasonably long distances, but the whole "security" thing at airports really does a great job at making me reevaluate that. And is not actually improving security at all.
gollark: How does hyperloop compare to regular maglevs?
gollark: The Thought Police ~~would like to~~ know your location.
gollark: Yes.
gollark: It seems like score voting (or approval I guess, easiest change) would be the best system for voting. But there are a lot of annoying tradeoffs and weird issues. Also Arrow's theorem, but IIRC that only affects ranked ones.
See also
- List of lunar eclipses
- List of 20th-century lunar eclipses
Notes
- Hermit Eclipse: Saros cycle 120
- Mathematical Astronomy Morsels, Jean Meeus, p.110, Chapter 18, The half-saros
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.

