1848 Democratic National Convention
The 1848 Democratic National Convention was a presidential nominating convention that met from May 22 to May 25 in Baltimore, Maryland. It was held to nominate the Democratic Party's candidates for president and vice president in the 1848 election. The convention selected Senator Lewis Cass of Michigan for president and former Representative William O. Butler of Kentucky for vice president.
| 1848 presidential election | |
  Nominees Cass and Butler | |
| Convention | |
|---|---|
| Date(s) | May 22–25, 1848 |
| City | Baltimore, Maryland[1] |
| Venue | Universalist Church[1] |
| Candidates | |
| Presidential nominee | Lewis Cass[1] of Michigan |
| Vice presidential nominee | William O. Butler[1] of Kentucky |
As incumbent Democratic President James K. Polk declined to seek re-election, the Democratic Party nominated a new presidential candidate for the 1848 election. The major competitors for the presidential nomination were Cass, Secretary of State James Buchanan of Pennsylvania, and Supreme Court Justice Levi Woodbury of New Hampshire. Cass led on the first presidential ballot, and he continued to gain delegates until he clinched the nomination on the fourth ballot. Butler won the vice presidential nomination on the second ballot, defeating former Governor John A. Quitman of Mississippi and several other candidates. The Democratic ticket was defeated in the 1848 election by the Whig ticket of Zachary Taylor and Millard Fillmore.
Proceedings
Former Speaker of the House Andrew Stevenson of Virginia was made the president (chair) of the convention. After readopting the two-thirds rule for selecting the nominee, the assembly turned to the thorny problem of competing delegations representing different factions of the New York party.[1] The convention adopted a compromise (by a vote of 133 to 118) of splitting the thirty-six votes between the pro-Van Buren faction and the Hunkers that opposed them. Unsatisfied, the pro-Van Burenite Barnburners withdrew and the remaining New Yorkers refused to vote.
The Democratic National Committee was established at this convention.[2]
Presidential nomination
Presidential candidates

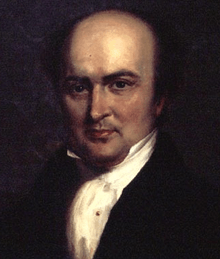
Associate Justice
Levi Woodbury
of New Hampshire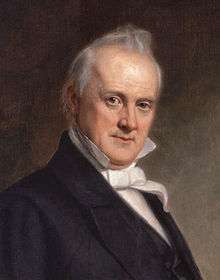

Former President
Martin Van Buren
from New York
(withdrew before first ballot)
The major competitors for the nomination were Senator Lewis Cass of Michigan, Secretary of State James Buchanan from Pennsylvania, and Supreme Court Justice Levi Woodbury from New Hampshire. On the first ballot Cass received a big lead with 125 of the 290 delegate votes with Buchanan and Woodbury trailing with 55 and 53 votes, respectively.[1] On the next two ballots Cass's total went up while the other candidates began to fall. With 179 votes out of 255 actually voting on the fourth ballot, the chair declared Cass the presidential nominee, having surpassed the two-thirds majority of 170 votes.
| Ballots | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lewis Cass | 125 | 133 | 156 | 179 |
| Levi Woodbury | 53 | 56 | 53 | 38 |
| James Buchanan | 55 | 54 | 40 | 33 |
| John C. Calhoun | 9 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| William Jenkins Worth | 6 | 5 | 5 | 1 |
| George M. Dallas | 3 | 3 | 0 | 0 |
| William Orlando Butler | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3 |
| Abstaining | 39 | 39 | 36 | 36 |

1st Presidential Ballot 
2nd Presidential Ballot 
3rd Presidential Ballot 
4th Presidential Ballot
Vice Presidential nomination
Vice Presidential candidates

Former Representative
William O. Butler
of Kentucky
Former Governor
John A. Quitman
of Mississippi
Former Senator
William R. King
of Alabama


Declined
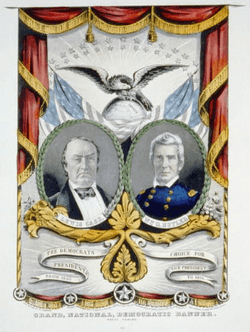
Turning to the choice of a vice presidential running mate, the convention picked General William O. Butler of Kentucky[1] over General John A. Quitman of Mississippi, former Senator and Minister to France William R. King of Alabama, Secretary of the Navy John Y. Mason of Virginia, and Representative James Iver McKay of North Carolina. Before it adjourned on May 25, this convention also appointed the first Democratic National Committee.[1]
| 1st | 2nd Before shifts |
2nd After shifts | |
|---|---|---|---|
| William Orlando Butler | 114 | 179 | 254 |
| John A. Quitman | 74 | 62 | 0 |
| William R. King | 26 | 8 | 0 |
| John Y. Mason | 24 | 5 | 0 |
| James Iver McKay | 13 | 0 | 0 |
| Jefferson Davis | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| Abstaining | 38 | 36 | 36 |

1st Presidential Ballot 
2nd Vice Presidential Ballot Before Shifts 
2nd Vice Presidential Ballot After Shifts
See also
References
- Klunder, William (1996). Lewis Cass and the Politics of Moderation. Kent, Ohio: Kent State University Press. pp. 184–186. Retrieved 9 April 2015 – via Questia.
- Smith, Melissa M.; Williams, Glenda C.; Powell, Larry; Copeland, Gary A. (2010). Campaign Finance Reform: The Political Shell Game. Lexington Books. p. 13. ISBN 9780739145678.
- Levin Hudson Coe, Tennessee Encyclopedia, August 7, 2018
External links
- Democratic Party Platform of 1848 at The American Presidency Project
| Preceded by 1844 Baltimore, Maryland |
Democratic National Conventions | Succeeded by 1852 Baltimore, Maryland |
