1952 United States presidential election in Arizona
The 1952 United States presidential election in Arizona took place on November 4, 1952, as part of the 1952 United States presidential election. State voters chose four[3] representatives, or electors, to the Electoral College, who voted for president and vice president.
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
All 4 Arizona votes to the Electoral College | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
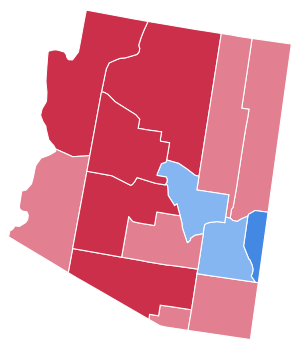 County Results
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Elections in Arizona | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 | ||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||
Arizona was won by Columbia University President Dwight D. Eisenhower (R–New York), running with California Senator Richard Nixon, with 58.35% of the popular vote, against Adlai Stevenson (D–Illinois), running with Alabama Senator John Sparkman, with 41.65% of the popular vote.[4][5]
With his win in the state, Eisenhower became the first Republican presidential candidate since Herbert Hoover in 1928 to win the state.
Results
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Republican | Dwight D. Eisenhower | 152,042 | 58.35% | |
| Democratic | Adlai Stevenson | 108,528 | 41.65% | |
| Total votes | 260,570 | 100% | ||
Results by county
| County | Dwight David Eisenhower Republican |
Adlai Stevension II Democratic |
Margin | Total votes cast[6] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| # | % | # | % | # | % | ||
| Apache | 1,767 | 59.70% | 1,193 | 40.30% | 574 | 19.40% | 2,960 |
| Cochise | 6,495 | 53.52% | 5,640 | 46.48% | 855 | 7.04% | 12,135 |
| Coconino | 3,827 | 61.38% | 2,408 | 38.62% | 1,419 | 22.76% | 6,235 |
| Gila | 3,770 | 43.34% | 4,928 | 56.66% | -1,158 | -13.32% | 8,698 |
| Graham | 2,191 | 49.90% | 2,200 | 50.10% | -9 | -0.20% | 4,391 |
| Greenlee | 1,377 | 31.32% | 3,019 | 68.68% | -1,642 | -37.36% | 4,396 |
| Maricopa | 77,249 | 60.57% | 50,285 | 39.43% | 26,964 | 21.14% | 127,534 |
| Mohave | 1,746 | 62.09% | 1,066 | 37.91% | 680 | 24.18% | 2,812 |
| Navajo | 3,478 | 57.29% | 2,593 | 42.71% | 885 | 14.58% | 6,071 |
| Pima | 32,113 | 60.19% | 21,237 | 39.81% | 10,876 | 20.38% | 53,350 |
| Pinal | 4,985 | 52.44% | 4,522 | 47.56% | 463 | 4.88% | 9,507 |
| Santa Cruz | 1,716 | 55.70% | 1,365 | 44.30% | 351 | 11.40% | 3,081 |
| Yavapai | 6,567 | 63.17% | 3,828 | 36.83% | 2,739 | 26.34% | 10,395 |
| Yuma | 4,761 | 51.72% | 4,444 | 48.28% | 317 | 3.44% | 9,205 |
| Totals | 152,042 | 58.31% | 108,728 | 41.69% | 43,314 | 16.62% | 260,770 |
gollark: I expect iGPUs in a few generations to actually be good enough for me to happily game on.
gollark: The issue is more of scaling them up and making them more efficient (they're already doing that) and adding the ability to actually run on a dedicated card (they're doing that).
gollark: But they've made iGPUs for ages.
gollark: I mean, some, yes.
gollark: Hardly.
References
- "United States Presidential election of 1952 - Encyclopædia Britannica". Retrieved July 25, 2017.
- "U.S. presidential election, 1952". Facts on File. Archived from the original on October 29, 2013. Retrieved October 24, 2013.
Eisenhower, born in Texas, considered a resident of New York, and headquartered at the time in Paris, finally decided to run for the Republican nomination
- "1952 Election for the Forty-Second Term (1953-57)". Retrieved July 25, 2017.
- "1952 Presidential General Election Results – Arizona". Retrieved July 25, 2017.
- "The American Presidency Project – Election of 1952". Retrieved July 25, 2017.
- Scammon, Richard M. (compiler); America at the Polls: A Handbook of Presidential Election Statistics 1920-1964; p. 42 ISBN 0405077114
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.


