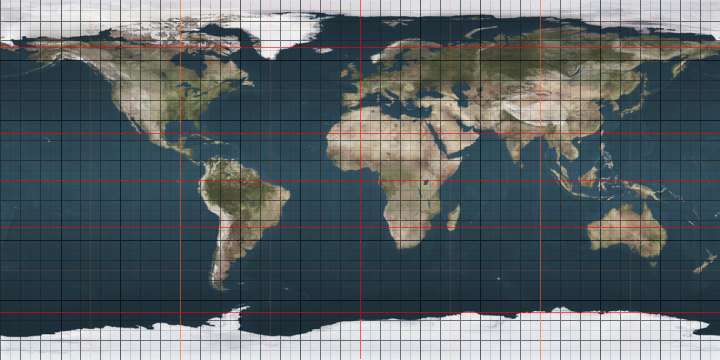
46th parallel north
The 46th parallel north is a circle of latitude that is 46 degrees north of the Earth's equatorial plane. It crosses Europe, Asia, the Pacific Ocean, North America, and the Atlantic Ocean.
.svg.png)
46°
46th parallel north
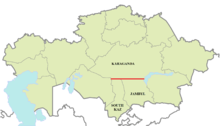
In the Kazakhstan, the parallel defines part of the border between Karaganda Region, South Kazakhstan Region and Jambyl Region.
At this latitude the sun is visible for 15 hours, 45 minutes during the summer solstice and 8 hours, 38 minutes during the winter solstice.[1]
Around the world
Starting at the Prime Meridian and heading eastwards, the parallel 46° north passes through:
gollark: My friend likes Haskell but also spends time reading incomprehensible papers on logic and type theory and such.
gollark: Possibly. People *allegedly* use them for real world applications occasionally.
gollark: Degree?
gollark: `let 2 + 2 = 5 in 2 + 2` is totally valid (but undefined for anything but `2 + 2`).
gollark: There actually are programming languages where `=` just defines relations between things and variables can't be mutated. Notably Haskell.
See also
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.