Indazole
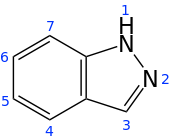
Indazole, also called isoindazole, is a heterocyclic aromatic organic compound. This bicyclic compound consists of the fusion of benzene and pyrazole.
 | |||
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| IUPAC name
1H-indazole | |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol) |
|||
| ChEBI | |||
| ChEMBL | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.005.436 | ||
PubChem CID |
|||
| UNII | |||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C7H6N2 | |||
| Molar mass | 118.14 g/mol | ||
| Melting point | 147 to 149 °C (297 to 300 °F; 420 to 422 K) | ||
| Boiling point | 270 °C (518 °F; 543 K) | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |||
| Infobox references | |||
Indazole derivatives display a broad variety of biological activities.
Indazoles are rare in nature. The alkaloids nigellicine, nigeglanine, and nigellidine are indazoles. Nigellicine was isolated from the widely distributed plant Nigella sativa L. (black cumin). Nigeglanine was isolated from extracts of Nigella glandulifera.
The Davis–Beirut reaction can generate 2H-indazoles.
Indazole, C7H6N2, was obtained by E. Fischer (Ann. 1883, 221, p. 280) by heating ortho-hydrazine cinnamic acid,[1]
| C6H4 | CH = CH·COOH | =C2H4O2+C7H6N2. |
| NH·NH2 |
Some derivatives
- indazole-3-carboxylic acid
Having a carboxylic acid group on carbon 3. Can be further modified to lonidamine & tolnidamine.
gollark: That's not code in the screenshot. That's network traffic.
gollark: Elytra are stupidly expensive, but actually getting one doesn't require more than borrowing an elytra to copy, an eye of ender, some weapons (beds, even), and a ghast tear.
gollark: By the end portal I mean the exit portal.
gollark: We should really do something about the monopolisation of the end portal, which is necessary for renewable elytra.
gollark: It doesn't have the relay, that's why.
See also
- Indole, an analog with only one nitrogen atom in position 1.
- Benzimidazole, an analog with the nitrogen atoms in positions 1 and 3.
- Simple aromatic rings
- 7-Nitroindazole, an indazole-based nitric oxide synthase inhibitor
References
- Chisholm, Hugh, ed. (1911). . Encyclopædia Britannica. 14 (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press. p. 371.
- Synthesis: W. Stadlbauer, in Science of Synthesis 2002, 12, 227, and W. Stadlbauer, in Houben-Weyl, 1994, E8b, 764.
- Review: A. Schmidt, A. Beutler, B. Snovydovych, Recent Advances in the Chemistry of Indazoles, Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2008, 4073 – 4095.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.