Dihydropteroate synthase inhibitor
A dihydropteroate synthase inhibitor is a drug that inhibits the action of dihydropteroate synthase. Most are sulfonamides.
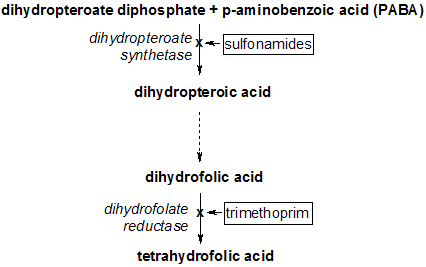
In bacteria, antibacterial sulfonamides act as competitive inhibitors of the enzyme dihydropteroate synthase, DHPS. DHPS catalyses the conversion of PABA (para-aminobenzoate) to dihydropteroate, a key step in folate synthesis.[1] Folate is necessary for the cell to synthesize nucleic acids (nucleic acids are essential building blocks of DNA and RNA), and in its absence cells will be unable to divide. Hence the sulfonamide antibacterials exhibit a bacteriostatic rather than bactericidal effect.[2]
Uses
Folate is not synthesized in mammalian cells, but is instead a dietary requirement. This explains the selective toxicity to bacterial cells of these drugs.[1] These antibiotics are used to treat Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia, urinary tract infections, and shigellosis.
References
- Bauman, Robert W. (2015). Microbiology: With Diseases by Body System (4th ed.). Boston: Pearson. p. 296. ISBN 9780321918550.
- "Sulfonamides and Sulfonamide Combinations". Merck Veterinary Manual. Retrieved 2017-06-18.
Big text