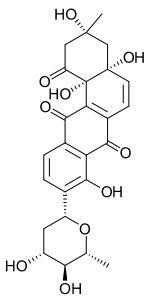
Aquayamycin
Aquayamycin is an anthraquinone derivative.[2] It is an inhibitor of the enzyme tyrosine hydroxylase.
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
(3R,4aR,12bS)-9-[(2R,4R,5S,6R)-4,5-dihydroxy-6-methyloxan-2-yl]-3,4a,8,12b-tetrahydroxy-3-methyl-2,4-dihydrobenzo[a]anthracene-1,7,12-trione | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| MeSH | aquayamycin |
PubChem CID |
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C25H26O10 | |
| Molar mass | 486.47 g/mol |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Saquayamycins (saquayamycins A, B, C and D) are antibiotics of the aquayamycin group found in Streptomyces nodosus cultures broth.[3]
References
- Aquayamycin - Compound Summary, PubChem.
- Sezaki, M.; Kondo, S.; Maeda, K.; Umezawa, H.; Ono, M. (1970). "The structure of aquayamycin". Tetrahedron. 26 (22): 5171–5190. doi:10.1016/S0040-4020(01)98726-5. PMID 5499897.
- Uchida, T.; Imoto, M.; Watanabe, Y.; Miura, K.; Dobashi, T.; Matsuda, N.; Sawa, T.; Naganawa, H.; Hamada, M.; Takeuchi, T.; Umezawa, H. (1985). "Saquayamycins, new aquayamycin-group antibiotics". The Journal of Antibiotics. 38 (9): 1171–1181. doi:10.7164/antibiotics.38.1171. PMID 3840796.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.