Istria County
Istria County (/ˈɪstriə/; Croatian: Istarska županija; Italian: Regione istriana, lit. "Istrian Region") is the westernmost county of Croatia which includes the biggest part of the Istrian peninsula (2,820 km2 (1,089 sq mi) out of 3,160 km2 (1,220 sq mi), or 89%).
Istria County | |
|---|---|
 Flag  Coat of arms | |
| Anthem: Krasna zemljo (Croatian) "Beautiful land" | |
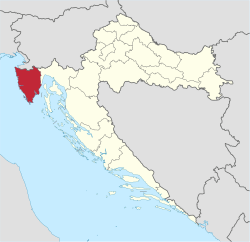 Istria County within Croatia | |
| Country | |
| County seat | Pazin |
| Government | |
| • Župan | Fabrizio Radin (IDS) |
| • Assembly | 45 members
|
| Area | |
| • Total | 2,813 km2 (1,086 sq mi) |
| Population (2011)[2] | |
| • Total | 208,055 |
| • Density | 74/km2 (190/sq mi) |
| Languages | |
| • Official languages | Croatian and Italian |
| Area code | 052 |
| ISO 3166 code | HR-18 |
| HDI (2018) | 0.854[3] very high · 3rd |
| Website | www |
Administrative centers are Pazin, Pula and Poreč.[4] Istria County is the most prominent Italian-speaking part of Croatia.
History
The caves near Pula/Pola (in latinium Pietas Julia), Lim fjord, Šandalja and Roumald's cave, house Stone Age archaeological remains. Less ancient Stone Age sites, from the period between 6000 and 2000 BC, can also be found in the area. More than 400 locations are classified as Bronze Age (1800–1000 BC) items. Numerous findings including weapons, tools, and jewelry) which are from the earlier iron era around the beginning of common era.
The Istrian peninsula was known to Romans as the terra magica. Its name is derived from the Histri, an Illyrian tribe who, as accounted by the geographer Strabo, lived in the region. Romans described them as pirates who were hard to conquer due to the difficulty of navigating their territory. After two military campaigns, Roman legions finally subdued them in 177 BC.
With the fall of the Western Roman Empire in 476, Istria was conquered by the Goths, and then by the Byzantines. During Byzantine rule, it was shortly ruled by Avars. Istria was annexed by the Lombards in 751, by the Avars in 774 and then by the Franks during the reign of Charlemagne in 789, then successively controlled by various dukes, (Carinthia, Merano, Bavaria), and the patriarchs of Aquileia.
In 1267 the Republic of Venice annexed the western and southern coast of the Istrian peninsula because of the strong presence of the autochthonous Italian community; it was in this period that the region prospered. The major Istrian cities were reborn under Italian government, and it was in this half millennium that they developed their typical beauty and atmosphere. The eastern half of Istria was administered by the Habsburgs, and was referred to as "Imperial Istria" with its capital at Pisino (German: Mitterburg).
In 1797, with the Treaty of Campo Formio written by Napoleon, the peninsula, with the whole Republic of Venice, passed to the Habsburgs of Austria. The Treaty of Pressburg in 1805 handed Istria to the Kingdom of Italy. The Treaty of Schönbrunn in 1809 transferred Istria to France. In 1815, the Congress of Vienna confirmed Austria's possession on the Northern Adriatic Sea with Istria, regional guvernative units were formed in Gorizia (Gorizia county), Trieste (Istrian area), Rijeka (Pazin county and Kvarner Gulf), from 1849 united in Austrian Littoral. Free port of Trieste presented individual guvernative unit, outside of other guvernative areas. Starting in 1861 till 1918/1920 the seat to a Regional Parliament in Austro-Hungarian Empire was in Parenzo (today: Poreč).
After World War I, according to the peace treaty of Rapallo, Istria became part of Italy in 1920. Fascism and, later, Nazi occupation spoiled otherwise tolerant ethnic relations. After World War II, Istria was assigned to Yugoslavia and many ethnic Italians left in the Istrian exodus. With the collapse of Communist Yugoslavia, Istria became part of an independent Croatia and the region saw no fighting in the ensuing war. Today it is one of the economically most developed parts of Croatia.
Famous individuals like Robert Koch and writer James Joyce lived and worked in Istria. Writer Jules Verne was inspired to write his novel Mathias Sandorf after hearing of quarry and cave in Pazin and the poet Dante Alighieri visited and wrote a few lines about Istria.
Geography
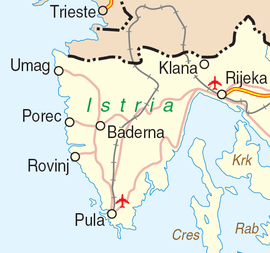
Its coastline is 445 km (277 mi) long with islands making up 539.9 km (335 mi). A smaller part of Istria also belongs to the Primorje-Gorski Kotar County of Croatia. Mirroring the bay of Venice across the Adriatic and the Quarnaro Gulf, the region is not far from the Julian Alps (Alpi Giulie/Julijske Alpe). The westernmost point is at Savudrija while the southernmost is near Premantura, on the local promontory Kamenjak.
The terrain consists of a limestone plateau, much of which lacks water owing to its karst topography. The northeastern section is an extension of the Dinaric Alps. The highest point is Vojak on Učka mountain 1,401 m (4,596.46 ft) above sea level while another range of mountains is Ćićarija.
There are so called "bijela", "siva", "crvena" Istra (white, grey and red Istria). White Istria is around the mountain peaks, Grey Istria is the fertile inner lands while Red Istria is the blood-red painted lands of terra rossa or "crljenica" near the coastline.
Sites such as the Grotto of Baredine near Poreč, the underground river Pazinčica and the karst Pazin pit (Pazinska jama) near Pazin are popular geologic attractions. The Limski Kanal is the only fjord resembling structure in continental Europe outside of Scandinavia (though actually not a fjord, but in fact a ria). The quarry near Rovinj/Rovigno d'Istria is specifically designed for studying geology. The longest river, the Mirna, is only 32 km (20 mi) long with its mouth near Novigrad/Cittanova d'Istria. Other rivers that pass through Istria include the Dragonja River and Raša River.
The continental plains and valleys, are primarily utilized for agriculture, such as growing cereals and vegetables. Closer to the sea, red lands are used for cultivation of grapes, vine, olives and figs. Agriculture and the production of ecological food, the olive gardens, and the production of quality wines, is the focus of Istria's agriculture sector. The coastline and nearby islands are rich in the maquis shrubland (mostly holm oak and strawberry tree. Woods, mostly oak and pine trees, cover a third of the territory.
The well-known natural reservations national park Brijuni and nature park Učka are legally protected landscapes. This mountain range fed the rivers and lakes in the eastern side of Istria all the way to Croatian: Rasa / Italian: Arsa river in the Croatian: Labinština peninsula. Other interesting localities are Lim Kanal, wood near Motovun, park woods Zlatni Rt and Šijana near Pula, protected landscape Kamenjak in the extreme south of Istria, the reservation Palud, (ornithology), near Rovinj. Brijuni archipelago is interesting as the habitat of about 680 plant species, also decorated by the most diverse vegetation and olive groves.
Climate
Protected from the north by the mountain chain of Alps as well the inner highland, the climate is Mediterranean, very pleasant, with the highest air temperature averaging 24 °C during August, and the lowest averaging 5 °C in January. Summers are usually warm during the day and cooler near the evening, although strange heat wave patterns are common. The weather also ranges from humid to dry with over 10 hours of sunshine daily. Primarily, there is a lot of moisture in the air, especially in the coastal towns of Istra such as Poreč, Vrsar, Rovinj, Pula and others. Temperatures above 10 °C last for more than 240 days a year. Excessive heat (above 30 °C) lasts for three weeks at most. Despite air temperatures being lower than those of in Dalmatia, the Adriatic sea is warmer, reaching up to 26 °C in August, coldest in March, (9-11 °C), while the freezing even in small, shallow bays is very rare. Two kinds of winds are here - the bora is bringing cold and clear weather from the north in winters, and the southern jugo (jug = south) bringing rain in summer. Maestral is the summer breeze blowing from the inland to the sea. The salinity of the sea water is 0.37%.
Demographics
| Year | Pop. | ±% |
|---|---|---|
| 1857 | 117,719 | — |
| 1869 | 133,518 | +13.4% |
| 1880 | 160,000 | +19.8% |
| 1890 | 176,196 | +10.1% |
| 1900 | 194,455 | +10.4% |
| 1910 | 236,981 | +21.9% |
| 1921 | 215,167 | −9.2% |
| 1931 | 223,949 | +4.1% |
| 1948 | 183,344 | −18.1% |
| 1953 | 175,094 | −4.5% |
| 1961 | 176,838 | +1.0% |
| 1971 | 175,199 | −0.9% |
| 1981 | 188,332 | +7.5% |
| 1991 | 204,346 | +8.5% |
| 2001 | 206,344 | +1.0% |
| 2011 | 208,055 | +0.8% |
| Source: Naselja i stanovništvo Republike Hrvatske 1857–2001, Croatian Bureau of Statistics, Zagreb, 2005 | ||
According to 2011 census total population of Istria County is 208,055 which amounts to 4.85 percent of Croatia's entire population. Population density is 73 inhabitants per km2, with an average age of 43 years.
Istria county is administratively subdivided into 41 local units of government - 10 of these are officially designated as cities/towns and 31 are largely rural municipalities. More than 70 percent of the county's population lives in these ten urban areas:
There are also 31 municipalities:
- Bale / Valle (1,127)
- Barban/ Barbana (2,721)
- Brtonigla / Verteneglio (1,626)
- Cerovlje / Cerreto (1,677)
- Fažana / Fasana (3,635)
- Gračišće / Gallignana (1,419)
- Grožnjan / Grisignana (736)
- Kanfanar / Canfanaro (1,543)
- Karojba / Caroiba (1,438)
- Kaštelir-Labinci / Castellier-Santa Domenica (1,463)
- Kršan / Chersano (2,951)
- Lanišće / Lanischie (329)
- Ližnjan / Lisignano (3,965)
- Lupoglav / Lupogliano (924)
- Marčana / Marzana (4,253)
- Medulin / Medolino (6,481)
- Motovun / Montona (1,004)
- Oprtalj / Portole (850)
- Pićan / Pedena (1,827)
- Raša / Arsia (3,183)
- Sveta Nedelja / Santa Domenica d'Albona (2,987)
- Sveti Lovreč / San Lorenzo di Pesenatico (1,015)
- Sveti Petar u Šumi / San Pietro di Selve (1,065)
- Svetvinčenat / Sanvincenti (2,202)
- Tar-Vabriga / Torre-Abrega (1,990)
- Tinjan / Antignana (1,684)
- Višnjan / Visignano (2,274)
- Vižinada / Visinada (1,158)
- Vrsar / Orsera (2,162)
- Žminj / Gimino (3,483)
- Funtana / Fontane (907)
Besides official Croatian, the Chakavian dialect of the Croatian language is often in use, as in most coastal counties. Italian is also recognized in the county as an official language.

In 2011 the population was 208,055 and the main ethnic groups were as follows:[5]
- Croats – 142,173 (68.33%)
- Italians – 12,543 (6.03%)
- Serbs – 7,206 (3.46%)
- Bosniaks – 6,146 (2.95%)
- Albanians – 2,393 (1.15%)
Before World War I and until World War II, Istria contained a large autochthonous Romance language speaking community consisting of Venetian dialects, Istriot and Istro-Romanian along with Italian, plus various local Slavic dialects, some of which were likewise unique to Istria. Today, apart from the local dialects and the official Croatian language, one still finds in this region a small community of people, the Istro-Romanians, who speak the Istro-Romanian language, closely related to Romanian, other districts where Venetian dialects and Istriot are still spoken.
Due to its traditional bond with Europe and its level of international integration, in 1994 Istria County was the first Croatian region to become a member of the Assembly of European Regions.[6]
Communication
Istria is well connected with the rest of Croatia and Europe. Due to its connection with a wider European area, road development suitably covers all needs and contributes to a balanced development of the coastal area and the Istrian interior.
Initially, the need for railroads in Istria was based upon fast development of industrial activities; shipbuilding, construction material, machine and electric industries, as well as Austrian military interests. After Vienna and Trieste were connected in 1876, the railway between Divača, (in today's Slovenia) and Pula/Pola, (122 km (76 mi) long with 21 km (13 mi) long branch Kanfanar - Rovinj/Rovigno d'Istria), was opened. Despite numerous initiatives, the western part of Istria have been connected with the railroad only in 1902, with construction of the narrow-gauge track Poreč/Parenzo - Trieste. The famous 123.1 km (76 mi) long "Parenzana", or Parenzaner Bahn, was cancelled in 1935. To this day, Istria County's rail connections are only towards Slovenia, and despite the fact that some plans to build railroad tunnel through Učka mountain date from decades ago,[7] there are no projections about financing and works are not scheduled to start any time soon. The connection to the rest of Croatian rail network is by HŽ national railways' bus service from Lupoglav junction to Rijeka Station via Učka road tunnel
Croatian Istria County's highway system is callen "The Istrian Y". Highway A8 connects the county to the rest of Croatia from Rijeka/Matulji (A7/ further A6) interchange through Učka Tunnel to Kanfanar interchange, and highway A9 connects Pula via Kanfanar to Umag, connecting the county to Slovenian Istria and further to Italy.
The only significant airport with scheduled commercial service is Pula Airport. Large majority of flights are only seasonal.
Economy
.jpg)
Well-developed are processing industry, with traditional agriculture, sea fishing and growing, construction and production of construction materials (lime, cement, brick, stone), trade and transport. Most developed branches of industry are shipbuilding (In the early 1970s its shipyard Uljanik was building the biggest ships in the world as Berge Adria and others), metal processing, wood industry, furniture industry, automotive components industry, electric machines and appliances industry, glass, plastic, textile, tobacco industry. According to economic indicators, the leading activities are processing industry, tourism, and trade.
Great attention is being given to agriculture and the production of ecologic food, the wine and olive growing. Historically cultivated local wine varietals include Malvasia (white) and Teran (red).
Tourism
Organized tourism in Istria goes back to the Romans, when emperor Vespasian, for the entertainment of that time, built the amphitheater (Arena) in Pula/Pola. During the reign of Austro-Hungarian Empire in (1866), Austrian and Hungarian royalty and aristocracy started visiting local resorts and discovered Poreč/Parenzo.
Significant efforts were made after World War II to develop the tourist infrastructure and to accentuate its importance. In combination with the natural beauties, rich history and cultural heritage, investments paid off and resulted in highly developed, competitive service all along the western coast in Poreč/Parenzo, Pula/Pola, Rovinj/Rovigno d'Istria, Umag/Umago, Novigrad/Cittanova d'Istria, and Vrsar/Orsera.
One growing trend among the centrally located cities, especially Kanfanar/Canfanaro, is agritourism. Beginning with La Casa di Matiki in 1994 after the war, a number of eccentric agritouristic Bed and Breakfasts have sprung up in central Istria, providing opportunities for individuals, couples, and families to experience a very authentic Istrian experience while learning about the Istrian agricultural lifestyle.
In the eastern part, as part of another county, there are resorts like Rabac/Porto Albona, Opatija/Abbazia. Istria was and still is the most important tourist destination in Croatia, hosting the western and central European visitors, mostly from Germany, Slovenia, Austria and Italy.[8] Area is the most visited tourist region with 27% of all visitors and 35% of time spent in all of Croatia.
County government
.svg.png)
Current Prefect of Istria County is Fabrizio Radin (IDS).[9]
The county assembly is composed of 45 representatives from the following political parties:
- Istrian Democratic Assembly (17)
- Social Democratic Party of Croatia (5)
- Croatian Democratic Union (5)
- Human Shield (3)
- Bridge of Independent Lists (3)
- Croatian Party of Pensioners (2)
- Croatian People's Party – Liberal Democrats (1)
- Independent Democratic Serb Party (1)
- Croatian Social Liberal Party (1)
- Istrian Party of Pensioners (1)
- Green Alliance (1)
- Independents - All associated with IDS (5)
References
- Ostroški, Ljiljana, ed. (December 2015). Statistički ljetopis Republike Hrvatske 2015 [Statistical Yearbook of the Republic of Croatia 2015] (PDF). Statistical Yearbook of the Republic of Croatia (in Croatian and English). 47. Zagreb: Croatian Bureau of Statistics. p. 62. ISSN 1333-3305. Retrieved 27 December 2015.
- "Population by Age and Sex, by Settlements, 2011 Census". Census of Population, Households and Dwellings 2011. Zagreb: Croatian Bureau of Statistics. December 2012.
- "Sub-national HDI - Area Database - Global Data Lab". hdi.globaldatalab.org. Retrieved 2018-09-13.
- "Regione Istriana: Struttura organizzativa" (in Italian).
- "Population by Ethnicity, by Towns/Municipalities, 2011 Census: County of Istria". Census of Population, Households and Dwellings 2011. Zagreb: Croatian Bureau of Statistics. December 2012.
- "Skupština europskih regija (SER)" (in Croatian). Istria County. Retrieved 19 July 2012.
- "Raška pruga". istra.lzmk.hr. Retrieved 7 April 2018.
- "DOLASCI I NOĆENJA TURISTA U ISTRI PO ZEMLJAMA PORIJEKLA" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2016-03-04. Retrieved 2015-07-19.
- https://www.istra-istria.hr/index.php?id=3
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Istria County. |
- Official website
