Bed
A bed is a piece of furniture which is used as a place to sleep, relax, or engage in sexual activity.[1][2]
.jpg)
Most modern beds consist of a soft, cushioned mattress on a bed frame, the mattress resting either on a solid base, often wood slats, or a sprung base. Many beds include a box spring inner-sprung base, which is a large mattress-sized box containing wood and springs that provide additional support and suspension for the mattress. Beds are available in many sizes, ranging from infant-sized bassinets and cribs, to small beds for a single person or adult, to large queen and king-size beds designed for two people. While most beds are single mattresses on a fixed frame, there are other varieties, such as the murphy bed, which folds into a wall, the sofa bed, which folds out of a sofa, and the bunk bed, which provides two mattresses on two tiers as well as a ladder to get to the upper tier. Temporary beds include the inflatable air mattress and the folding camp cot. Some beds contain neither a padded mattress nor a bed frame, such as the hammock. Some beds are made especially for animals.
Beds may have a headboard for resting against, and may have side rails and footboards (or "footers"). "Headboard only" beds may incorporate a "dust ruffle", "bed skirt", or "valance sheet" to hide the bed frame. To support the head, a pillow made of a soft, padded material is usually placed on the top of the mattress. Some form of covering blanket is often used to insulate the sleeper, often bed sheets, a quilt, or a duvet, collectively referred to as bedding. Bedding is the removable non-furniture portion of a bed, which enables these components to be washed or aired out.
History
Ancient history
.jpg)
Early beds were little more than piles of straw or some other natural material (e.g. a heap of palm leaves, animal skins, or dried bracken). An important change was raising them off the ground, to avoid drafts, dirt, and pests. 23-5 million years ago, before the advent of humans, apes began creating beds composed of a sleeping platform including a wooden pillow.[3] Bedding dated around to 3600 BC was discovered in Sibudu Cave, South Africa.[4] The bedding consists of sedge and other monocotyledons topped with the leaves of Cryptocarya woodii Engl.[4] Beds found in a preserved northern Scottish village, which were raised boxes made of stone and likely topped with comfortable fillers, were dated to between 3200 BC and 2200 BC.[5] The Egyptians had high bedsteads which were ascended by steps, with bolsters or pillows, and curtains to hang around. The elite of Egyptian society such as its pharaohs and queens even had beds made of wood, sometimes gilded. Often there was a head-rest as well, semi-cylindrical and made of stone, wood, or metal. Ancient Assyrians, Medes, and Persians had beds of a similar kind, and frequently decorated their furniture with inlays or appliques of metal, mother-of-pearl, and ivory.

The adjacent image showcases a headrest. Headrests like this were used in life to support the head while sleeping. They are also found supporting a mummy's head in the coffin. This headrest perhaps was made specifically for the tomb, since the offering prayer has been inscribed on the supporting column, although the prayer may have been added after the death of the owner.[6]
The oldest account of a bed is probably that of Odysseus: a charpoy[7] woven of rope plays a role in the Odyssey. A similar bed can be seen at the St Fagans National History Museum in Wales. Odysseus also gives an account of how he crafted the nuptial bed for himself and Penelope, out of an ancient, huge olive tree trunk that used to grow on the spot before the bridal chamber was built. His detailed description finally persuades the doubting Penelope that the shipwrecked, aged man is indeed her long-lost husband. Homer also mentions the inlaying of the woodwork of beds with gold, silver, and ivory. The Greek bed had a wooden frame, with a board at the head and bands of hide laced across, upon which skins were placed. At a later period the bedstead was often veneered with expensive woods; sometimes it was of solid ivory veneered with tortoise-shell and with silver feet; often it was of bronze. The pillows and coverings also became more costly and beautiful; the most celebrated places for their manufacture were Miletus, Corinth and Carthage. Folding beds, too, appear in the famous Ancient Greek vase paintings.
Roman mattresses were stuffed with reeds, hay, or wool. Feathers were used towards the end of the Republic, when custom demanded luxury. Small cushions were placed at the head and sometimes at the back. The bedsteads were high and could only be ascended by the help of steps. They were often arranged for two people, and had a board or railing at the back, as well as the raised portion at the head. The counterpanes were sometimes very costly, generally purple embroidered with figures in gold; and rich hangings fell to the ground masking the front. The bedsteads themselves were often of bronze inlaid with silver, and Elagabalus had one of solid silver. In the walls of some houses at Pompeii bed niches are found which were probably closed by curtains or sliding partitions. Ancient Romans had various kinds of beds for repose. These included:
- lectus cubicularis, or chamber bed, for normal sleeping
- lectus genialis, the marriage bed, it was much decorated, and was placed in the atrium opposite the door
- lectus discubitorius, or table bed, on which they ate—for they ate while lying on their left sides—there usually being three people to one bed, with the middle place accounted the most honorable position
- lectus lucubratorius, for studying
- and a lectus funebris, or emortualis, on which the dead were carried to the pyre[8]
Post-classical history
The ancient Germans lay on the floor on beds of leaves covered with skins, or in a kind of shallow chest filled with leaves and moss. In the early Middle Ages they laid carpets on the floor or on a bench against the wall, placed upon them mattresses stuffed with feathers, wool, or hair, and used skins as a covering. Curtains were hung from the ceiling or from an iron arm projecting from the wall.[9] They appear to have generally lain naked in bed, wrapping themselves in large linen sheets which were stretched over the cushions.

In the 12th century, luxury increased and bedsteads were made of wood much decorated with inlaid, carved, and painted ornamentation. They also used folding beds, which served as couches by day and had cushions covered with silk laid upon leather. At night a linen sheet was spread and pillows placed, while silk-covered skins served as coverlets. The Carolingian manuscripts show metal bedsteads much higher at the head than at the feet, and this shape continued in use until the 13th century in France, many cushions being added to raise the body to a sloping position. In 12th-century manuscripts, the bedsteads appear much richer, with inlays, carving, and painting, and with embroidered coverlets and mattresses in harmony. Curtains were hung above the bed and a small hanging lamp is often shown.
In the 14th century the woodwork became of less importance, generally being entirely covered by hangings of rich materials. Silk, velvet, and even cloth of gold were frequently used. Inventories from the beginning of the 14th century give details of these hangings lined with fur and richly embroidered. It was then that the Four poster bed (also known as a tester bed) made its first appearance, the bed being slung from the ceiling or fastened to the walls, a form which developed later into a room within a room, shut in by double curtains, sometimes even to exclude all drafts. The space between bed and wall was called the ruelle, and very intimate friends were received there. The 14th century is also the time when feather beds became highly prized possessions.[9]
In the 15th century beds became very large, reaching 7 to 8 feet (2.1 to 2.4 m) by 6 to 7 feet (1.8 to 2.1 m). The mattresses were often filled with pea-shucks, straw, or feathers. At this time great personages were in the habit of carrying most of their property about with them, including beds and bed-hangings, and for this reason the bedsteads were for the most part mere frameworks to be covered up; but about the beginning of the 16th century bedsteads were made lighter and more decorative, since the lords remained in the same place for longer periods.
Modern history
In the 17th century, which has been called "the century of magnificent beds", the style a la duchesse, with tester and curtains only at the head, replaced the more enclosed beds in France, though they lasted much longer in England. Louis XIV had an enormous number of sumptuous beds, as many as 413 being described in the inventories of his palaces. Some of them had embroideries enriched with pearls, and figures on a silver or golden ground. The great bed at Versailles had crimson velvet curtains on which "The Triumph of Venus" was embroidered. So much gold was used that the velvet scarcely showed.

In the 18th century feather pillows were first used as coverings in Germany, which in the fashions of the bed and the curious etiquette connected with the bedchamber followed France for the most part. The beds were a la duchesse, but in France itself there was great variety both of name and shape. The custom of the "bed of justice" upon which the king of France reclined when he was present in parliament, the princes being seated, the great officials standing, and the lesser officials kneeling, was held to denote the royal power even more than the throne.
Louis XI is credited with its first use and the custom lasted until the end of the monarchy. In the chambre de parade, where the ceremonial bed was placed, certain persons, such as ambassadors or great lords, whom it was desired to honour, were received in a more intimate fashion than the crowd of courtiers. At Versailles women received their friends in their beds, both before and after childbirth, during periods of mourning, and even directly after marriage—in fact in any circumstances which were thought deserving of congratulation or condolence. During the 17th century this curious custom became general, perhaps to avoid the tiresome details of etiquette. Portable beds were used in high society in France until the end of the Ancien Régime. The earliest of which mention has been found belonged to Charles the Bold. They had curtains over a light framework, and were in their way as fine as the stationary beds.
Iron beds appear in the 18th century; the advertisements declare them as free from the insects which sometimes infested wooden bedsteads. Elsewhere, there was also the closed bed with sliding or folding shutters, and in England—where beds were commonly quite simple in form—the four poster was the usual citizen's bed until the middle of the 19th century.
Bed sizes
Bed sizes vary considerably around the world, with most countries having their own standards and terminology. These are discussed in detail in the Bed size article as there are too many variations for even a summary to be given here.
Notable examples

One of the largest beds in the world is the Great Bed of Ware, made in about 1580. It is 3.26 metres (10.7 ft) wide, 3.38 metres (11.1 ft) long. The bed is mentioned by Shakespeare in Twelfth Night. It is now in the Victoria and Albert Museum (V&A) in London. Another bed in the V&A is the Golden Bed created by William Burges in 1879.[10]
In 1882, an Indian Maharajah had a bed made of solid silver. At each corner of the bed there was a life-sized statue of a naked woman holding a fan. When the Maharajah lay on the bed, his weight started a mechanism that made the women wave their fans.[11]
In 1865, a convertible bed in the form of an upright piano was available, which could provide home entertainment while saving space.[12]
Types
There are many varieties of beds:
- An adjustable bed is a bed that can be adjusted to a number of different positions. Most hospital beds are adjustable, so that a patient can have different parts of her body elevated for medical reasons. Some people have adjustable beds in private homes. Some adjustable beds are designed for couples; they use two separate mattresses and adjustment mechanisms. This permits one partner to be lying flat to sleep while the other has the head and shoulders elevated to watch television or read. Couple adjustable beds also permit partners with different medical conditions to select a mattress positioning that best suits them.
- An air bed uses an air-inflated mattress, sometimes connected to an electric air pump and having variable, firmness controls. The portable version of an air bed can also be rolled up and packed; so is meant for travel or temporary guest use.
- A bassinet is a bed specifically for newborns.
- A box-bed is a bed having the form of a large box with wooden roof, sides, and ends, opening in front with two sliding panels or shutters; often used in cottages in Scotland: sometimes also applied to a bed arranged to fold up into a box.
- A brass bed has a frame constructed from brass. A brass-plated bed is a cheaper bed of iron with a thin covering of brass, which with time peels off and the iron is exposed.
- A bunk bed is two or more beds one atop the other. Bunk beds are used for adults in military barracks and in some ski lodges. Bunk beds are used for children and teens in summer camps. Some inexpensive hostels provide bunk beds for guests. Bunk beds are used for children in private homes.
- A loft bed is similar to a bunk bed, except there is no lower bunk. This leaves space underneath for storage, other furniture, a desk etc.
- A captain's bed[14] (also known as a "captain bed", "chest bed", or "cabin bed") is a platform bed with drawers and storage compartments built in underneath.
- A camp bed (also "cot") is a simple, temporary, portable bed used by armies and by campers. Cots are also used to provide a sleeping surface for refugees and other homeless people during disasters, floods, or other crises.
- A canopy bed is similar to a four poster bed, but the posts usually extend higher and are adorned or draped with cloth, sometimes completely enclosing the bed. Examples include the Polish bed and the lit a la turque.
- A curtained bed is a luxury bed with curtains.
- A daybed is a couch that is used as a seat by day and as a bed by night. Usually it has pop up trundle which is used as bed in the night.
- A futon is a traditional style of Japanese bed using a mattress on a wooden frame. Futons are also available in a larger Western style which can fold halfway for sitting. Futons were traditionally made with cotton, but in the 2000s, many futons include synthetic foam.
- A four poster bed is a bed with four posts, one in each corner, that support a tester.
- A hammock is a piece of suspended fabric or netting, used on ships and in some homes.
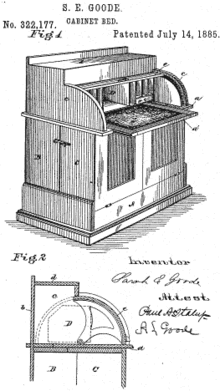
- A hideaway bed, invented by Sarah E. Goode in response to the needs of apartment-dwellers, folds up into another piece of furniture, such as a shelf or desk, when not in use.
- A hospital bed is specifically designed to facilitate convalescence, traditionally in a hospital or nursing facility, but increasingly in other settings, such as a private residence. Hospital beds are typically adjustable, so that the head or feet can be raised or lowered. Modern hospital beds commonly have wheels to assist in moderate relocation, but they are larger and generally more permanently placed than a trolley (US: gurney). The "hospital bed" is also a common unit of measurement for the capacity of any type of inpatient medical facility, though it is just as common to shorten the term to "bed" in that usage (e.g. The hospital has 250 beds...).
- An infant bed (also "crib" or "cot") is a small bed specifically for babies and infants.
- An iron bed, developed in the 1850s, is constructed of iron and steel.
- A kang bed-stove is a Chinese ceramic room heater used as the platform for a bed.
- A Manjaa is a traditional Punjabi bed made of tied ropes bordered by a wooden frame.
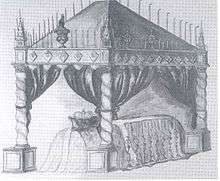
- A mourning bed ("illustration") is a formal canopied bed, with the deceased, a wax effigy, or symbols of rank.
- A Murphy bed or wallbed is a bed that can fold up into a wall or cabinet to save space.
- An Ottoman bed (in the UK) is a type of storage bed in which the storage area is placed underneath the mattress base and accessed by lifting the hinged mattress frame with the help of a spring or hydraulic mechanism.
- A pallet is a thin, lightweight mattress.
- A platform bed is a mattress resting on a solid, flat raised surface, either free-standing or part of the structure of the room.
- A roll-away bed is a bed whose frame folds in half and rolls in order to be more easily stored and moved. This is used in different settings, including hotels for either free or a nominal fee per night, where more people than expected may need to sleep in the same room, e.g. 5 people in a hotel room for 4 (two twin beds).
- A rope bed is a pre-modern bed whose wooden frame includes crossing ropes to support the typically down-filled single mattress.
- A sofabed ("pull-out" or "pull-out bed") is a folding bed that is stored inside a sofa. Sofa beds are also called “convertibles” and “hideaways.”
- A state bed developed in Early Modern Europe from a hieratic canopy of state.
- A toddler bed is a small bed for young children.
- A trundle bed or "truckle bed" is a bed usually stored beneath another bed during the day. They have been in use for centuries. In the modern era they are sometimes referred to as a "sleepover bed" or "daybed with pop up trundle.”
- A vibrating bed (also known as a Magic Fingers bed) is typically a coin-operated novelty found in a vintage (c. 1960s-early 1980s) motel. For a nominal fee, the mattress vibrates for a duration of time. Alternatively it is a modern bed which vibrates by use of an off-centre motor. It is controlled by electronics for varying time and amplitude settings and is used therapeutically to ease back pains or as an erotic aid.
- A waterbed is a flexible plastic mattress full of water. The plastic container needs a strong frame around it.
Frames
Bed frames, also called bed steads, are made of wood or metal. The frame is made up of head, foot, and side rails. For heavy duty or larger frames (such as for queen- and king-sized beds), the bed frame also includes a center support rail. These rails are assembled to create a box for the mattress or mattress/box spring to sit on.
Types include:
- platform – typically used without a box spring
- captain – has drawers beneath the frame to make use of the space between the floor and the bed frame
- waterbed – a heavy-duty frame built specifically to support the weight of the water in the mattress (Mainly used on larger models)
Although not truly parts of a bed frame, headboards, footboards, and bed rails can be included in the definition. Headboards and footboards can be wood or metal. They can be stained, painted, or covered in fabric or leather.
Bed rails are made of wood or metal and are attached to a headboard and footboard. Wooden slats are placed perpendicular to the bed rails to support the mattress/mattress box spring. Bed rails and frames are often attached to the bed post using knock-down fittings.[15][16] A knock-down fitting enables the bed to be easily dismantled for removal. Primary knock-down fittings for bed rails are as follows:
- Pin-and-hook fastener. A mortise or slot is cut vertically in the bedpost. Pins are inserted horizontally in the bed post so that the pins perpendicularly intersect the mortise. For example, if one looked in the mortise, one might see part of one horizontal pin at the bottom of the mortise and a part of a second pin toward the top of the mortise. Hooks are installed at the end of the rail. Usually these hooks are part of a plate that is attached to the rail. The hooks then are inserted into the bed post mortise and hook over the pins.
- Plate-and-hook fastener. Instead of pins inserted horizontally into the bedpost, an eye plate (post plate) is installed on the bedpost. The hooks are installed on the rail, either as surface mount or recessed. Depending on the hardware, the bedpost may require a mortise in order to allow the hooks to fasten to the plate. This is also referred to as a keyhole fastener, especially if the connector is more of a "plug" than a "hook".
- Bed bolts ("through-bolts") are a different means of a knock-down connection. A hole is typically drilled through the bedpost. The bolt head is inset and covered with a plug. In the rail, a dowel nut or other type of nut receives the bolt. The springs are made from metal, which are swirled for maximum comfort
Safety rails, or cot sides, can be added to the sides of a bed (normally a child or elderly person's bed) to stop anyone falling out of the sides of the bed.[17] A safety rail is normally a piece of wood that attaches to the side rails on one or both sides of the bed. They are made so that they can be easily removed when no longer required.
See also
References
- "Bed". The Free Dictionary By Farlex. Retrieved 16 May 2012.
- "Bed". Merriam-Webster. Retrieved 16 May 2012.
- "Chimpanzees Make Beds That Offer Them Best Night's Sleep". National Geographic News. 18 April 2014. Retrieved 30 March 2018.
- Wadley L, Sievers C, Bamford M, Goldberg P, Berna F, Miller C. (2011). Middle Stone Age Bedding Construction and Settlement Patterns at Sibudu, South Africa. Science 9 December 2011: Vol. 334 no. 6061 pp. 1388-1391
- "Skara Brae – The Furniture". orkneyjar.com.
- "Headrest with Two Images of the God Bes". Retrieved 8 July 2014.
- "Definition of CHARPOY". Retrieved 30 December 2016.
-

- "Medieval Furniture & Home Decor". furniturestyles.net. Retrieved 26 November 2010.
- "The Golden Bed". Victoria and Albert Museum. Retrieved 26 May 2013.
- Independent. "India's royal riches: The maharajas' opulent lifestyle". Retrieved 31 July 2017.
- Brooklyn Museum. "Decorative Arts: Convertible Bed in Form of Upright Piano". Retrieved 11 March 2012.
- (in English) "Bed (Lit à la Polonaise)". getty.edu. Archived from the original on 1 March 2009. Retrieved 26 January 2009.
- "Captain's bed". Dictionary.com. Retrieved 26 May 2012.
- "Historical Guide: Bed Hardware". whitechapel-ltd.com. Archived from the original on 12 March 2006.
- "Bed Rail Fastener Options". home-improvement-and-financing.com. Archived from the original on 15 April 2017. Retrieved 15 April 2008.
- "Bed Safety Rails". sleepcompare.com. Retrieved 15 November 2018.