Chrysanthemyl diphosphate synthase
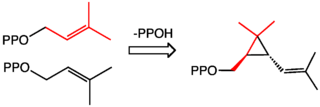
In enzymology, a chrysanthemyl diphosphate synthase (EC 2.5.1.67) is an enzyme involved in the biosynthesis of terpenoids. This enzyme is also known as CPPase. It catalyzes the chemical reaction shown below (color-coded to show how precursors link):
| Chrysanthemyl diphosphate synthase | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Identifiers | |||||||||
| EC number | 2.5.1.67 | ||||||||
| Databases | |||||||||
| IntEnz | IntEnz view | ||||||||
| BRENDA | BRENDA entry | ||||||||
| ExPASy | NiceZyme view | ||||||||
| KEGG | KEGG entry | ||||||||
| MetaCyc | metabolic pathway | ||||||||
| PRIAM | profile | ||||||||
| PDB structures | RCSB PDB PDBe PDBsum | ||||||||
| |||||||||
The substrate of CPPase is dimethylallyl diphosphate. The two products are diphosphate and chrysanthemyl diphosphate.
This enzyme is involved in the biosynthesis of pyrethrins, highly potent insecticides found in some flowers. The systematic name of this enzyme class is dimethylallyl-diphosphate:dimethylallyl-diphosphate dimethylallyltransferase (chrysanthemyl-diphosphate-forming).
References
- Shattuck-Eidens DM, Wrobel WM, Peiser GD, Poulter CD (2001). "Chrysanthemyl diphosphate synthase: isolation of the gene and characterization of the recombinant non-head-to-tail monoterpene synthase from Chrysanthemum cinerariaefolium". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 98 (8): 4373–8. doi:10.1073/pnas.071543598. PMC 31842. PMID 11287653.
- Erickson HK, Poulter CD (2003). "Chrysanthemyl diphosphate synthase. The relationship among chain elongation, branching, and cyclopropanation reactions in the isoprenoid biosynthetic pathway". J. Am. Chem. Soc. 125 (23): 6886–8. doi:10.1021/ja034520g. PMID 12783539.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.