Bissekty Formation
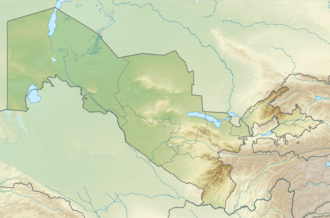
The Bissekty Formation (sometimes referred to as Bissekt) is a geologic formation which crops out in the Kyzyl Kum desert of Uzbekistan, and dates to the Late Cretaceous Period. Laid down in the mid to late Turonian, it is dated to about 92 to 90 Ma (million years ago).[1]
| Bissekty Formation Stratigraphic range: Mid-Late Turonian ~92–90 Ma | |
|---|---|
| Type | Geological formation |
| Underlies | Aitym Formation |
| Overlies | Dzheirantui Formation |
| Thickness | up to 80 m (260 ft) |
| Lithology | |
| Primary | Sandstone |
| Other | Conglomerate, mudstone, siltstone |
| Location | |
| Coordinates | 42.1°N 62.7°E |
| Approximate paleocoordinates | 36.8°N 57.0°E |
| Region | Navoiy & Xorazm Regions |
| Country | |
| Extent | Kyzylkum Desert |
 Bissekty Formation (Uzbekistan) | |
The Bissekty Formation is characterised by a mix of marine, brackish, freshwater, and terrestrial animal fossils. This stands in contrast the strictly marine fossils found in the underlying Dzheirantui Formation, and indicates that the Bissekty was formed during the regression of a saltwater sea. The coastline expanded inland again in the upper portion of the Bissekty, represented by a proportional increase of fully aquatic species, which were almost completely absent from the middle period of the formation. Semi-aquatic species remained abundant during this middle period, and the geology of the formations indicates that a braided river system took the place of the coastline. Eventually the area was again completely underwater, during the time period represented by the later Aitym Formation, which preserves coastal marine sediments.[2]
Geology
The lithology of the sediment largely consists of cross bedded sandstones with interbeds of massive sandstone, well cemented intraformational conglomerate, siltstones and mudstones. Most of the fossils are found as clasts within the conglomerates.[2]
Invertebrates
An indeterminate species of marine coral.
Arthropods
| Arthropods of the Bissekty Formation | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Genus | Species | Location | Stratigraphic position | Abundance | Notes | |
|
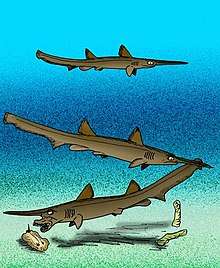
Linuparus dzheirantuiensis |
Marine. |
|||||
Molluscs
An indeterminate species of marine placenticeratid ammonite. An indeterminate species of marine teredinid shipworm. An indeterminate marine trigoniid bivalve. An indeterminate marine veneroid bivalve.
| Molluscs of the Bissekty Formation | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Genus | Species | Location | Stratigraphic position | Abundance | Notes | |
|
Crassatelites |
Indeterminate |
A marine crassatellid bivalve. | ||||
|
Mytiloides |
Mytiloides labiatus |
a marine inoceramid bivalve. | ||||
|
Indeterminate |
A marine limoid bivalve. | |||||
|
Quadratotrigonia |
Indeterminate |
A marine trigoniid bivalve. | ||||
|
Indeterminate |
An indeterminate species of marine shipworm. | |||||
Vertebrates
The Bissekty Formation is notable for preserving the most abundant Turonian land animal fossils in Eurasia, and the most diverse fauna of Late Cretaceous eutherians (placental mammals and relatives) in the world.[2]
Listings and accompanying information are based on a survey of the Bissekty Formation published by Cory Redman and Lindsey Leighton in 2009 unless otherwise noted.[2] Aquatic and semi-aquatic species are restricted to freshwater unless otherwise noted.
Amphibians
An indeterminate species of salamander-like albanerpetontid amphibian. An indeterminate gobiatid species.
| Amphibians of the Bissekty Formation | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Genus | Species | Location | Stratigraphic position | Abundance | Notes | |
|
Aralobatrachus robustus |
A frog. | |||||
|
Eoscapherpeton asiaticum |
A scapherpetontid salamander. | |||||
|
Gobiates sosedkoi |
A gobiatid frog. | |||||
|
Gobiates spp. |
Additional indeterminate species of Gobiates. | |||||
|
Itemirella cretacea |
A possible discoglossid frog. | |||||
|
Kizylkuma antiqua |
A possible discoglossid frog. Marine. | |||||
|
Mynbulakia surgai |
A batrachosauroidid salamander. | |||||
Cartilaginous fish
| Cartilaginous fishes of the Bissekty Formation | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Genus | Species | Location | Stratigraphic position | Abundance | Notes | Images |
|
Cretodus crassidens |
A cretoxyrhinid. Marine. |
| ||||
|
Indeterminate |
A bullhead shark. Marine. | |||||
|
Hispidaspis |
Indeterminate |
A sand shark. Tolerant of brackish water. | ||||
|
Indeterminate |
A hybodontid. Tolerant of brackish water. | |||||
|
Ischyrhiza serra |
A sclerorhynchid. Tolerant of brackish water. | |||||
|
Myledaphus tritus |
A rhinobatoid. Tolerant of brackish water. | |||||
|
Polyacrodus |
Indeterminate |
A polyacrodontid. Tolerant of brackish water. | ||||
|
Scapanorhynchus rhaphiodon |
A goblin shark. Tolerant of brackish water. | |||||
Crocodylomorphs
| Crocodylomorphs of the Bissekty Formation | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Genus | Species | Location | Stratigraphic position | Abundance | Notes | |
|
Kansajsuchus borealis |
A possible goniopholidid mesoeucrocodylian. | |||||
|
Tadzhikosuchus macrodentis |
A possible alligatoroid eusuchian. | |||||
|
Zholsuchus procevus |
A possible mesoeucrocodylian. | |||||
|
Zhyrasuchus angustifrons |
A possible eusuchian. | |||||
Lizards
An indeterminate gekkonid. An indeterminate priscagamid. An indeterminate scincid.
| Lizards of the Bissekty Formation | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Genus | Species | Location | Stratigraphic position | Abundance | Notes | |
|
Buckantaus |
Buckantaus crassidens |
A macrocephalosaurid. | ||||
|
Ekshmer |
Ekshmer bissektensis |
A priscagamid. | ||||
Mammals and other therapsids
| Mammaliaformes of the Bissekty Formation | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Genus | Species | Location | Stratigraphic position | Abundance | Notes | |
|
Aspanlestes |
A. aptap |
A zhelestid. | ||||
|
Bulaklestes |
B. kezbe |
An asioryctitherian. | ||||
|
Daulestes |
D. inobservabilis |
An asioryctitherian. | ||||
|
D. kulbeckensis |
An asioryctitherian. | |||||
|
Eoungulatum |
E. kudukensis |
A zhelestid. | ||||
|
Kulbeckia |
K. kulbecke |
|||||
|
Paranyctoides |
P. quadrans |
A eutherian. | ||||
|
Parazhelestes |
P. mynbulakensis |
A zhelestid. | ||||
|
P. robustus |
A zhelestid. | |||||
|
Shalbaatar |
S. bakht |
A symmetrodont. | ||||
|
S. karakshi |
A deltatheroid. | |||||
|
Uchkudukodon |
U. nessovi |
An asioryctitherian. | ||||
|
U. kizylkumensis |
A cimolodont. | |||||
|
Zhelestes |
Z. temirkazyk |
A zhelestid. | ||||
Ornithischians
Color key
|
Notes Uncertain or tentative taxa are in small text; |
| Ornithischians reported from the Bissekty Formation | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Genus | Species | Location | Stratigraphic position | Material | Description | Images |
|
A. archibaldi[3] |
Reclassified as Bissektipelta[4] |
| ||||
|
B. archibaldi[4] |
"Partial skull."[5] |
An ankylosaur | ||||
|
C. kyslkumensis |
"Fragmentary dentary [=maxilla], vetebrae, tibia."[6] |
Nomen dubium | ||||
|
G. arkhangelskyi |
Nomen dubium | |||||
|
L. transoxiana |
"Braincases." |
A hadrosauroid | ||||
|
T. tardabilis[3] |
A ceratopsian[7] | |||||
Plesiosaurs
| Plesiosaurs of the Bissekty Formation | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Genus | Species | Location | Stratigraphic position | Abundance | Notes | Images |
|
Indeterminate |
Marine, possibly tolerant of brackish water. |
|||||
Pterosaurs
| Pterosaurs of the Bissekty Formation | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Genus | Species | Location | Stratigraphic position | Abundance | Notes | Images |
|
Azhdarcho lancicollis |
Dzhara-Kuduk |
Taykarshinskaya unit |
An azhdarchid |
| ||
Ray-finned fish
An indeterminate acipenserid. An indeterminate albulid (bonefish) species. An indeterminate albulid (bonefish) species. An indeterminate pholidophoriform species.
| Ray-finned fish of the Bissekty Formation | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Genus | Species | Location | Stratigraphic position | Abundance | Notes | Images |
|
Aidachar paludalis |
An ichthyodectiform tolerant of brackish water. |
 A living Amia. | ||||
|
Amia Extant |
Amia limosa |
A bowfin tolerant of brackish water. | ||||
|
Atractosteus turanensis |
A gar tolerant of brackish water. | |||||
|
Belonostomus aciculifer |
An aspidorhynchid. | |||||
|
Psephuroides |
Psephuroides kazakhorum |
A paddlefish. | ||||
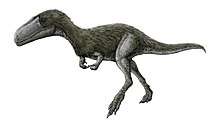
Theropods
An unnamed ornithomimosaur, known from fragmentary remains.[8] An indeterminate tyrannosaurid species, known from isolated teeth.[9]
| Non-Enantiornithine Theropod dinosaurs reported from the Bissekty Formation | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Genus | Species | Location | Stratigraphic position | Material | Description | Images |
|
A. bissektensis |
"Metatarsals."[10] |
A dubious ornithomimosaur. |
| |||
|
C. martinsoni |
"[Two] partial mandibles."[11] |
|||||
|
E. asiaticus |
A possible troodontid based on isolated teeth.[12][13][14] |
|||||
|
I. medullaris |
||||||
|
K. mengi[15] |
"[Two] synsacra."[15] |
|||||
|
Platanavis[3] |
P. nana[3] |
"Sacrum."[16] |
||||
|
Indeterminate |
Partial crania also preserving some teeth and some postcranial elements including pedal bones (from multiple individuals) |
At least two different therizinosauroids. | ||||
|
T. euotica |
Two braincases, dentary, and miscellaneous postcranial elements (from multiple individuals) |
A non-tyrannosaurid tyrannosauroid. | ||||
|
Unnamed species |
A troodontid, known from isolated teeth.[19] | |||||
|
Z. kashkarovi |
A possible ornithurine. | |||||
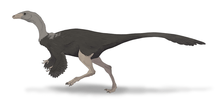
Enantiornithines
| Enantiornithines reported from the Bissekty Formation | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Genus | Species | Location | Stratigraphic position | Material | Description | Images |
|
A. bonaparti |
A possible enantiornithine.[20] A possible second species of Abavornis in the Bissekty Formation is known from a partial coracoid.[20] |
|||||
|
C. anachoretus |
A possible enantiornithine. | |||||
|
E. nessovi |
An enantiornithine. Possible third and fourth species of Explorornis in the Bissekty Formation are known from partial coracoids.[20] | |||||
|
E. walkeri |
"Coracoid."[21] |
|||||
|
I. minusculus |
"Dorsal vertebra."[16] |
An enantiornithine originally but incorrectly identified as a species of Ichthyornis.[22] | ||||
|
I. martini |
Known from a partial coracoid.[20] |
A possible enantiornithine.[20] | ||||
|
I. silvae |
Known from a partial coracoid.[20] |
A possible enantiornithine.[20] | ||||
|
K. cretacea[3] |
"Distal humerus."[21] |
An enantiornithine. | ||||
|
K. mengi |
"[Two] synsacra."[15] |
An enantiornithine. | ||||
|
L. maltshevskyi[3] |
"Synsacrum."[21] |
A possible enantiornithine. | ||||
|
cf. Nanantius |
An enantiornithine, similar to Nanantius eos. | |||||
|
S. prisca[3] |
"Distal tibiotarsus."[23] |
An enantiornithine. | ||||
|
Z. kashkarovi[3] |
"Synsacrum."[23] |
|||||
|
Z. logunovi[3] |
"Synsacrum."[23] |
|||||
Turtles
An indeterminate trionychid (soft-shell) turtle species that was tolerant of brackish water.
| Turtles of the Bissekty Formation | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Genus | Species | Location | Stratigraphic position | Abundance | Notes | |
|
"Adocus" |
"Adocus" aksary |
An adocid tolerant of brackish water. | ||||
|
Indeterminate |
A "macrobaenid" tolerant of brackish water. | |||||
|
Khunnuchelys kizylkumensis |
A trionychid tolerant of brackish water. | |||||
|
Lindholmemys |
Lindholmemys elegans |
A "lindholmemydid" tolerant of brackish water. | ||||
|
Shachemys |
Shachemys ancestralis |
An adocid tolerant of brackish water. | ||||
References
- Averianov, Alexander; Sues, Hans-Dieter (April 2012). "Skeletal remains of Tyrannosauroidea (Dinosauria: Theropoda) from the Bissekty Formation (Upper Cretaceous: Turonian) of Uzbekistan". Cretaceous Research. 34: 284–297. doi:10.1016/j.cretres.2011.11.009. ISSN 0195-6671.
- Redman & Leighton, 2009
- "Dinosaur distribution (Bissekty Formation)." Weishampel, et al. (2004). Pg. 594.
- Averianov, 2002
- "Table 17.1," in Weishampel, et al. (2004). Page 367.
- "Table 20.1," in Weishampel, et al. (2004). Page 442.
- Sues & Averianov, 2009
- Sues & Averianov, 2016
- Archibald, James David; Sues, Hans-Dieter; Averianov, Alexander; King, Chris; Ward, David John; Tsaruk, Oleg; Danilov, Igor; Rezvyi, Anton; Veretennikov, Boris; Khodjaev, Anvar (1998). "Precis of the Cretaceous paleontology, biostratigtaphy and sedimentology at Dzharakuduk (Turonian?-Santonian), Kyzylkum Desert, Uzbekistan". Bulletin of the New Mexico Museum of Natural History and Science. 14: 21–27.
- "Table 6.1," in Weishampel, et al. (2004). Page 139.
- "Table 8.1," in Weishampel, et al. (2004). Page 166.
- "Table 10.1," in Weishampel, et al. (2004). Page 199.
- "Table 9.1," in Weishampel, et al. (2004). Page 185.
- Nesov, A. (1995). "Dinosaurs of Northern Eurasia: new data about assemblages, ecology and paleobiogeography." Scientific Research Institute of the Earth's Crust. St. Petersburg State University, St. Petersburg, Russia: 156 pp. + 14 pl. [in Russian with short English, German, and French abstracts].
- "Table 11.1," in Weishampel, et al. (2004). Page 212.
- "Table 11.1," in Weishampel, et al. (2004). Page 216.
- Sues, H.-D.; Averianov, A. (2016). "Therizinosauroidea (Dinosauria: Theropoda) from the Upper Cretaceous of Uzbekistan". Cretaceous Research. 59: 155–178. doi:10.1016/j.cretres.2015.11.003.
- Stephen L. Brusatte; Alexander Averianov; Hans-Dieter Sues; Amy Muir; Ian B. Butler (2016). "New tyrannosaur from the mid-Cretaceous of Uzbekistan clarifies evolution of giant body sizes and advanced senses in tyrant dinosaurs". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 113 (13): 3447–3452. doi:10.1073/pnas.1600140113. PMC 4822578. PMID 26976562.
- Averianov, A.O.; Sues, H.-D. (2007). "A new troodontid (Dinosauria: Theropoda) from the Cenomanian of Uzbekistan, with a review of troodontid records from the territories of the former Soviet Union". Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology. 27 (1): 87–98. doi:10.1671/0272-4634(2007)27[87:ANTDTF]2.0.CO;2.
- Panteleev (1998). ""New species of enantiornithines (Aves: Enantiornithes) from the Upper Cretaceous of Central Kyzylkum." Russkii Ornitologicheskii Zhurnal". Ekspress-vy.pvsk. 35: 3–15.
- "Table 11.1," in Weishampel, et al. (2004). Page 213.
- Kurochkin. (1996). "A new Enantiornithid of the Mongolian Late Cretaceous, and a general appraisal of the Infraclass Enantiornithes (Aves)." Russian Academy of Sciences, special issue: 50pp.
- "Table 11.1," in Weishampel, et al. (2004). Page 214.
Bibliography
- Averianov, A.O. 2002. An ankylosaurid (Ornithischia: Ankylosauria) braincase from the Upper Cretaceous Bissekty Formation of Uzbekistan. Bulletin de l'Institute Royal des Sciences Naturelles de Belgique, Sciences de la Terre 72. 97–110. Accessed 2019-03-22.
- Redman, C.M., and L.R. Leighton. 2009. Multivariate faunal analysis of the Turonian Bissekty Formation: Variation in the degree of marine influence in temporally and spatially averaged fossil assemblages. PALAIOS 24. 18–26. Accessed 2019-03-22.
- Sues, H-D., and A. Averianov. 2016. Ornithomimidae (Dinosauria: Theropoda) from the Bissekty Formation (Upper Cretaceous: Turonian) of Uzbekistan. Cretaceous Research 57. 90–110. Accessed 2019-03-22.
- Sues, H.-D., and A. Averianov. 2009. Turanoceratops tardabilis—the first ceratopsid dinosaur from Asia. Naturwissenschaften 96. 645–652. Accessed 2019-03-22.
- Weishampel, David B.; Peter Dodson, and Halszka (eds.) Osmólska. 2004. The Dinosauria, 2nd edition, 1–880. Berkeley: University of California Press. Accessed 2019-02-21. ISBN 0-520-24209-2
Further reading
- Averianov, A.O.; J.D. Archibald, and E.G. Ekdale. 2010. New material of the Late Cretaceous deltatheroidan mammal Sulestes from Uzbekistan and phylogenetic reassessment of the metatherian-eutherian dichotomy. Journal of Systematic Palaeontology 8. 301–330. Accessed 2019-03-22.
- Averianov, A.O. 2007. New records of azhdarchids (Pterosauria, Azhdarchidae) from the Late Cretaceous of Russia, Kazakhstan, and Central Asia. Paleontological Journal 41. 189–197. Accessed 2019-03-22.
- Feldmann, R.M.; C.E. Schweitzer; C.M. Redman; N.J. Morris, and D.J. Ward. 2007. New Late Cretaceous lobsters from the Kyzylkum Desert of Uzbekistan. Journal of Paleontology 81. 701–713. Accessed 2019-03-22.
- Storrs, G.W., and M.B. Efimov. 2000. Mesozoic crocodyliforms of north-central Eurasia, 402–419. In M. J. Benton, M. A. Shishkin, D. M. Unwin, E. N. Kurochkin (eds.), The Age of Dinosaurs in Russia and Mongolia. Accessed 2019-03-22.
- Sues, H.-D., and A. Averianov. 2014. Dromaeosauridae (Dinosauria: Theropoda) from the Bissekty Formation (Upper Cretaceous: Turonian) of Uzbekistan and the phylogenetic position of Itemirus medullaris Kurzanov, 1976. Cretaceous Research 51. 225–240. Accessed 2019-03-22.
- N. V. Zelenkov and A. O. Averianov. 2011. Synsacrum of a primitive bird from the Upper Cretaceous of Uzbekistan. Paleontological Journal 45(3):314-319