1884 United States elections
The 1884 United States elections was held on November 4, electing the members of the 49th United States Congress. The election took place during the Third Party System.
| Presidential election year | |
| Election day | November 4 |
|---|---|
| Incumbent president | Chester A. Arthur (Republican) |
| Next Congress | 49th |
| Presidential election | |
| Partisan control | Democratic Gain |
| Popular vote margin | Democratic +0.6% |
| Electoral vote | |
| Grover Cleveland (D) | 219 |
| James G. Blaine (R) | 182 |
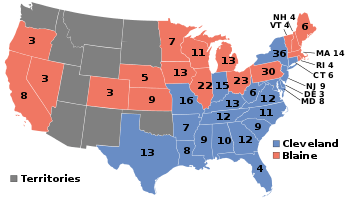  | |
| 1884 presidential election results. Red denotes states won by Blaine, blue denotes states won by Cleveland. Numbers indicate the electoral votes won by each candidate. | |
| Senate elections | |
| Overall control | Republican Hold |
| Seats contested | 27 of 76 seats[1] |
| Net seat change | Democratic -2[2] |
| House elections | |
| Overall control | Democratic Hold |
| Seats contested | All 325 voting members |
| Net seat change | Republican +23[2] |
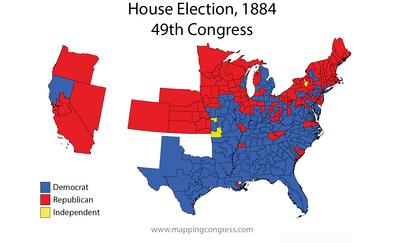 | |
| 1884 House of Representatives election results
Democratic seat | |
In the Presidential election, Democratic Governor Grover Cleveland of New York defeated Republican former Secretary of State James G. Blaine.[3] Though Cleveland won the popular vote by less than 1%, he won by a fairly comfortable margin in the electoral college. Cleveland won the South and the critical state of New York, while Blaine took most of the rest of the country. This was the most recent example of an incumbent President being denied nomination by his party for another term, as Blaine defeated President Chester A. Arthur at the 1884 Republican National Convention. Cleveland took the Democratic nomination on the second ballot of the 1884 Democratic National Convention, defeating Delaware Senator Thomas F. Bayard and several other candidates. Cleveland's win made him the first Democratic President to win election since the 1856 election.
Republicans picked up several seats in the House, but Democrats continued to command a majority in the chamber.[4] In the Senate, Republicans made moderate gains and established a clear majority.[5]
See also
References
- Not counting special elections.
- Congressional seat gain figures only reflect the results of the regularly-scheduled elections, and do not take special elections into account.
- "1884 Presidential Election". The American Presidency Project. Retrieved 25 June 2014.
- "Party Divisions of the House of Representatives". United States House of Representatives. Retrieved 25 June 2014.
- "Party Division in the Senate, 1789-Present". United States Senate. Retrieved 25 June 2014.