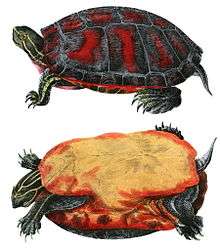
Alabama red-bellied cooter
The Alabama red-bellied cooter (Pseudemys alabamensis) or Alabama red-bellied turtle, is native to Alabama.[1][2] It belongs to the turtle family Emydidae, the pond turtles. It is the official reptile of the state of Alabama.[5]
| Alabama red-bellied cooter | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Reptilia |
| Order: | Testudines |
| Suborder: | Cryptodira |
| Superfamily: | Testudinoidea |
| Family: | Emydidae |
| Genus: | Pseudemys |
| Species: | P. alabamensis |
| Binomial name | |
| Pseudemys alabamensis | |
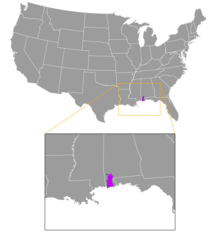 | |
| Alabama red-bellied cooter range[3] | |
| Synonyms[4] | |
| |
Life history
The red-belly inhabits the fresh to brackish waters of the Mobile-Tensaw River Delta in Mobile and Baldwin counties.[2] It feeds on aquatic vegetation[6] and can be found sunning itself on logs. Nesting of the red-bellied turtle occurs from May through July. Female turtles lay their eggs on dry land, digging nests in sandy soil, where 4 to 9 eggs are laid. Hatchlings usually emerge during the summer. However, when the turtles nest in late July, hatchlings may overwinter in the nest and emerge the following spring.
A mature female can be 14 inches, while a mature male can be 12 inches.[6]
Location
As of June 2009 the turtle has been seen in the central part of Alabama, in the Elmore County region.
This turtle has also been found in south-eastern Mississippi,[7] in Harrison and Jackson counties.[6]
Protection
In 2007, a 3.4 miles (5.5 km) chain-link fence has been constructed along part of the US 98 causeway (Battleship Parkway) that separates the Mobile-Tensaw delta from Mobile Bay.[8] Hatchling deaths dropped 80% from 2007 to 2008.
Gallery
- hatchling
 hatchling, bottom shell
hatchling, bottom shell hatchling, carapace view
hatchling, carapace view
References
- Rhodin 2011, p. 000.181
- Tortoise & Freshwater Turtle Specialist Group (1996). "Pseudemys alabamensis". The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. IUCN. 1996: e.T18458A97296493. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.1996.RLTS.T18458A8295960.en. Listed as Endangered (EN B1+2c v2.3)
- U.S. Geological Survey (2017). "Alabama Red-bellied Cooter (Pseudemys alabamensis) rARBCx_CONUS_2001v1 Range Map". Gap Analysis Project. doi:10.5066/F7Z31XTN.
- Fritz Uwe; Peter Havaš (2007). "Checklist of Chelonians of the World" (PDF). Vertebrate Zoology. 57 (2): 192. Archived from the original (PDF) on 1 May 2011. Retrieved 29 May 2012.
- "Official Alabama Reptile". Alabama Emblems, Symbols and Honors. Alabama Department of Archives & History. 12 July 2001. Retrieved 19 March 2007.
- "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 16 April 2014. Retrieved 7 October 2018.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)
- Southern Wonder: Alabama's Surprising Biodiversity by R. Scot Duncan, University of Alabama Press, 2013, page 367, ISBN 9780817357504
- http://baldwinreport.com/2007/11/14/turtle-protectors-on-the-causeway/
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Pseudemys alabamensis. |
- Save the Alabama Red-bellied turtle—Alabama red-bellied turtle alliance