Geographic regions of Greece
The traditional geographic regions of Greece (Greek: γεωγραφικά διαμερίσματα, literally "geographic departments") are the country's main historical-geographic regions, and were also official administrative regional subdivisions of Greece until the 1987 administrative reform.[1] Despite their replacement as first-level administrative units by the newly defined administrative regions (Greek: περιφέρειες), the nine traditional geographic divisions—six on the mainland and three island groups—are still widely referred to in unofficial contexts and in daily discourse.
| This article is part of a series on |
| Politics of Greece |
|---|
 |
|
Judiciary
|
|
|
|
As of 2011, the official administrative divisions of Greece consist of 13 regions (Greek: περιφέρειες)—nine on the mainland and four island groups—which are further subdivided into 74 regional units and 325 municipalities. Formerly, there were also 54 prefectures or prefectural-level administrations.
|
The regions shown on the map but not in the list are geographic regions, but they are not major. |
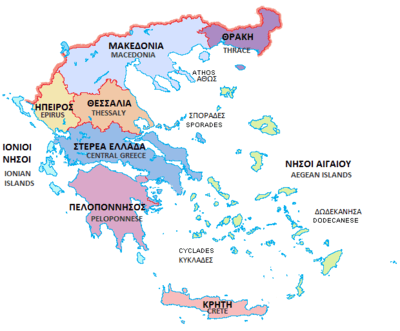 Map showing Regions of Greece
|
See also
Notes
- Π.Δ. 51/87 "Καθορισμός των Περιφερειών της Χώρας για το σχεδιασμό κ.λ.π. της Περιφερειακής Ανάπτυξης" (Determination of the Regions of the Country for the planning etc. of regional development, ΦΕΚ A 26/06.03.1987
- In Macedonia there is one autonomous region, Mount Athos (Ayion Oros, or "Holy Mountain"), a monastic state under Greek sovereignty. It is located on the easternmost of the three large peninsulas jutting into the Aegean from the Macedonian mainland.