Ústí nad Labem Region
Ústí nad Labem Region or Ústecký Region (Czech: Ústecký kraj, German: Region Aussig), is an administrative unit (Czech: kraj) of the Czech Republic, located in the north-western part of the historical land of Bohemia, and named after the capital, Ústí nad Labem. It covers the majority of the former North Bohemia province (Czech: Severočeský kraj) and is part of the broader area of North Bohemia.
Ústí nad Labem Region Ústecký kraj | |
|---|---|
 | |
 Flag  Coat of arms | |
 | |
| Coordinates: 50°31′N 13°51′E | |
| Country | Czech Republic |
| Capital | Ústí nad Labem |
| Districts | Děčín District, Litoměřice District, Louny District, Most District, Teplice District, Ústí nad Labem District |
| Government | |
| • Governor | Oldřich Bubeníček (KSČM) |
| Area | |
| • Total | 5,334.52 km2 (2,059.67 sq mi) |
| Highest elevation | 1,113 m (3,652 ft) |
| Population (2020-01-01[1]) | |
| • Total | 820,965 |
| • Density | 150/km2 (400/sq mi) |
| ISO 3166 code | CZ-US |
| Vehicle registration | U |
| Website | www.kr-ustecky.cz |
The region borders the regions of Liberec (east), Central Bohemia (south), Plzeň (southwest), Karlovy Vary (west) and the German region of Saxony to the north.
The Ústí region comprises a range of very different types of landscape. Between the high escarpment of the Ore Mountains (Czech: Krušné hory) range and the Bohemian Central Uplands with many volcanic hills, there are vast areas devastated by surface coal mining (the North Bohemian Basin), partly being recultivated into an artificial landscape with ponds, plains and groves. The Elbe river runs through the Central Uplands in a winding gorge of the Porta Bohemica. The southern part of the region, Polabí, is flat and fertile, while in the northeast are the sandstone formations of Bohemian Switzerland, including the monumental Pravčická brána, a natural sandstone arch.
The geographical location of the area, between Prague and Germany, has been a significant factor in the region’s development.[2]
Administrative divisions
The Ústí nad Labem Region is divided into 7 districts:
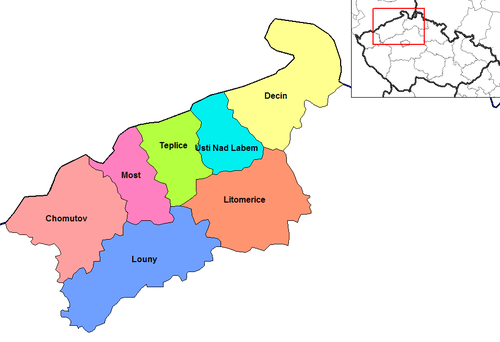 | |||||||||||||||||
Districts of Ústí nad Labem Region
| |||||||||||||||||
The districts are further subdivided into 16 ORP districts (administrative districts of the municipalities with extended competence).
Population
As of 1 January 2019, the region had 820,789 inhabitants, the fifth most populous in the Czech Republic. The population density is higher than the national average, and the region is the fourth most densely populated in the country. The most densely populated areas of the region are the areas on the brown coal basin while areas with a lower population density are the Ore Mountains and the Louny District and Litoměřice District, which predominantly contain smaller country settlements. The largest municipality is Ústí nad Labem, the region's seat, with 92,952 inhabitants.
The Ústí nad Labem region has the third youngest population; the average age is 42.0 years. The Ústí nad Labem Region ranks second-highest in the Czech Republic in the number of live births per 1,000 inhabitants, alongside the Liberec Region (11.5), but also has one of the highest mortality rates (10.6 deaths per 1,000 inhabitants). The Ústí nad Labem Region ranks second nationally in the number of divorces per 1,000 inhabitants (3.4) and first in the number of abortions per 100 live births (47.5).
The region has 46 cities and towns, in which 80.7% of its inhabitants reside, and 354 villages. 54% of the region's villages have a population greater than 500, but only 5.8% of the region's inhabitants live there.[2]
The composition of the population according to nationality is:
- Czech: 92.12%
- Slovak: 2.71%
- German: 1.25%
- Romani: 0.23%
- Polish: 0.2%
- Moravian: 0.13%
- Other: 3.45%
Cities and towns
The table shows cities and towns in the region that had more than 10,000 inhabitants (as of January 1, 2019).[3]
| Name | Population | Area (km²) | District |
|---|---|---|---|
| 92,952 | 94 | Ústí nad Labem | |
| 66,186 | 87 | Most | |
| 49,575 | 24 | Teplice | |
| 48,809 | 118 | Děčín | |
| 48,720 | 29 | Chomutov | |
| 24,001 | 18 | Litoměřice | |
| 23,884 | 41 | Most | |
| 19,299 | 17 | Chomutov | |
| 19,133 | 43 | Louny | |
| 18,351 | 24 | Louny | |
| 18,202 | 66 | Chomutov | |
| 17,166 | 32 | Teplice | |
| 15,297 | 26 | Děčín | |
| 14,533 | 54 | Chomutov | |
| 12,967 | 17 | Litoměřice | |
| 12,624 | 47 | Teplice | |
| 11,082 | 25 | Děčín | |
Other significant towns and villages of the Ústí nad Labem Region
- Česká Kamenice;
- Lovosice;
- Račice, international rowing and flatwater canoeing venue;
- Srbská Kamenice, site of JAT Yugoslav Flight 364 crash in 1972;
- Štětí;
- Terezín, a former military fortress.
Geography

The total area of the region is 5,335 km2, 6.8% of the territory of the Czech Republic. The region's geography is very diverse.
The area along the German borders is dominated by the Ore Mountains (Czech: Krušné hory), the sandstone rocks of Labe (Czech: Labské pískovce) and the Lužice Mountains. The Ore Mountains are very old and formed of volcanic rocks or Palaeozoic schist.
In contrast, the south-eastern part of the region is formed by the plains that originate from Mesozoic era (Czech Cretaceous Formation, Czech: Česká křídová tabule). The Bohemian Central Uplands (Czech: České Středohoří) and Říp Mountain (which is, according to legend, associated with the earliest Czech ancestors arriving in Bohemia) are both located in this area. The Bohemian Central Uplands originated from volcanic activity in the Tertiary.
The highest point of the region (1225 m) lies on the hillside of Klínovec, which is the highest peak of the Ore Mountains. However, the top of the mountain is located in the territory of the Karlovy Vary Region. Not taking into account the bottoms of surface mines, the lowest point of the region, and the whole country, is the surface of the Elbe River at Hřensko, at 115 metres above sea level .
The Elbe River is the largest watercourse in the region. Other main rivers in the region include Ohře (Eger), Bílina, Ploučnice and Kamenice, all tributaries of the Elbe. The largest water area is the Nechranice reservoir built on the Ohře River in the western part of the region. The region also contains a number of mineral and thermal springs.[4]
Economy
In 2010, the region's gross domestic product accounted for 6.6% of the national GDP. The regional GDP per capita was 83.4% of the national average. The regional employment is approximately 362,000 people. In 2013, the average wage in the region was CZK 22,172 (EUR 870). The unemployment rate was 11%.[5]
The Ústecký Region is one of the most industrialized areas in Central Europe. The economy used to be based on metallurgy and the chemical industry, though is now more diverse. The region's traditional branches of industry are chemicals and petrochemicals, engineering and thermal energy.[6] Historically, the economic importance of the Ústí nad Labem Region lay in its reserves of raw materials, especially deposits of brown coal, quality glass and foundry sands and building stone. The brown coal basin stretches under the hillsides of the Ore Mountains from Ústí nad Labem to Kadaň.
The region is part of the Black Triangle, an area of heavily industrialization and environmental damage on the three-way border of Poland, Germany, and the Czech Republic.[7]
The region contains a number of distinct economic regions. An area with highly developed industrial production is concentrated in the foothills of the Ore Mountains (the Chomutov, Most, and Teplice Districts, and part of the Ústí nad Labem District). Important economic sectors include the energy industry, coal mining, mechanical engineering, and chemical and glass industry. The area around Litoměřice and Louny is known for the production of hops and vegetables. The areas along the Elbe River and Ohře River are well-known fruit growing regions and are sometimes referred to as the Garden of Bohemia. Recently, the area around Most has become known as a wine-growing region, in which wine is grown mainly on lands that were reclaimed after brown coal mining. The sparsely-populated area of the Ore Mountains has limited economic activities. Similarly, the area of Děčín is neither a heavy industrial nor an agricultural area.
In recent years the region has been experiencing an influx of foreign investment in various sectors, including the automotive, chemical, engineering, electrical engineering and food industries. The focus is shifting towards light industry and is becoming more environmentally friendly.[6]
Among the largest employers of the region are coal-mining companies Mostecká uhelná společnost and Severočeské doly, Chemopetrol (a petrochemical company), and Krajská zdravotní, a.s. (a healthcare provider).[4]
Agricultural land covers nearly 52% of the region’s area, forests 30% and water areas 2%.[4] Agricultural production is focused on hops, fruits and vegetables.
Transportation
Ústí nad Labem Region is crossed by railway lines connecting Berlin via Prague to Vienna or Budapest, as well as the Elbe (Czech: Labe) water way. The region is also crossed by the D8 motorway, which connects Prague with the German border, and the I/13, connecting Karlovy Vary Region with Chomutov, Most, Teplice, Ústí nad Labem, Děčín and Liberec Region.
Places of interest
- Nunnery in Doksany
- Duchcov Chateau
- Hněvín Castle
- Pravčická brána in Bohemian Switzerland National Park
- Roudnice nad Labem
- Říp Mountain
- Terezín and Theresienstadt concentration camp
Photo gallery

- České středohoří








- Suburbs of Louny
See also
- Komořanské jezero
- Stolpersteine in the Ústecký kraj
References
- "Population of territorial units of the Czech republic". Czech Statistical Office. Retrieved 2020-04-30.
- "The Usti Region". Ústecký kraj Official website. Retrieved 23 July 2017.
- "Population of municipalities of the Czech republic". Czech Statistical Office. Retrieved 2019-04-30.
- Characteristics of the Ústecký Region, Available online at: "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 2013-10-13. Retrieved 2013-10-11.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)
- Charakteristika kraje, Available online at: http://www.czso.cz/xu/redakce.nsf/i/charakteristika_kraje
- "Usti nad Labem". Czech Invest. Retrieved 23 July 2017.
- "Archived copy" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2014-04-13. Retrieved 2014-04-16.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) page 9