Zenit-3F
The Zenit-3F, Zenit-3SLBF or Zenit-2SB/Fregat is an expendable carrier rocket. It is a member of the Zenit family of rockets, which were designed by the Yuzhnoye Design Office of Ukraine.
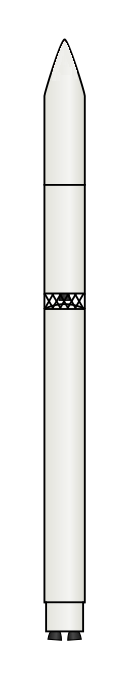 | |
| Function | Carrier rocket |
|---|---|
| Manufacturer | Yuzhnoye |
| Country of origin | Ukraine |
| Size | |
| Height | 59.6 metres (196 ft) |
| Diameter | 3.9 metres (13 ft) |
| Mass | 471,000 kilograms (1,038,000 lb) |
| Stages | Three |
| Capacity | |
| Payload to GTO | 4,000 kilograms (8,800 lb)[1] |
| Associated rockets | |
| Family | Zenit |
| Launch history | |
| Status | Active |
| Launch sites | Baikonur Site 45/1 |
| First flight | 20 January 2011 (Elektro-L No.1) |
| Last flight | 26 December 2017 (AngoSat 1) |
| First stage – Zenit-2SB First stage[2] | |
| Length | 32.9 m (108 ft) |
| Diameter | 3.9 m (13 ft) |
| Empty mass | 27,564 kg (60,768 lb) |
| Gross mass | 354,350 kg (781,210 lb) |
| Propellant mass | RG-1: 90,219 kg (198,899 lb) LOX: 236,567 kg (521,541 lb) |
| Engines | RD-171 |
| Thrust | Sea Level: 7,257 kN (1,631,000 lbf) Vacuum: 7,908 kN (1,778,000 lbf) |
| Specific impulse | Sea Level: 309.5 s (3.035 km/s) Vacuum: 337.2 s (3.307 km/s) |
| Burn time | 140-150 seconds |
| Fuel | LOX/RG-1 |
| Second stage – Zenit-2SB Second stage[2] | |
| Length | 10.4 m (34 ft) |
| Diameter | 3.9 m (13 ft) |
| Empty mass | 8,307 kg (18,314 lb) |
| Gross mass | 90,794 kg (200,167 lb) |
| Propellant mass | RG-1: 23,056 kg (50,830 lb) LOX: 59,431 kg (131,023 lb) |
| Engines | 1 RD-120 1 RD-8 |
| Thrust | RD-120: 912 kilonewtons (205,000 lbf) RD-8: 79.4 kilonewtons (17,800 lbf) |
| Specific impulse | Vacuum: RD-120: 350 s (3.4 km/s) RD-8: 342.8 s (3.362 km/s) |
| Burn time | 360-370 seconds |
| Fuel | LOX / RG-1 |
| Third stage – Fregat-SB | |
| Engines | 1 S5.92 |
| Thrust | 19.6 kilonewtons (4,400 lbf) |
| Specific impulse | 327 s |
| Burn time | 877 s |
| Fuel | dinitrogen tetraoxide / UDMH |
Launches of Zenit-3SLBF rockets are conducted from Baikonur Cosmodrome Site 45/1. The rocket consists of a Zenit-2SB (Zenit-2M) core vehicle, with a Fregat-SB upper stage, developed by NPO Lavochkin of Russia, in place of the Block-DM used on the Zenit-3SL and 3SLB.
The first launch of a Zenit-3F took place on 20 January 2011. The payload was an Elektro-L new generation weather satellite.[3] A Zenit-3F was also used to successfully launch the Spektr-R radio astronomy satellite on 18 July 2011.
Launches
| Flight No. | Date and time (UTC) | Payload | Orbit | Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 20 January 2011 12:29 |
Elektro-L No.1 | GEO | Success |
| 2 | 18 July 2011 02:31 |
Spektr-R | HEO | Success |
| 3 | 11 December 2015 13:45 |
Elektro-L No.2 | GEO | Success |
| 4 | 26 December 2017 19:00 |
AngoSat 1 | GEO | Success |
| References: [4] | ||||
gollark: Most commonly used programming languages are pretty similar conceptually and you just need to be good at the basic skills of translating what you mean into simple steps computers can actually run.
gollark: Although I'm imagining that many programs would run background tasks then totally fail to cleanup them.
gollark: CC doesn't expose a way to "daemonize" a function yet, which is a bit bees.
gollark: <@559076649598058497> cease CC 1.80pr1 utilization.
gollark: Oh dear.
References
- "Zenit-3SLBF". Yuzhnoye.
- "Zenit-2SB". Roscosmos (in Russian). Retrieved 7 April 2016.
- "Russia meteo satellite Electro-L successfully orbited". ITAR-TASS. 2011-01-21. Archived from the original on 2011-01-22.
- Krebs, Gunter. "Zenit family". Gunter's Space Page. Retrieved 2009-04-15.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.