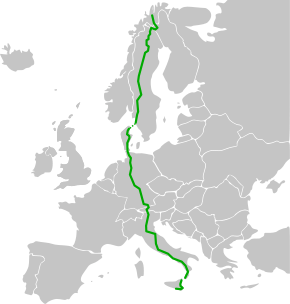
European route E45
The European route E45 goes between Norway and Italy, through Finland, Sweden, Denmark, Germany and Austria. With a length of about 5,190 kilometres (3,225 mi), it is the longest north-south European route (some east-west routes are longer).
| |
|---|---|
 | |
| Major junctions | |
| North end | Alta, Norway |
| South end | Gela, Italy |
| Location | |
| Countries | |
| Highway system | |
| International E-road network | |

The route passes through Alta (Norway) – Kautokeino – Hetta (Finland) – Palojoensuu – Kaaresuvanto – Gällivare (Sweden) – Porjus – Jokkmokk – Arvidsjaur – Östersund – Mora – Säffle – Åmål – Brålanda – Gothenburg … Frederikshavn (Denmark) – Aalborg – Randers – Århus – Vejle – Kolding – Frøslev – Flensburg (Germany) – Hamburg – Hanover – Hildesheim – Göttingen – Kassel – Fulda – Würzburg – Nuremberg – Munich – Rosenheim – Wörgl (Austria) – Innsbruck – Brenner – Fortezza (Italy) – Bolzano – Trento – Verona – Modena – Bologna – Cesena – Perugia – Fiano Romano – Naples – Salerno – Sicignano – Cosenza – Villa San Giovanni … Messina – Catania – Siracusa – Gela.[2]
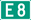
Norway and Finland
E45 is 172 km long in Norway and 101 km long in Finland. It has no other number in Norway, but follows routes 21 and 93 in Finland.
The E45 was not signposted in Finland after the 2006 extension,[3] since the official document[2] uses the Swedish version ("Karesuando") of the name of the village at the Finnish–Swedish border, hinting that it would start on the Swedish side. The Swedish government proposed the extension alone in 2005 and let the E45 end at the border, partly because of lack of interest from Finnish authorities. The gap between the end of E45 and the European route E8 was about 1 km along the existing Finnish regional road 959 Karesuvanto (FIN) – Karesuando (SWE)
In August 2016, after a political proposal in 2007, the governments of Norway and Finland applied for an extension of E45 Karesuando–Kaaresuvanto–Palojoensuu–Hetta–Kautokeino–Alta.[4] This was approved by the work group, and became valid on 5 December 2017.[5] E45 sign posts were mounted starting 9 February 2018, [6] replacing route 93 in Norway, and complementing road 959, 21 and 93 in Finland.
Sweden
In November 2006, the E45 was extended with the then existing Swedish national road 45, which makes it start from Karesuando at the Swedish–Finnish border (near the E8), over Östersund–Mora–Grums, to Gothenburg and on. This extended the length of the route by about 1,690 km (1,050 mi). The signs of road 45 was changed to E45 during the summer of 2007. The E45 has now no other national number. In Sweden the road is called Inlandsvägen.
The E45 in Sweden is mostly a standard road. Between Karesuando and Torsby (1370 km) the road is usually 6–8 meters wide, and goes mostly through sparsely populated forests, with occasional villages and only two cities above 10,000 people, Östersund and Mora. The E45 is a motorway for 6 km together with the E18 south of Grums. Between Säffle and Trollhättan several parts of it is 2+1 road with a middle barrier, totally around 40 km. Between Trollhättan and Surte there is a 52 km long motorway, finished in 2012. Between Surte and Gothenburg there is a 17 km road designed equivalently to a motorway. The exception is that there are two gaps in the Trollhättan–Surte motorway and there are two traffic lights along the Surte–Gothenburg road. The speed limit is usually 100 km/h north of Mora and usually 90 km/h south thereof. There are 27 road crossings or intersections where the Swedish E45 does not follow the straight direction. There are 26 level crossings with railways. There are 19 motorway exits and 29 other motorway-like exits.
The ferry Gothenburg–Frederikshavn has about 6 daily departures and takes 3½ hours.
Denmark
In Denmark the E45 is a motorway (speed limit 110 km/h – 130 km/h) from the south of Frederikshavn to the Denmark–Germany border. The E45 has no other national number. It connects to the E39 and E20 motorways.
1968.07.27.jpg)
In 1992 it was renamed from E3 (which actually before 1985 ended in Lisbon, Portugal) and until 2006, with the extension in Sweden, the northern endpoint was Frederikshavn.
The total length in Denmark is 357 km.
Exits in Denmark
| Name/Location | # | Destinations | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sæby N | 12 | Sekundærrute 180 Sæby, Vangen | |
| Rest area Øksenhede | |||
| Sæby S | 13 | Sekundærrute 180Sekundærrute 541 Sæby, Syvsten, to Sekundærrute 553 | |
| Flauenskjold | 14 | Sekundærrute 589 Flauenskjold, Dybvad, Voerså | |
| Jyske Ås | 15 | Klokkerholm | |
| Hjallerup N | 16 | Sekundærrute 559 Hjallerup, Asaa, Dronninglund, to Sekundærrute 180 | |
| Rest area Hjallerup Enge | Gas station on the east-side | ||
| Lyngdrup | 17 | Sekundærrute 180 Hjallerup, Grindsted | |
| Vodskov N | 18 | Vodskov, Langholt, to Sekundærrute 180 | |
| Vodskov | 19 | Vodskov, Hals | |
| Bouet | 20 | Nørresundby, to |
|
| Northbound exit, southbound entrance | |||
| Nørresundby N | 21 | Nørresundby, Lindholm |
|
| Nørresundby C | 22 | Sekundærrute 180 Nørresundby | Northbound exit, southbound entrance |
| 582 metres (1,909 ft) length. Max height 4,3m | |||
| Aalborg N | 23 | Aalborg, Rørdal | Southbound exit, northbound entrance |
| Ø. Uttrup Vej | 24 | Aalborg, Rørdal | |
| Humlebakken | 25 | Vejgaard, Aalborg Ø | Southbound exit, northbound entrance |
| Th. Sauers Vej | 26 | Sekundærrute 507 Sekundærrute 595 Aalborg | |
| Aalborg C | 27 | Aalborg | Northbound exit, southbound entrance |
| Aalborg S | 28 | Sekundærrute 187 Aalborg, Skalborg | |
| Rest area Dall/Limfjorden | Restaurant on the west-side | ||
| Svenstrup | 29 | Sekundærrute 180 Svenstrup, Ellidshøj | |
| Støvring N | 30 | Støvring | |
| Støvring S | 31 | Sekundærrute 519 Støvring, Sørup | |
| Service area Himmerland | |||
| Sønderup | 32 | Southbound exit, northbound entrance | |
| Haverslev | 33 | Sekundærrute 535 Haverslev, Arden | |
| Rest area Senhøj | |||
| Hobro N | 34 | ||
| Hobro V | 35 | Sekundærrute 579 Hobro | |
| Onsild | 36 | Sekundærrute 517 Sekundærrute 555 Onsild, Viborg, Mariager | |
| Handest | 37 | Sekundærrute 180 Handest, Hobro | |
| Rest area Glenshøj | |||
| Purhus | 38 | Purhus, Fårup | |
| Randers N | 39 | Sekundærrute 180Sekundærrute 507 Randers, Hadsund | |
| Randers C | 40 | ||
| Rest area Gudenå | |||
| Randers S | 42 | ||
| Sønder Borup | 43 | ||
| Hadsten | 44 | Sekundærrute 587 Hadsten, Ebeltoft, Grenaa |
|
| Århus N | 46 | Sekundærrute 505 Hinnerup, Lisbjerg | |
| Tilst | 47 | ||
| Rest area Pedersminde/Blankhøj | |||
| Århus S | 49 | Århus, Hasselager |
Southbound exit, northbound entrance |
| Hørning | 50 | Hørning, Hasselager | Southbound exit, northbound entrance |
| Sekundærrute 501 Hasselager, Hørning, Viby J, |
Northbound exit, southbound entrance | ||
| Skanderborg N | 51 | Sekundærrute 511 Skanderborg, Stilling | |
| Rest area Fuglsang | |||
| Skanderborg V | 52 | Sekundærrute 511 Skanderborg, Ry, Odder | |
| Skanderborg S | 53 | Sekundærrute 409 Skanderborg, Østbirk, Nørre Snede | Southbound exit, northbound entrance |
| Ejer Bavnehøj | 54 | Ejer Bavnehøj |
|
| Horsens N | 55 | Sekundærrute 461 Horsens, Østbirk | |
| Horsens V | 56 | ||
| Horsens C | 56b | Horsens, Hatting | |
| Horsens S | 57 | ||
| Rest area Merring/Nørremark | |||
| Hedensted | 58 | Hedensted, Løsning | |
| Hornstrup | 59 | ||
| Vejle N | 60 | Sekundærrute 170 Vejle, Juelsminde | |
| Vejle C | 61a | ||
| Vejle S | 61b | ||
| Service area Skærup | |||
| Southbound exit, northbound entrance | |||
| Northbound exit, southbound entrance. Concurrency with | |||
| Kolding Ø | 62 | Sekundærrute 170Sekundærrute 176 Kolding, Billund |
|
| Bramdrupdam | 63 | Bramdrupdam | |
| Kolding Vest | 64 | Concurrency with | |
| Rest area Hylkedal | |||
| Kolding S | 65a | ||
| Vonsild | 65b | Vonsild | |
| Christiansfeld | 66 | Christiansfeld | |
| Haderslev N | 67 | Haderslev | |
| Vojens | 68 | ||
| Service area Ustrup | |||
| Haderslev S | 69 | Sekundærrute 435 Haderslev, Tønder | |
| Rest area Øster Løgum | |||
| Aabenraa N | 70 | ||
| Rest area Årslev | Restaurant on east-side | ||
| Aabenraa | 71 | Southbound exit, northbound entrance | |
| Aabenraa S | 72 | ||
| Kliplev | 73 | ||
| Rest area Oksekær | |||
| Kruså | 74 | Kruså, Flensburg | Southbound exit, northbound entrance |
| Bov | 75 | Sekundærrute 401 Bov, Tønder, Padborg, Kruså, Egernsund | |
| Padborg | 76 | Padborg, Frøslev | Southbound exit, northbound entrance |
| Service area Frøslev | |||
| Padborg | 76 | Padborg, Frøslev | Northbound exit, southbound entrance |
Germany
The E45 follows:
- A7, Danish border–Würzburg
- A3, Würzburg–Nuremberg
- A9, Nuremberg–Munich
- A99, Munich Beltway
- A8, Munich–Rosenheim
- A93, Rosenheim–Austrian border
The length in Germany is 1022 km.
Between Nuremberg and Verona, Italy the E45 corresponds with the route of the old imperial road, the Via Imperii, though the Autobahns are newer roads.
Austria
The E45 follows:
- Inn Valley Autobahn A12, German border–Innsbruck
- Brenner Autobahn A13, Innsbruck–Italian border (at Brenner Pass)
The length in Austria is 109 km.
Italy
Owing to the greater recognition of motorways and nationally or locally numbered major roads in Italy, in colloquial usage "E45" often refers to the Cesena-Orte segment[7], possibly further expanded to include the Ravenna-Cesena section of the SS3bis (formally part of the E55, and forming together the Strada di Grande Comunicazione Ravenna-Orte) and/or the Orte-Rome segment.
Route









.svg.png)
.svg.png)
.svg.png)
.svg.png)
.svg.png)
.svg.png)
.svg.png)
.svg.png)
.svg.png)





































Footnotes
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to E45. |
| Wikivoyage has a travel guide for E45 through Europe. |
- Vägverket "Nya hastighetsgränser på nationella vägar"
- United Nations Economic Commission for Europe, Inland Transport Committee (2005-07-19). "Road Transport Infrastructure. European Agreement on Main International Traffic Arteries (AGR). Consideration of new proposals for amendments to Annex I to the AGR (TRANS/SC.1/2005/3)" (PDF). United Nations Economic and Social Council. Retrieved 2007-05-28.
- Karesuando och Karesuvanto... (Bilder) and SV: Skyltning efter vägarna !!
- ECE/TRANS/SC.1/2016/2 Amendments to the Agreement Submitted by the Governments Finland and Norway
- Report of the Working Party on Road Transport on its 112th session
- Klart for E45 (NRK 9 February 2018, in Norwegian)
- "Itinerari E45-E55 e Orte-Civitavecchia" (in Italian). Anas SpA. Retrieved 6 November 2019.


